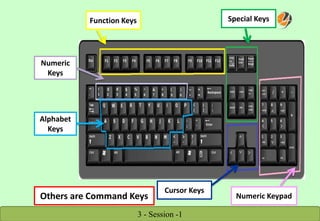
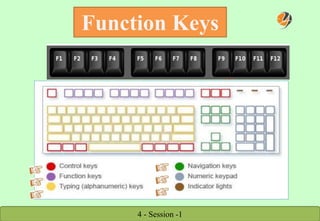
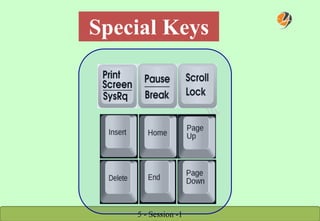
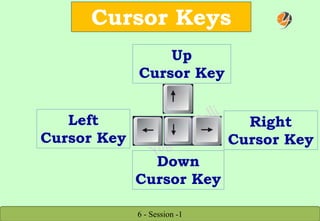
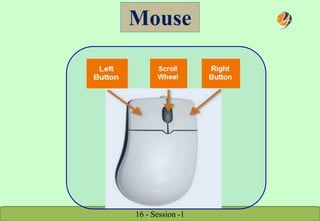
The document provides a comprehensive overview of keyboard and mouse functions, the definition and roles of computers, and a breakdown of hardware versus software. It classifies computers into categories such as microcomputers, mini computers, mainframe computers, and supercomputers, detailing their capabilities and uses. Additionally, it highlights the advantages of computers in modern life, emphasizing their role in convenience, communication, and information access.