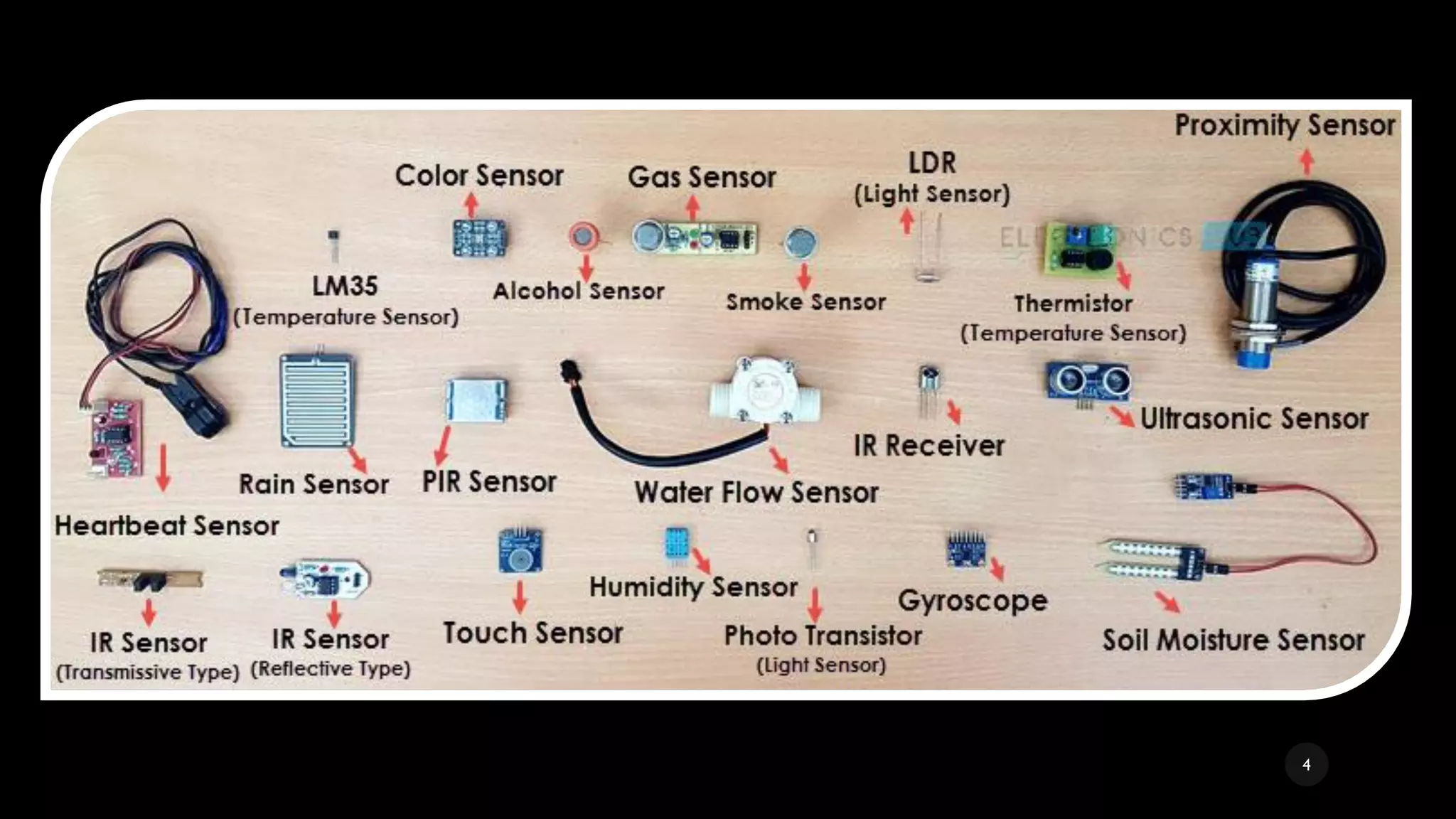
