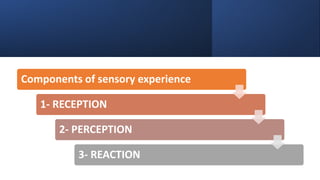
This document discusses sensory needs and deprivation. It begins by defining the five main human senses and how sensory needs occur when one has difficulties receiving and responding to sensory information. The three components of sensory experience are then explained as reception, perception, and reaction. Several factors that can affect sensory function are then outlined such as development, culture, stress, illness, and medication. Methods of assessing sensory alterations like deficits, deprivation, and overload are presented. Finally, prevention and management of clients with sensory issues are covered, focusing on preventing overload and deprivation through stimulation and modification of the environment and communication style.





















![SENSORY ALTERATION [ a small change in
something]
• Careful assessment help the client in reducing
sensory alteration and early identification/
management of disorders
• SENSORY DEFICIT
• SENSORY DEPRIVATION
• SENSORY OVERLOAD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sensoryneed-231025091918-0189a4f1/85/Sensory-need-pptx-24-320.jpg)










![• COMMUNICATION WITH APHASIA CLIENT [ aphasia
is loss of the ability to understanding the spoken or
written language ]
• Make sure that the client surrounding environment
should be quiet and relaxed
• Start conversation with general information to
specific details](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sensoryneed-231025091918-0189a4f1/85/Sensory-need-pptx-35-320.jpg)







