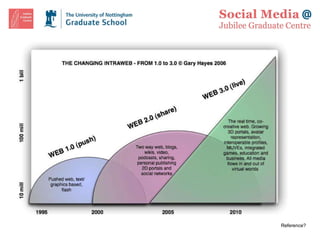
The document outlines an introduction to social media, detailing its significance, principles, and theories that inform its usage, particularly in academic and professional contexts. It emphasizes the evolution of social media from Web 1.0 to Web 2.0, highlighting the shift towards user-generated content and collaborative learning. Additionally, it discusses the implications of social media on identity and knowledge sharing, alongside ethical considerations such as copyright and fair use.


![Sessions: Overview Session One: Monday 18 January Introduction to Social Media Session Two: Friday 5 February Blogging, Knowledge Sharing, Tagging, Aggregating and Syndicating Content Session Three: Wednesday 17 February Social Networking and Collaboration Online Resource http://www.nottingham.ac.uk/jubileegraduatecentre/training-and-events/events-resources.phtml OR: http://tiny.cc/ruSBF Contact [email_address] Twitter #smjgc1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smjgcsession-one-100118123052-phpapp02/85/sm-jgc-Session-One-3-320.jpg)







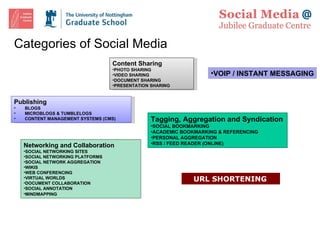

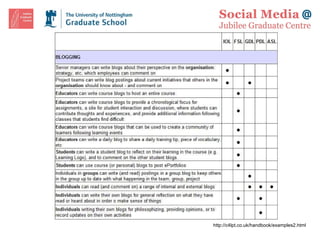










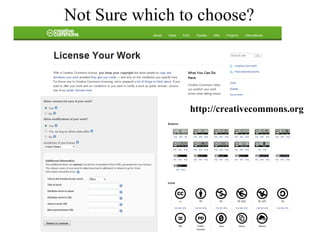





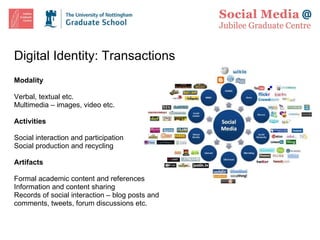

![Lunch: Further Discussion and Questions Graduate School Feedback Forms Please spend a few moments to fill in the feedback forms provided. Thanks. Our next session is on Friday 5 February: Blogging, Knowledge Sharing, Tagging, Aggregating and Syndicating Content Online Resource http://www.nottingham.ac.uk/jubileegraduatecentre/training-and-events/events-resources.phtml OR: http://tiny.cc/ruSBF Contact [email_address] Twitter #smjgc1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smjgcsession-one-100118123052-phpapp02/85/sm-jgc-Session-One-37-320.jpg)