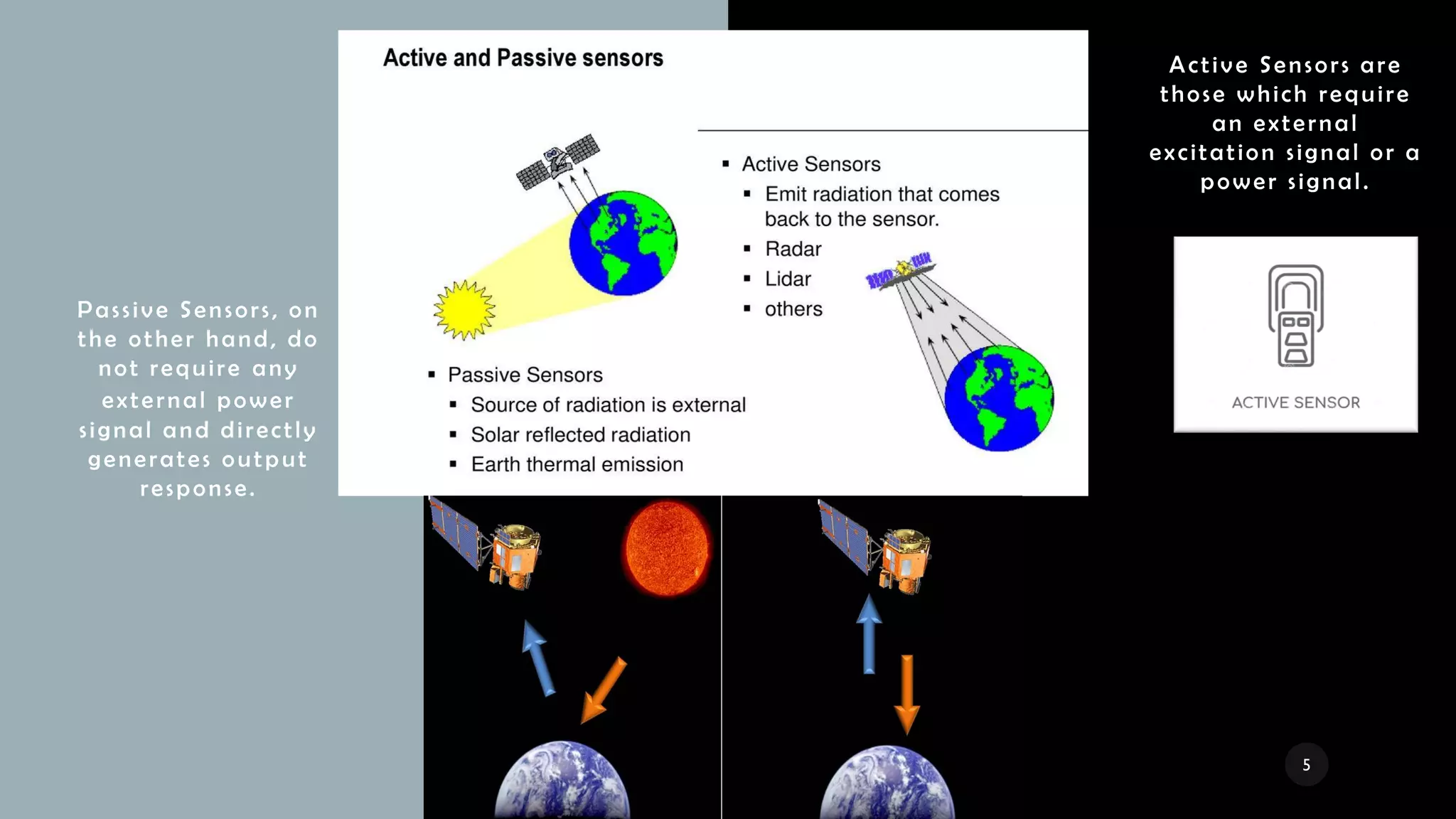
