The document is a comprehensive guide on computer studies for junior levels, covering terminology, types of computers, basic operations, and productivity tools like Microsoft Word and Excel. It also addresses networking, multimedia files, and essential computer components, providing definitions and examples of hardware and software. Additionally, the pamphlet includes learning objectives, questions for students, and practical usage tips to aid in understanding and preparation for exams.

































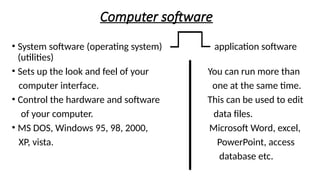
![(j) Explain the use of the most commonly
used application software (utilities)
Word processing [creating letters – faxes –
Memos –– producing catalogue containing
graphics –business document]
Excel Spreadsheet [Charts – financial projection
–working with budgets]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter1introductiontocomputersgrade8and9-250127170230-8e3ec875/85/CHAPTER-1-INTRODUCTION-TO-COMPUTERS-GRADE-8-and-9-pptx-36-320.jpg)
![Access database [sort large amount of
information – creating list of contact details]
PowerPoint presentation [create overhead
projections slides]
Web browsing[View web pages]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter1introductiontocomputersgrade8and9-250127170230-8e3ec875/85/CHAPTER-1-INTRODUCTION-TO-COMPUTERS-GRADE-8-and-9-pptx-37-320.jpg)







![(b) Explain the use of the mouse and keyboard input
devices.
Answer
Keyboard:
A keyboard is an input device that contains keys [buttons]
that the user presses to enter data into a computer
keyboard have 101 to 105 keys.
Mouse:
A mouse is a pointing device that fits under the palm of
one’s hand. Pointing devices minimize the amount of
typing a user has to do.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter1introductiontocomputersgrade8and9-250127170230-8e3ec875/85/CHAPTER-1-INTRODUCTION-TO-COMPUTERS-GRADE-8-and-9-pptx-46-320.jpg)


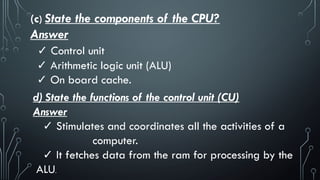
























![f) Define a printer
Answer
A printer produces hard copy [physical copy] of text
and graphics.
(g) How is the quality of a printer measured?
Answer
The resolution [quality] of a printer is measured in
dots per inch [DPI]. The higher the DPI, the higher
the print quality.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter1introductiontocomputersgrade8and9-250127170230-8e3ec875/85/CHAPTER-1-INTRODUCTION-TO-COMPUTERS-GRADE-8-and-9-pptx-77-320.jpg)
![(h) How is the speed of a printer measured?
Answer
The speed of a printer is measured in pages per
minute [PPM].
(i) Give three (3) Examples of types of
printers:
Answer
✓ LaserJet printers
✓ Inkjet printers
✓ Office jet printers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter1introductiontocomputersgrade8and9-250127170230-8e3ec875/85/CHAPTER-1-INTRODUCTION-TO-COMPUTERS-GRADE-8-and-9-pptx-78-320.jpg)




