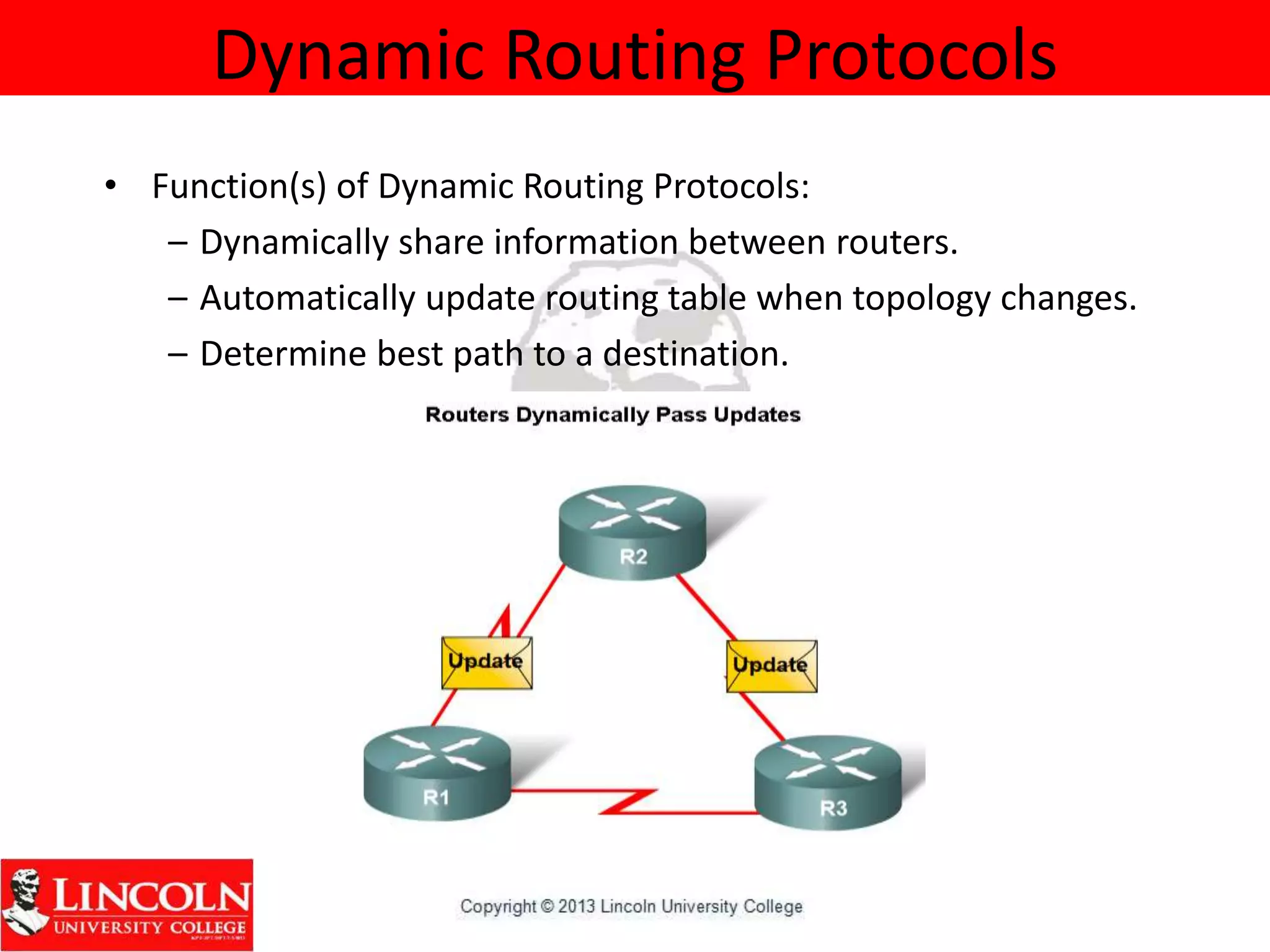
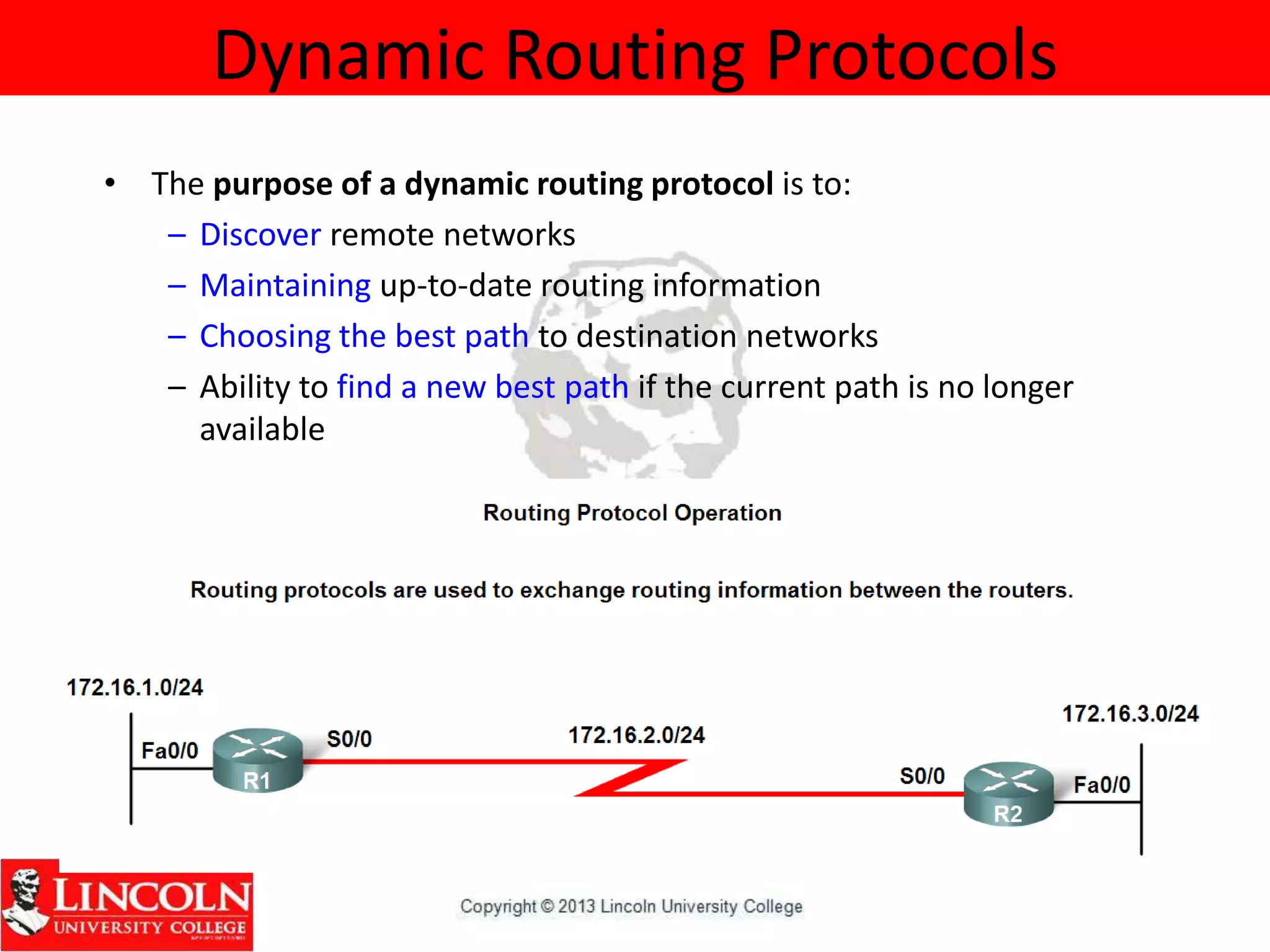
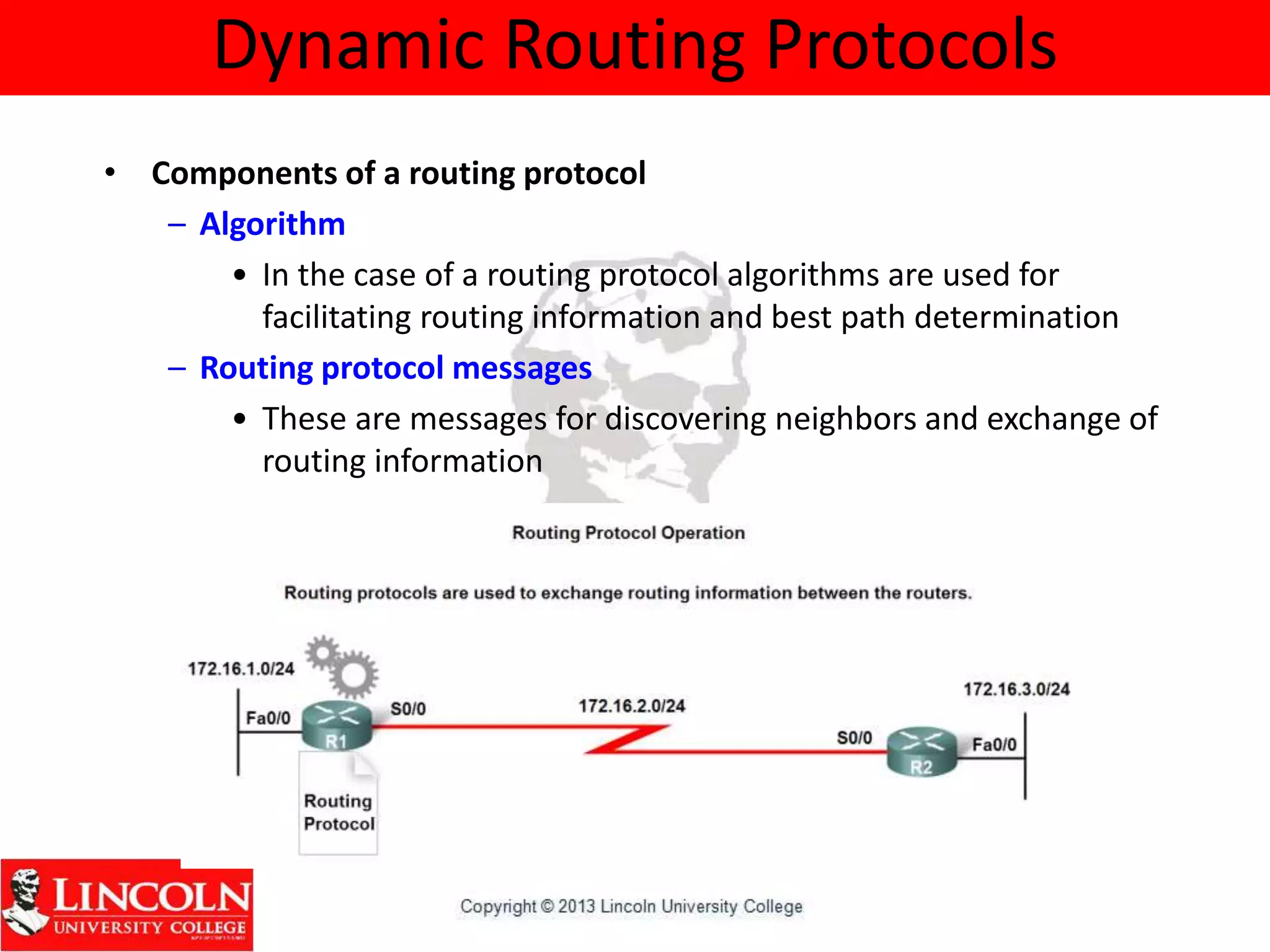