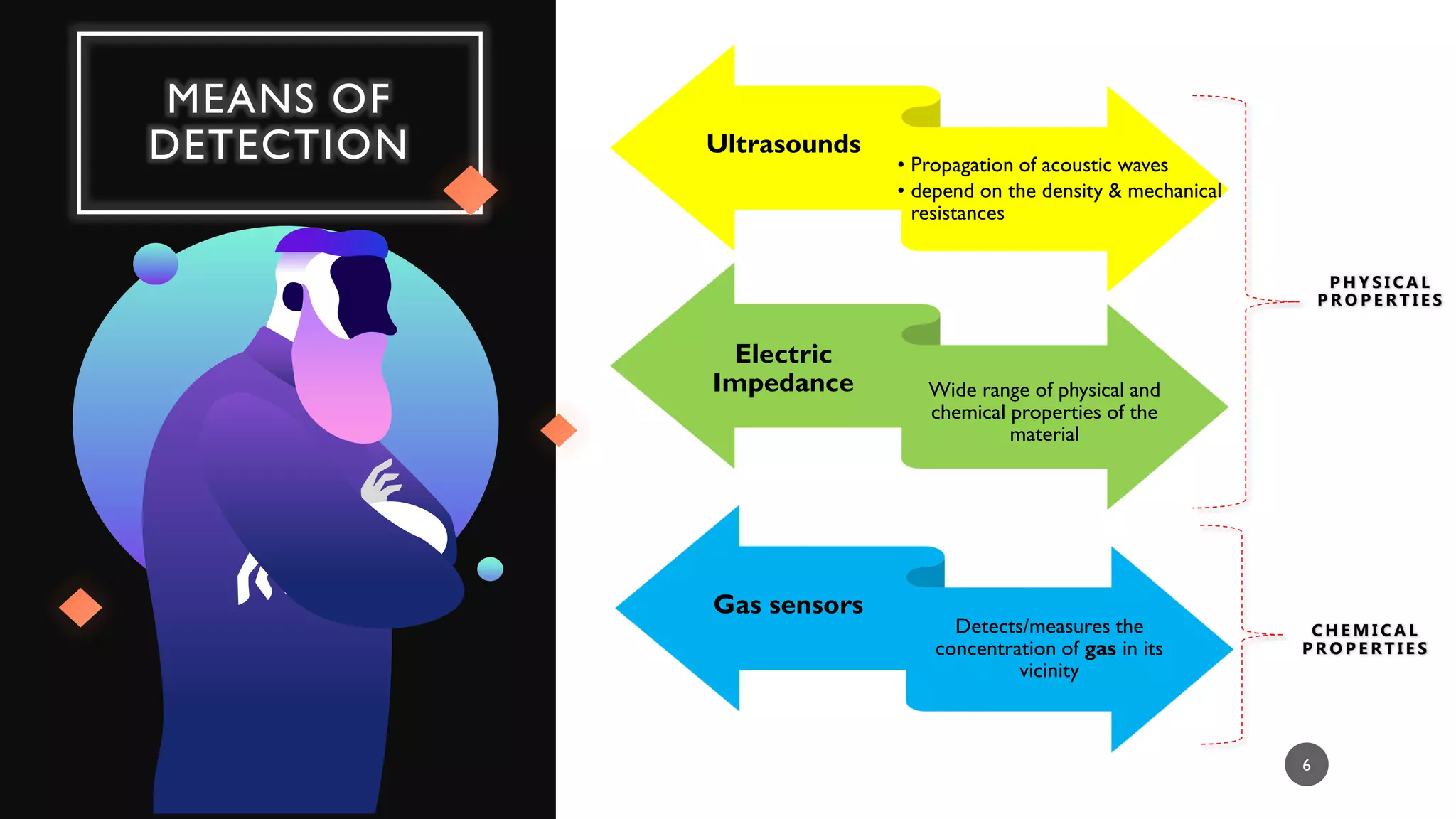
