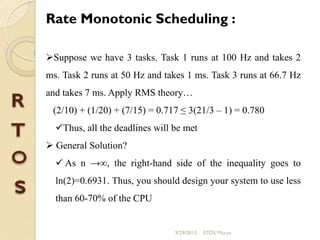
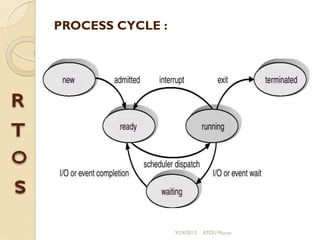
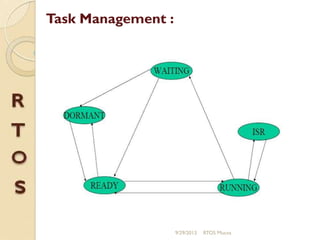
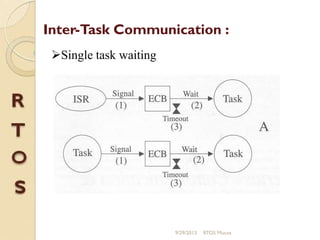
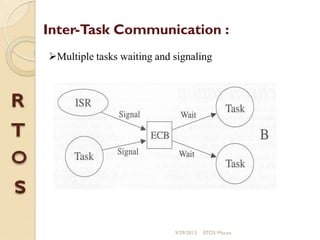
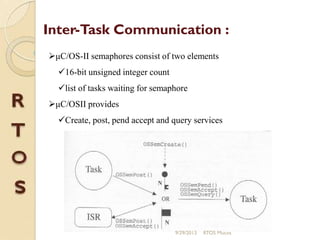
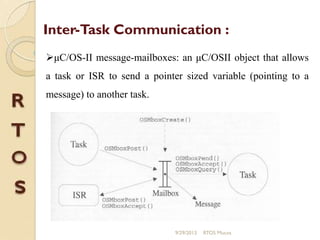
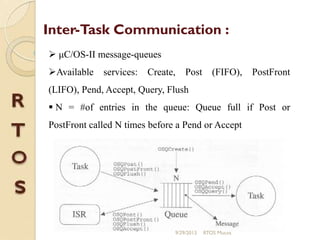
μc/os-ii is a priority-based real-time multitasking operating system kernel designed for microprocessors, primarily written in C, with a memory footprint of about 20kb. It supports up to 64 tasks and offers various services, including task management, memory management, and inter-task communication through semaphores and message queues. The kernel is highly portable, scalable, and optimized for use in embedded systems.