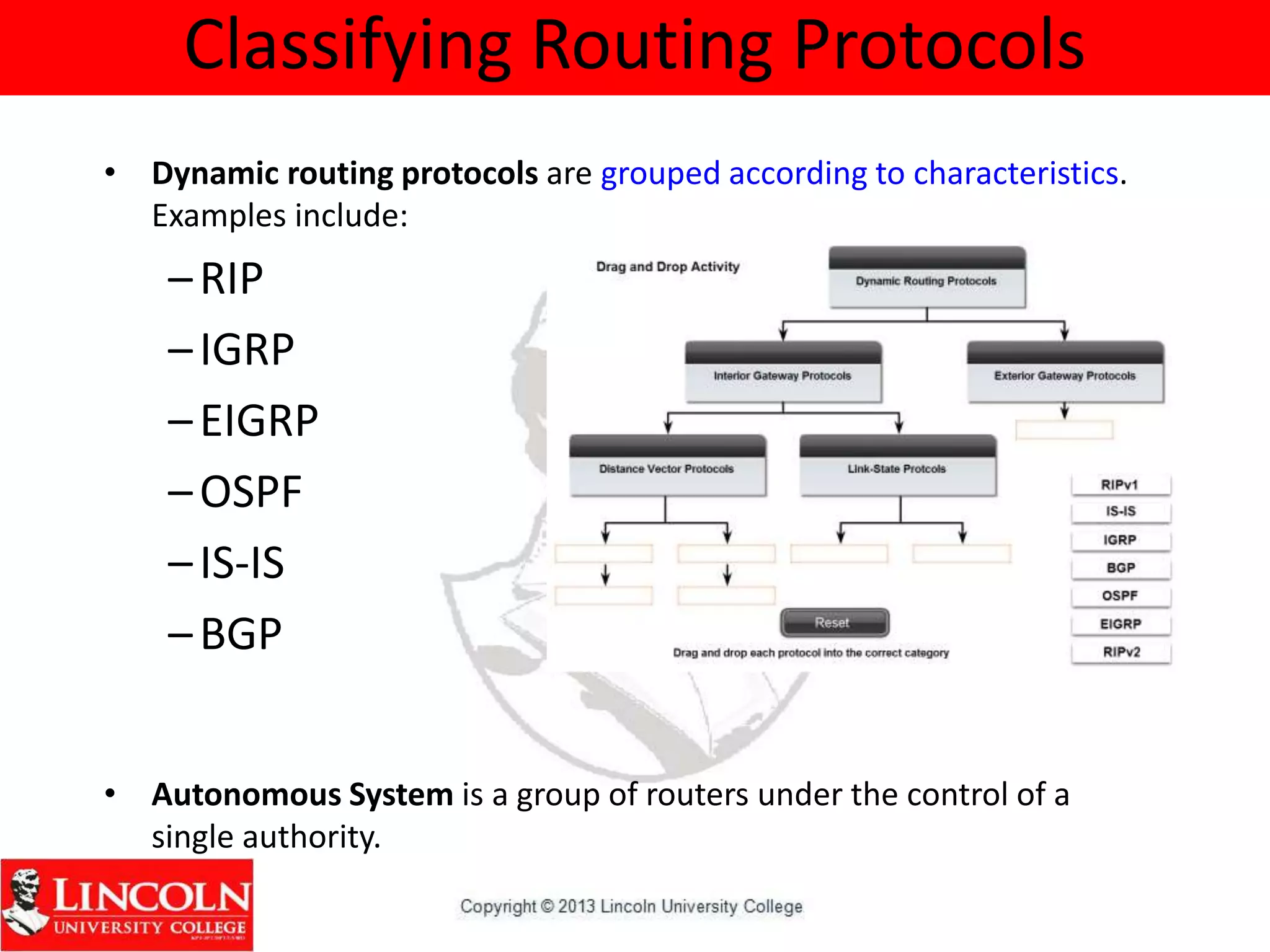
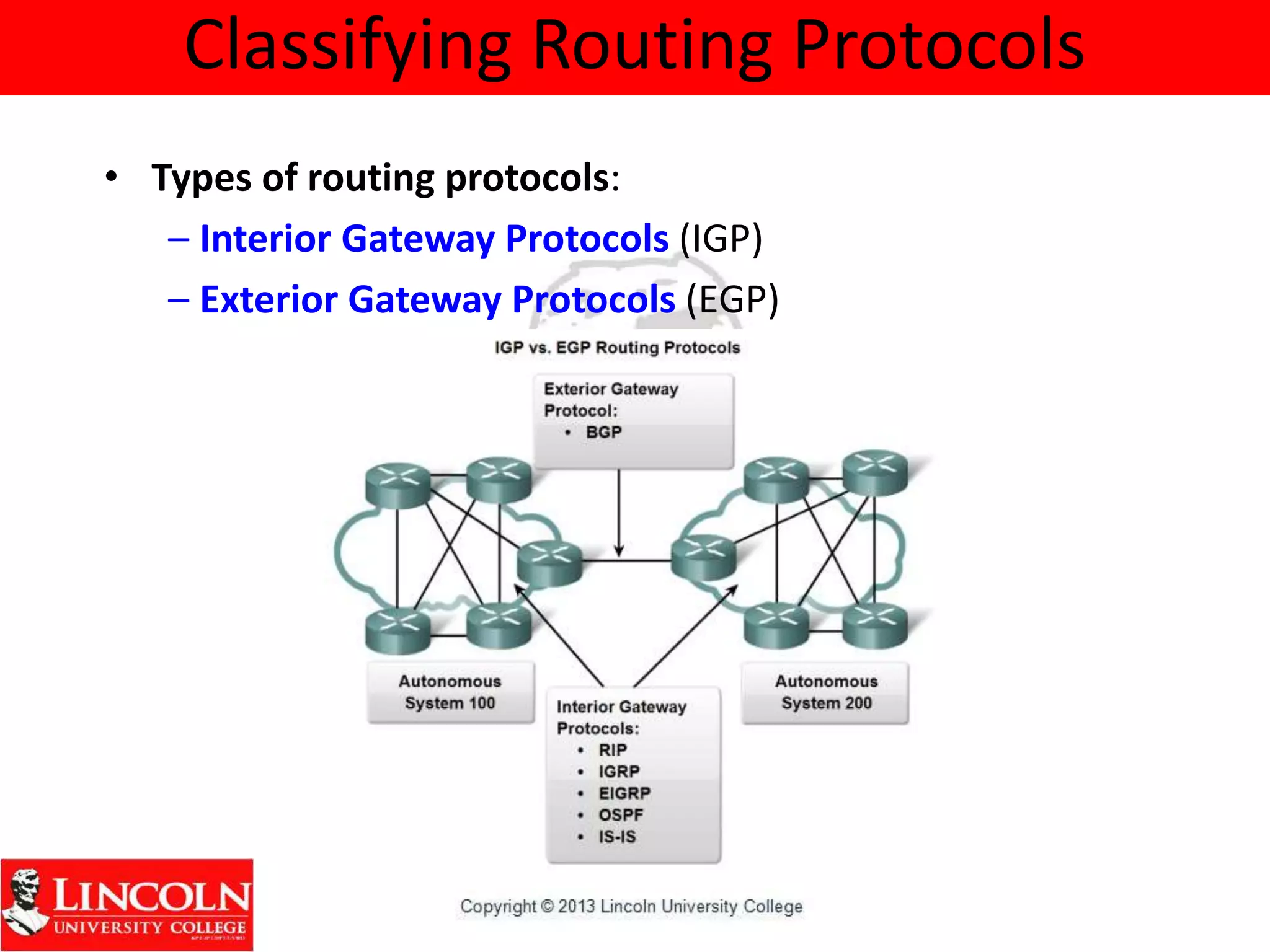
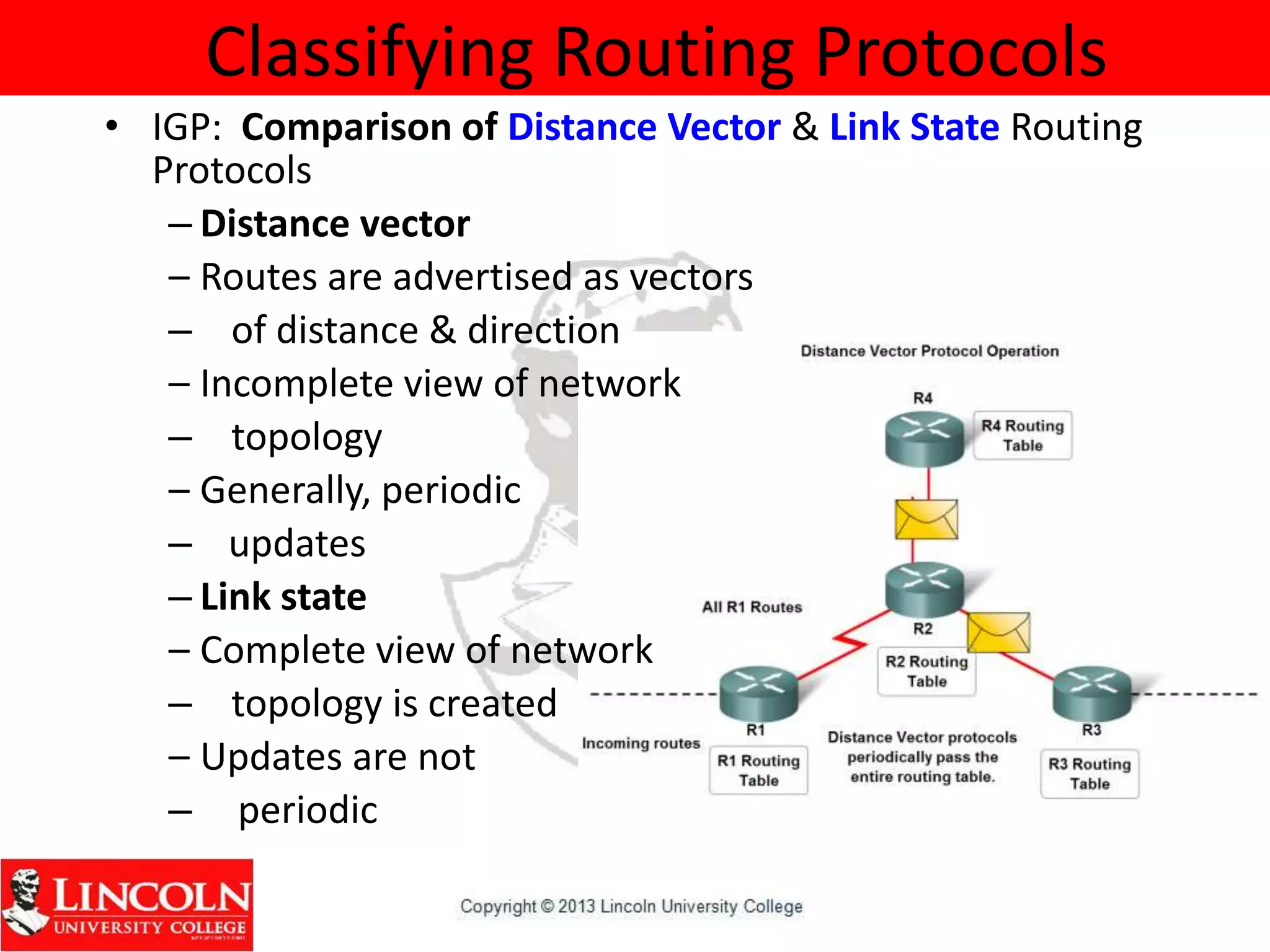
