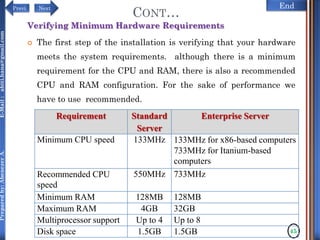
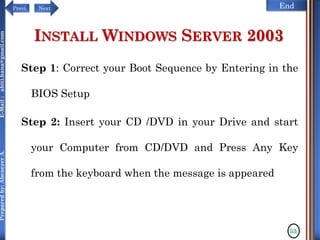
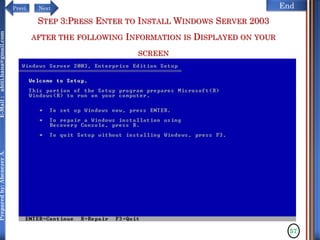
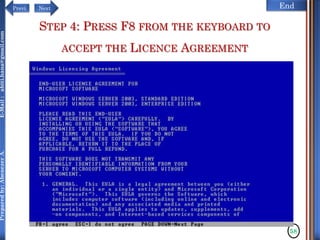
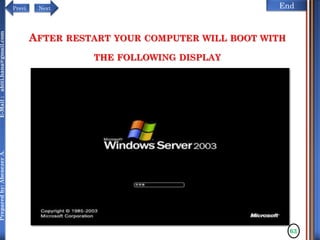
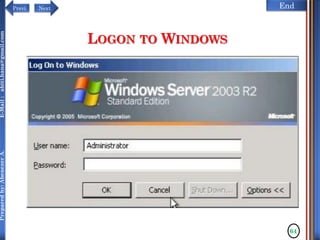
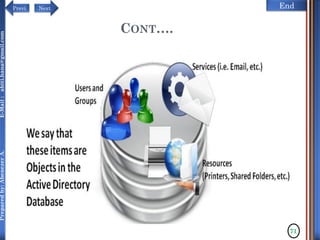
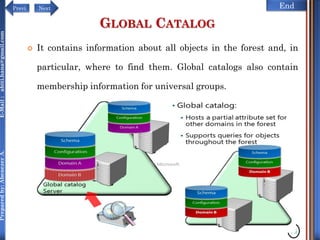
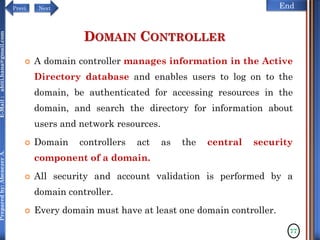
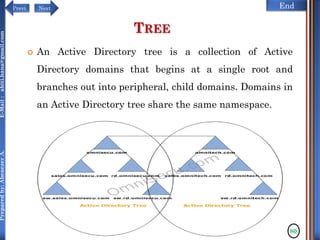
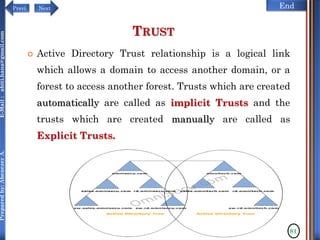
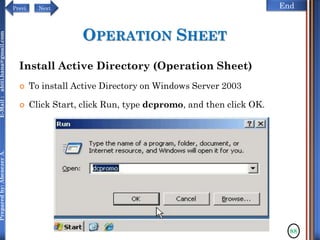
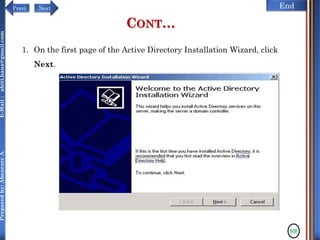
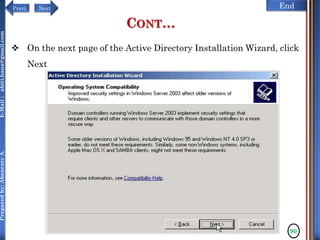
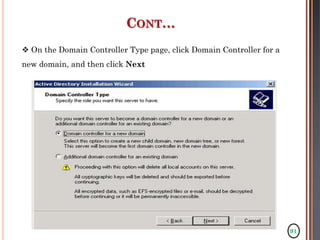
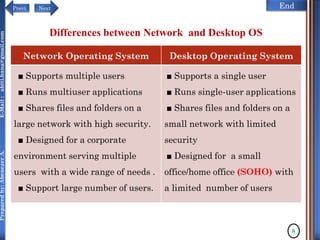
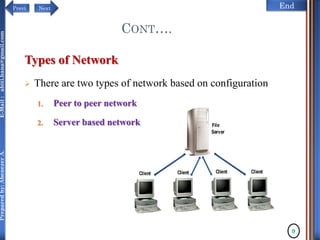
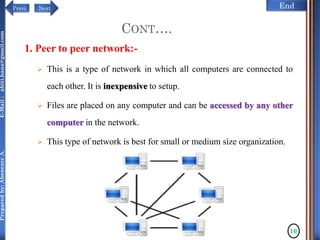
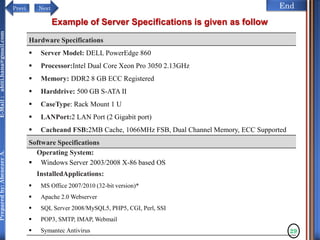
The document discusses configuring and administering servers. It defines network operating systems and their characteristics. A network OS is software that runs on a server and enables it to manage networking functions. It also defines servers and their roles in providing services and resources to users. The document outlines learning outcomes related to confirming server specifications, verifying compatibility and interoperability, and configuring and testing servers.






































![NextPrevi End
Preparedby:AbenezerA.E-Mail:abiti.hana@gmail.com
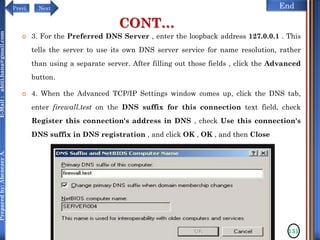
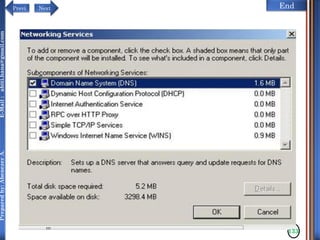
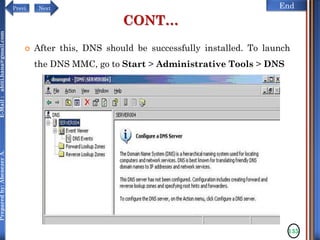
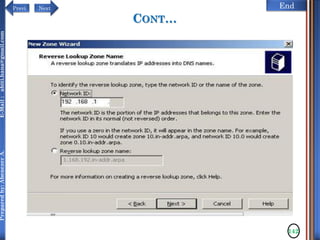
CONT…
An example is RAM chips, some of which can run at
a lower (or sometimes higher) clock rate than rated.
Hardware that was designed for one
operating system may not work for another, if
device or kernel drivers are unavailable.
For example, much of the hardware for Mac OS
X is proprietary hardware [1] with drivers
unavailable for use in operating systems such as
Linux.
43](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/configureandadministerserver-171218063752/85/Configure-and-administer-server-43-320.jpg)