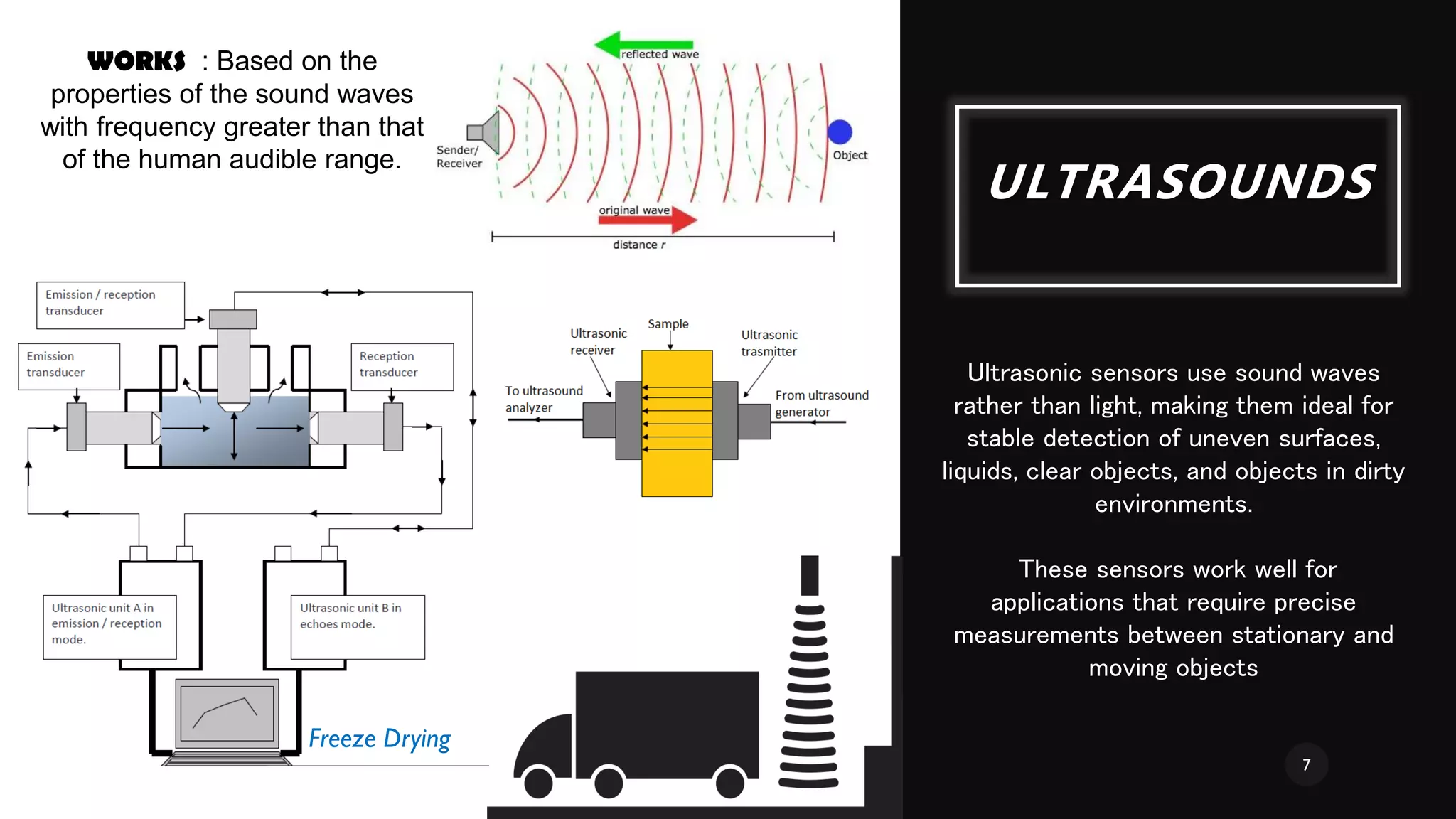
