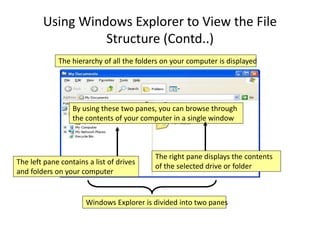
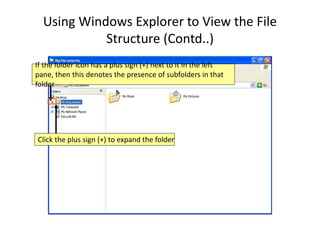
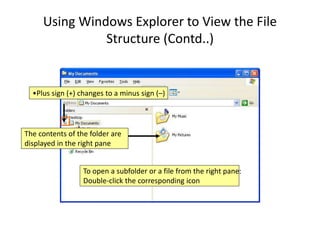
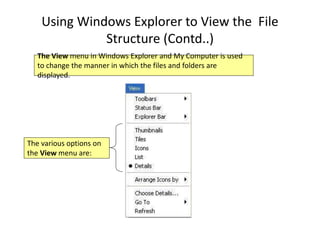
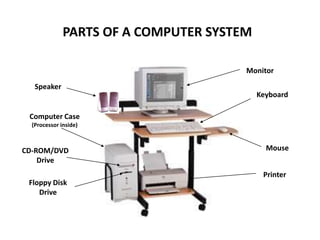
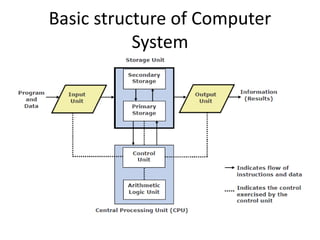
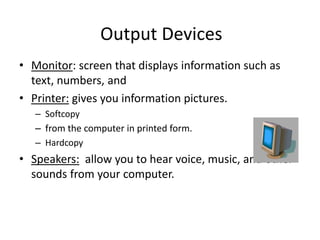
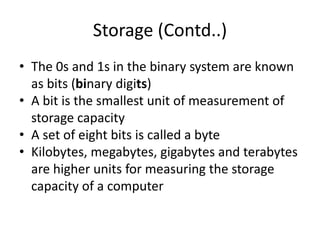
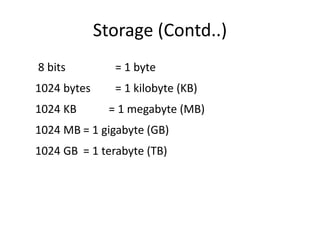
A computer is an electronic device that can perform calculations, create documents, maintain records, and analyze data. It uses input devices like a keyboard and mouse to receive data and instructions which are processed by the central processing unit. The output is displayed on monitors or printers. Computers have benefits like speed, accuracy, storage, and automation but require clear instructions to work. Common computer components include a monitor, keyboard, mouse, printer, speakers, and storage devices like a hard drive.












































































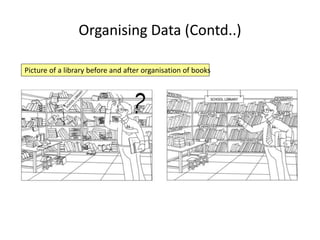
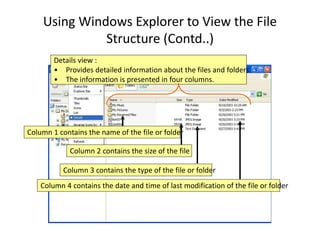
![Organising Data (Contd..)
Example for file name:
Lesson1.doc
A file name can contain:
– Letters
– Numbers
– Spaces
– Special characters, such as [ ] { } , ! $ ~ ` % @
Primary name Extension](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ict101unit-1-220911173742-4f177dbb/85/ict101_unit-1-ppt-107-320.jpg)