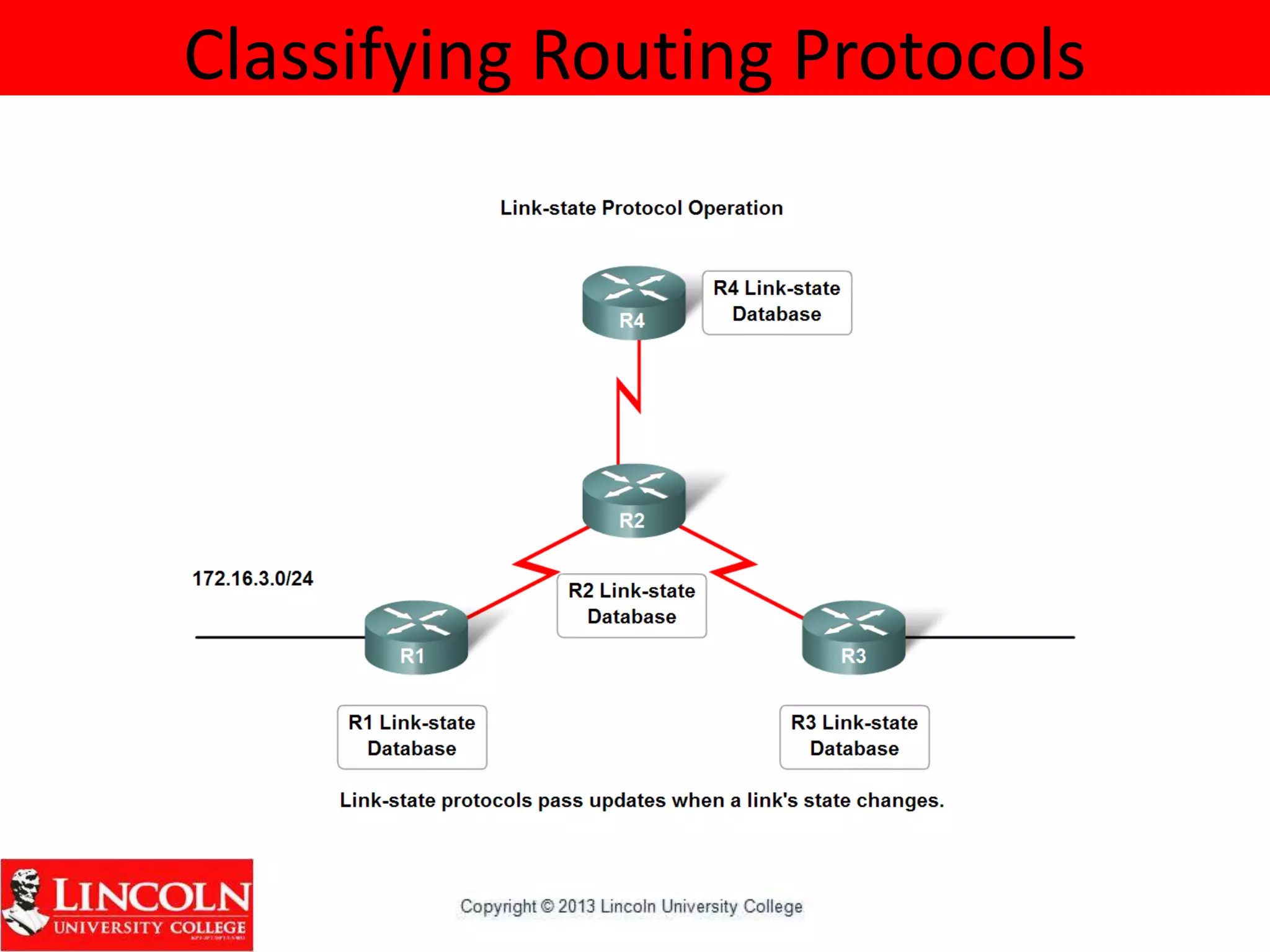
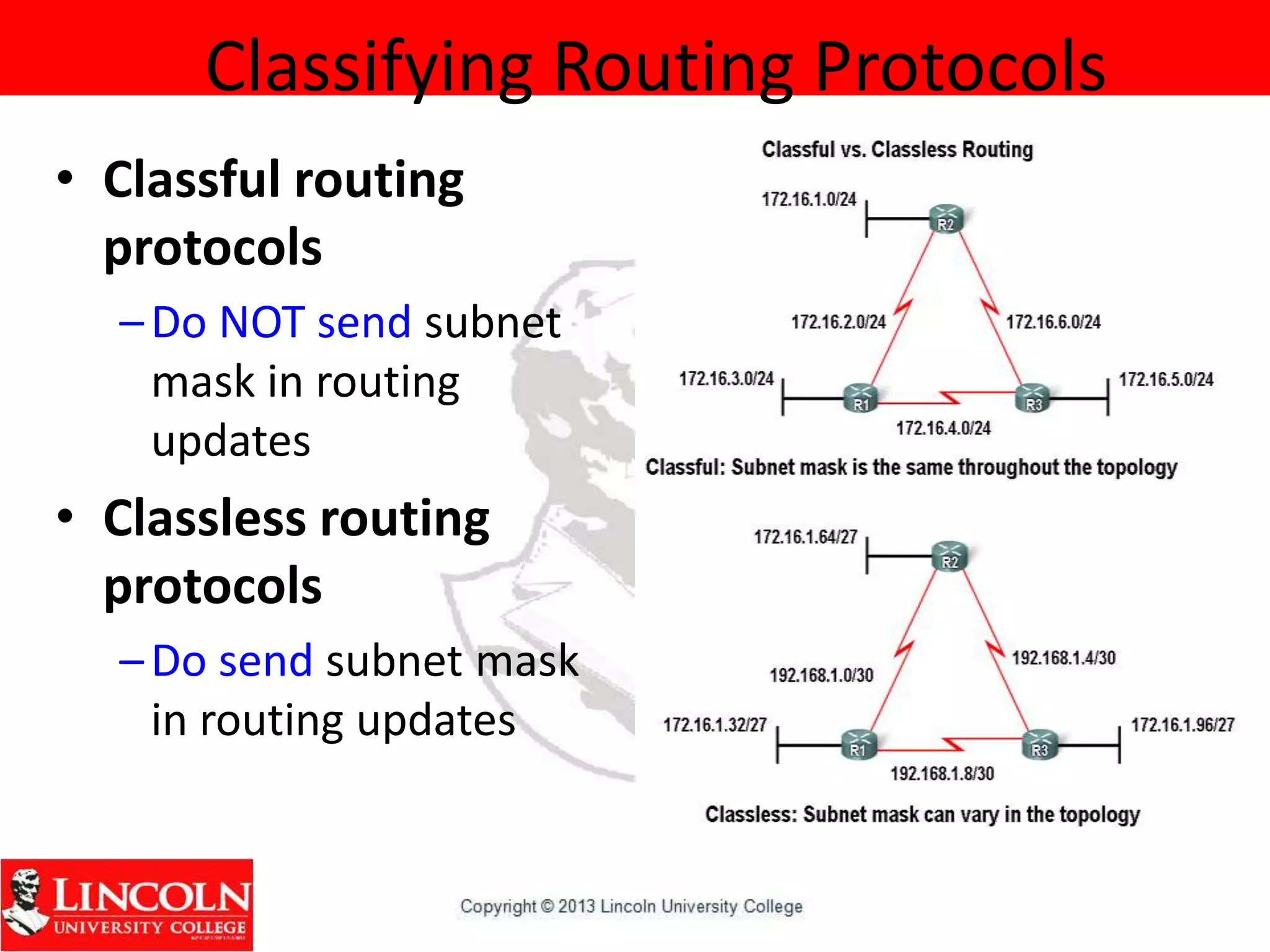
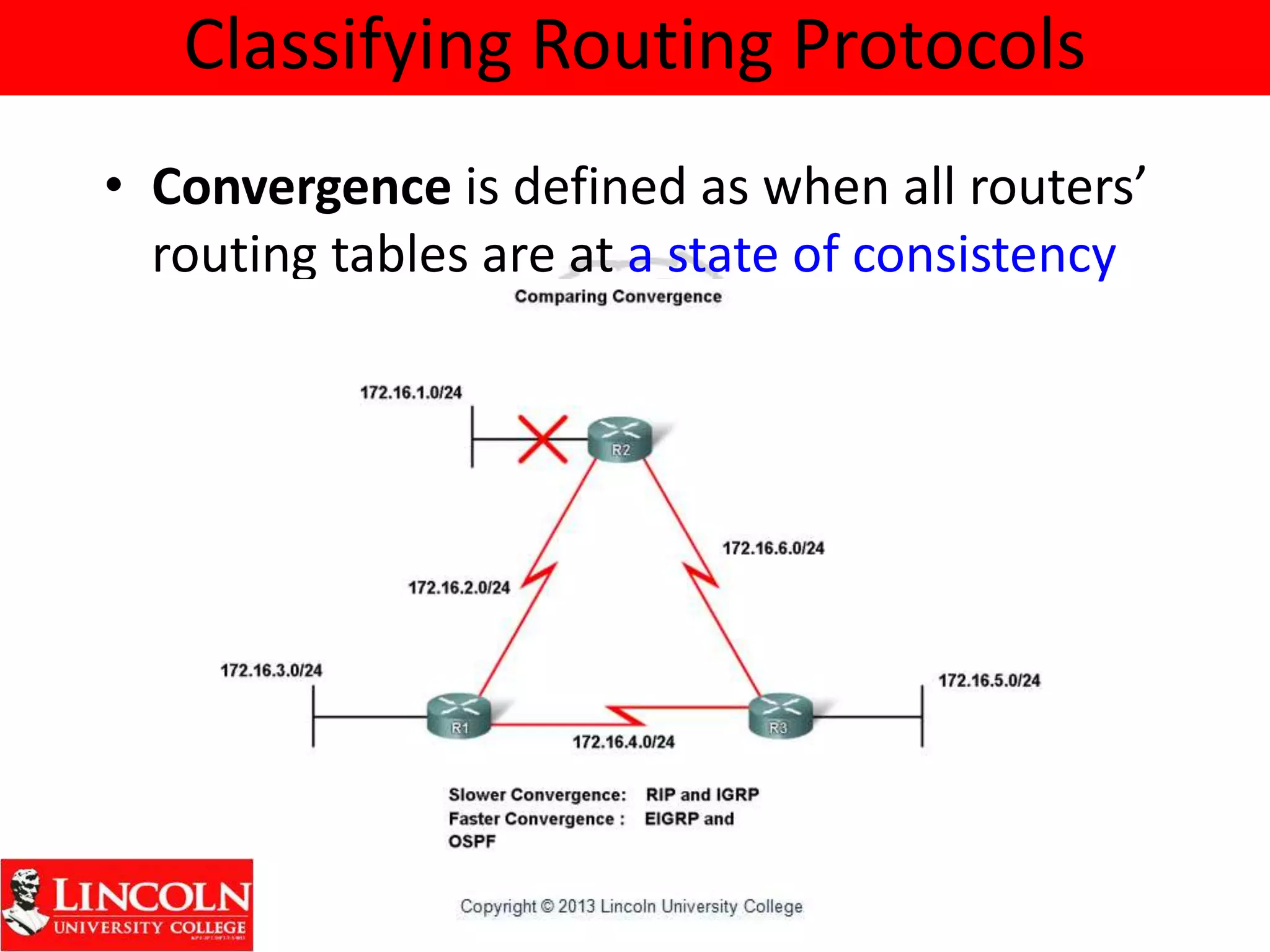
Dynamic routing protocols dynamically share routing information between routers to automatically update routing tables when network topologies change and determine the best path to destinations. They discover remote networks, maintain up-to-date routing information, choose the best path to destination networks, and find new paths when the current path is unavailable. Dynamic routing protocols are grouped and classified based on their routing algorithm, protocol messages, whether they are interior or exterior gateway protocols, and if they are distance vector or link state protocols.