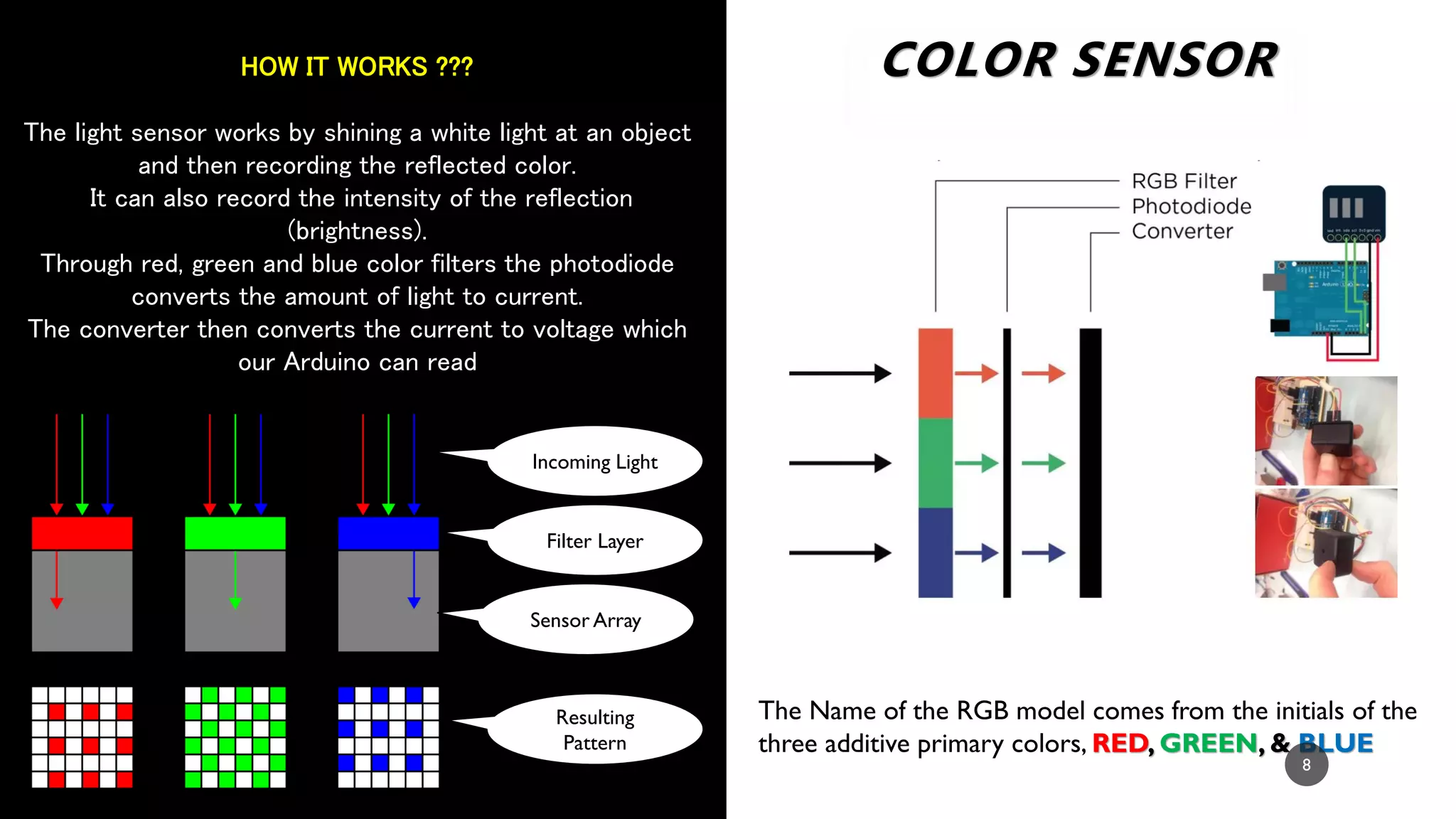
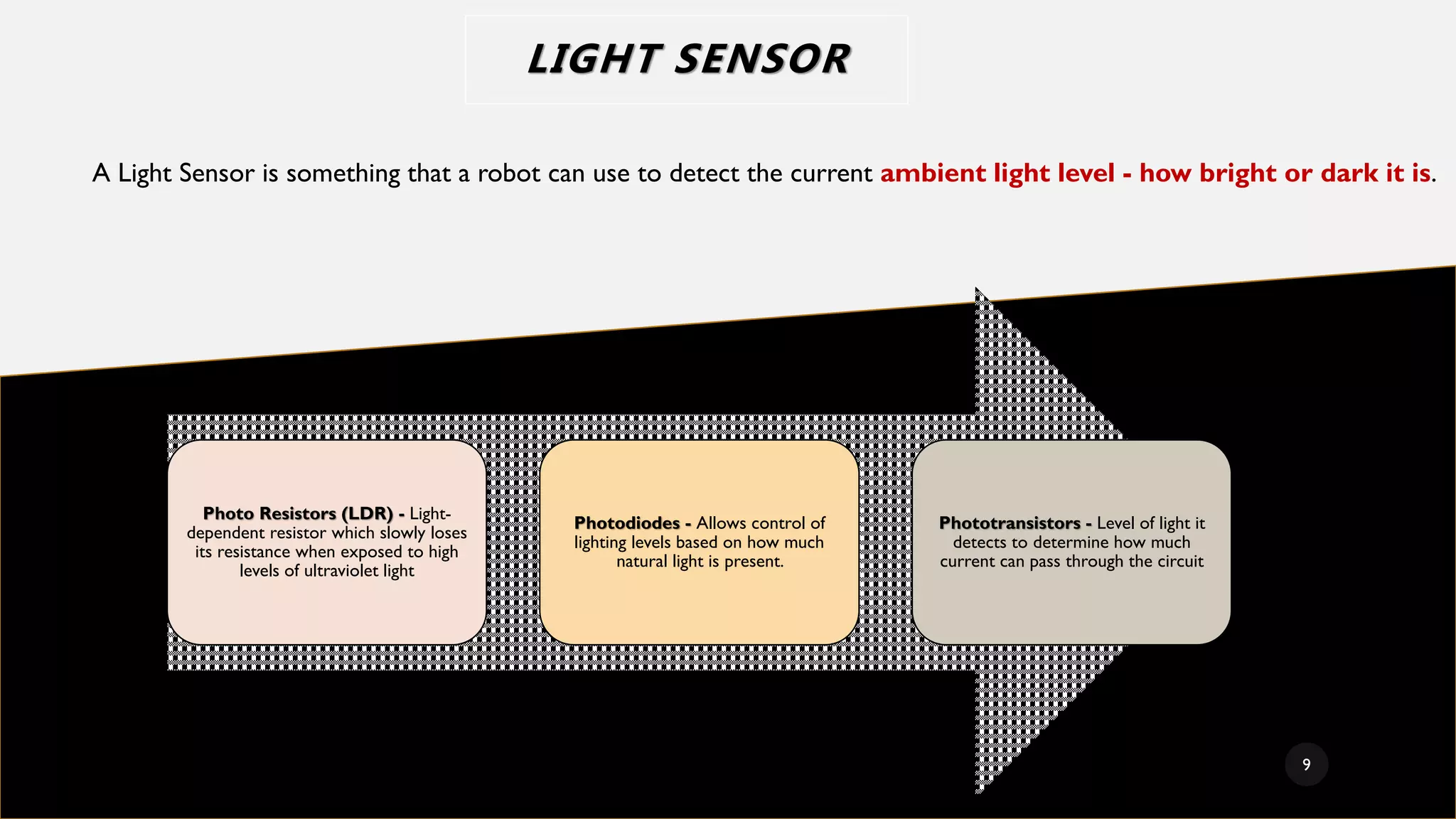
