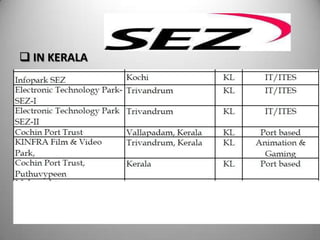
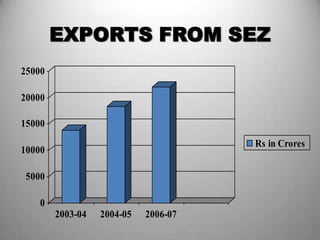
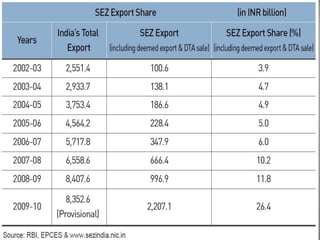
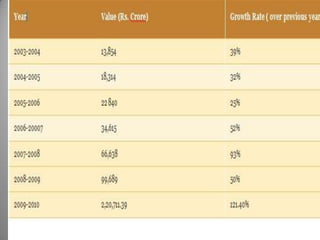
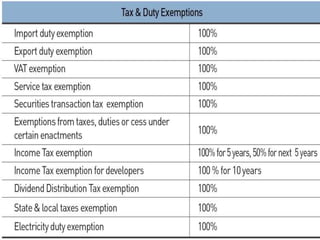
Special Economic Zones (SEZs) are geographical regions in India that have economic laws more oriented towards free market principles to increase foreign direct investment and GDP. SEZs cover various types of zones like free trade zones and industrial parks. They provide tax exemptions and other fiscal incentives. While SEZs aim to generate economic activity and jobs, there are concerns around land acquisition and impact on farmers' livelihoods. Overall, SEZs are intended to make India a more competitive investment destination but their success depends on factors like infrastructure and political stability.