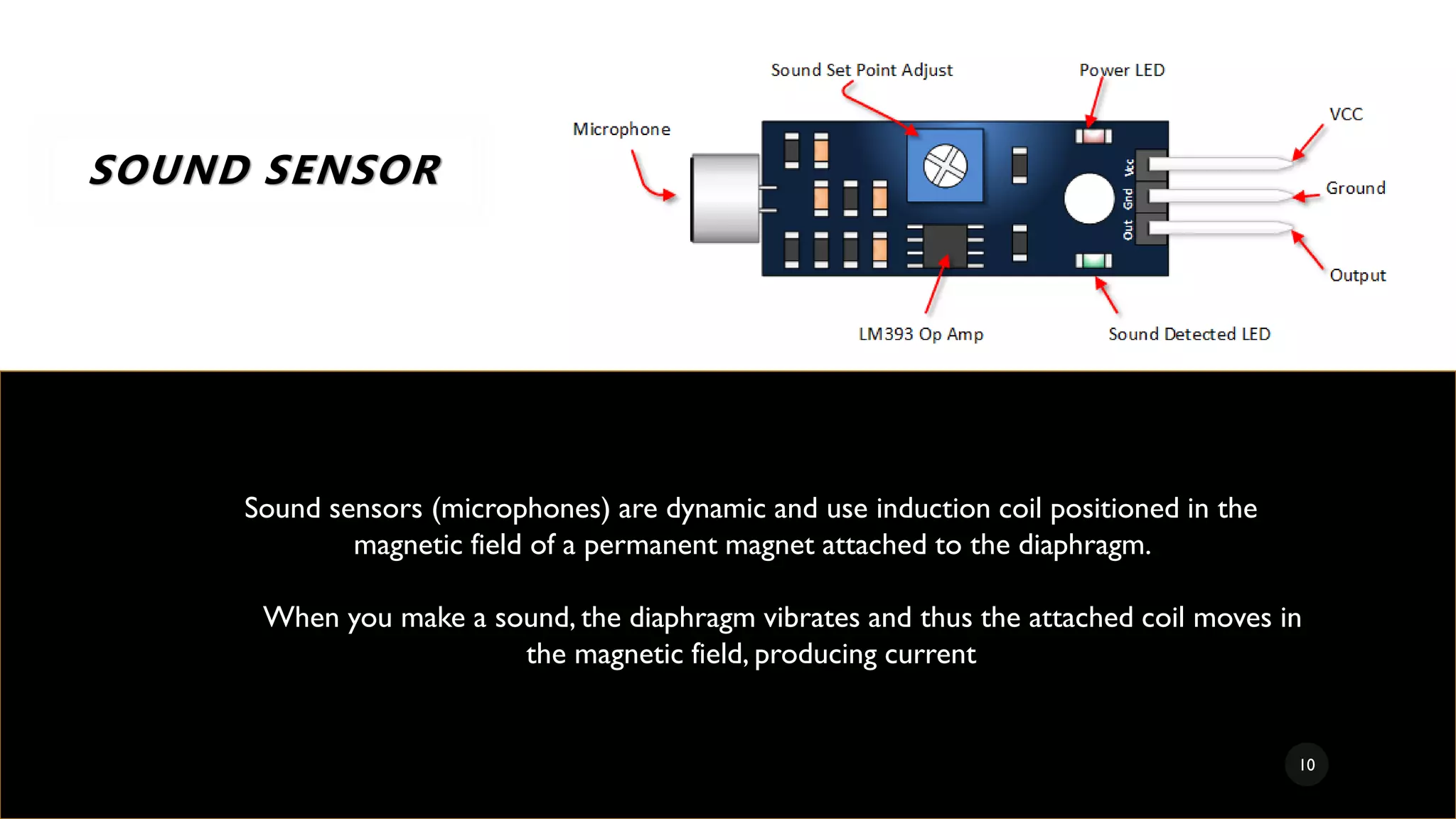
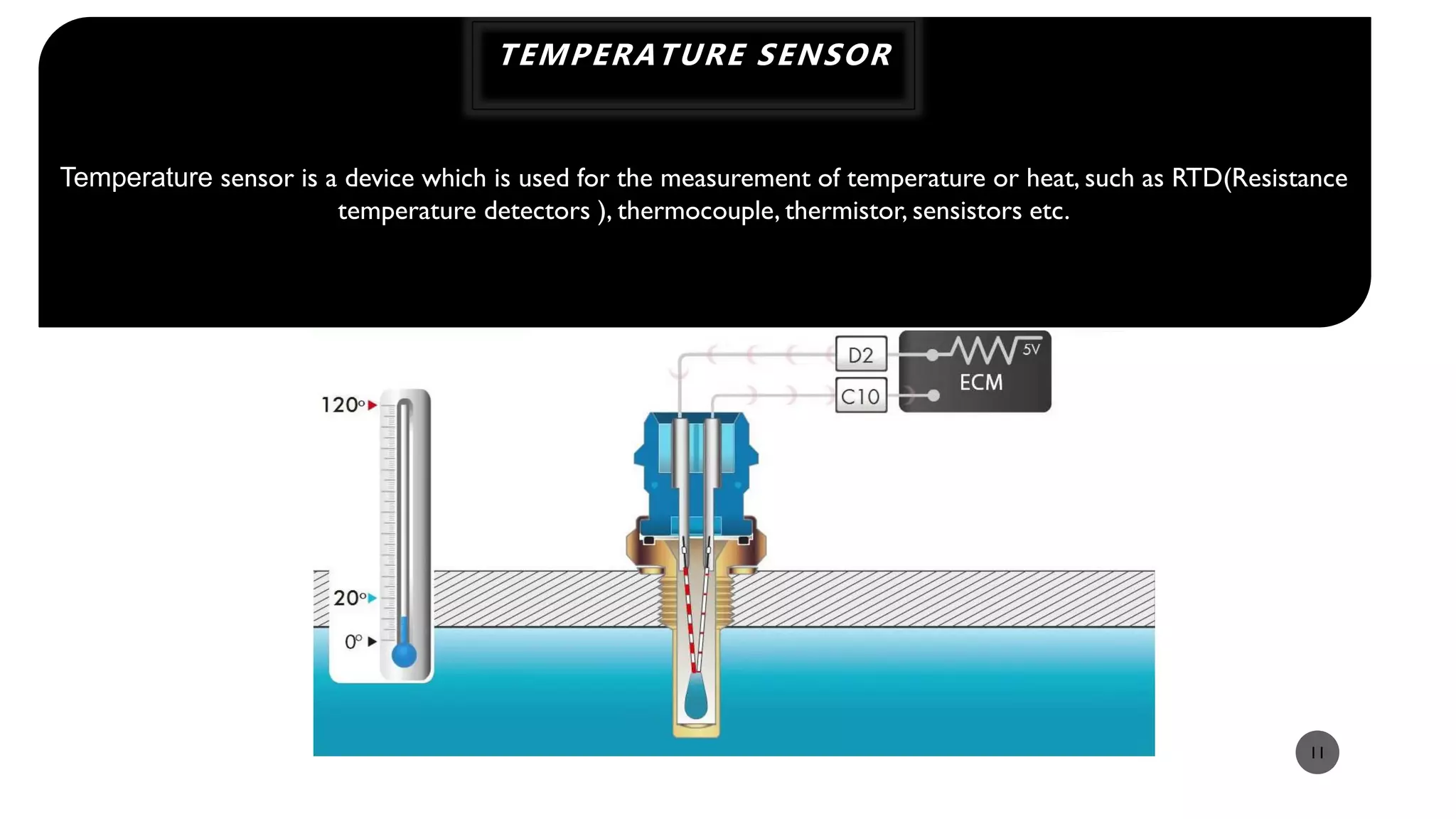
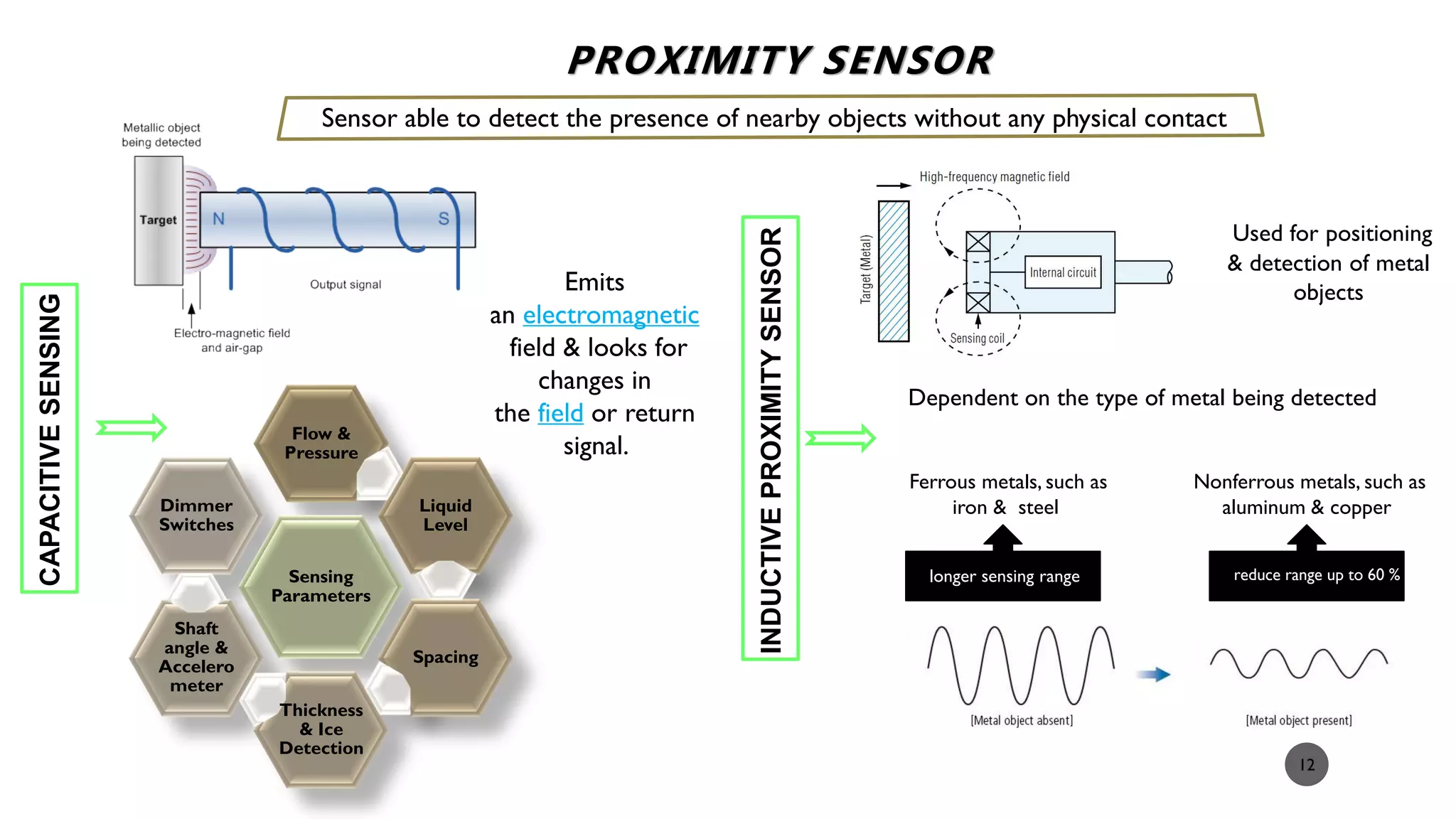
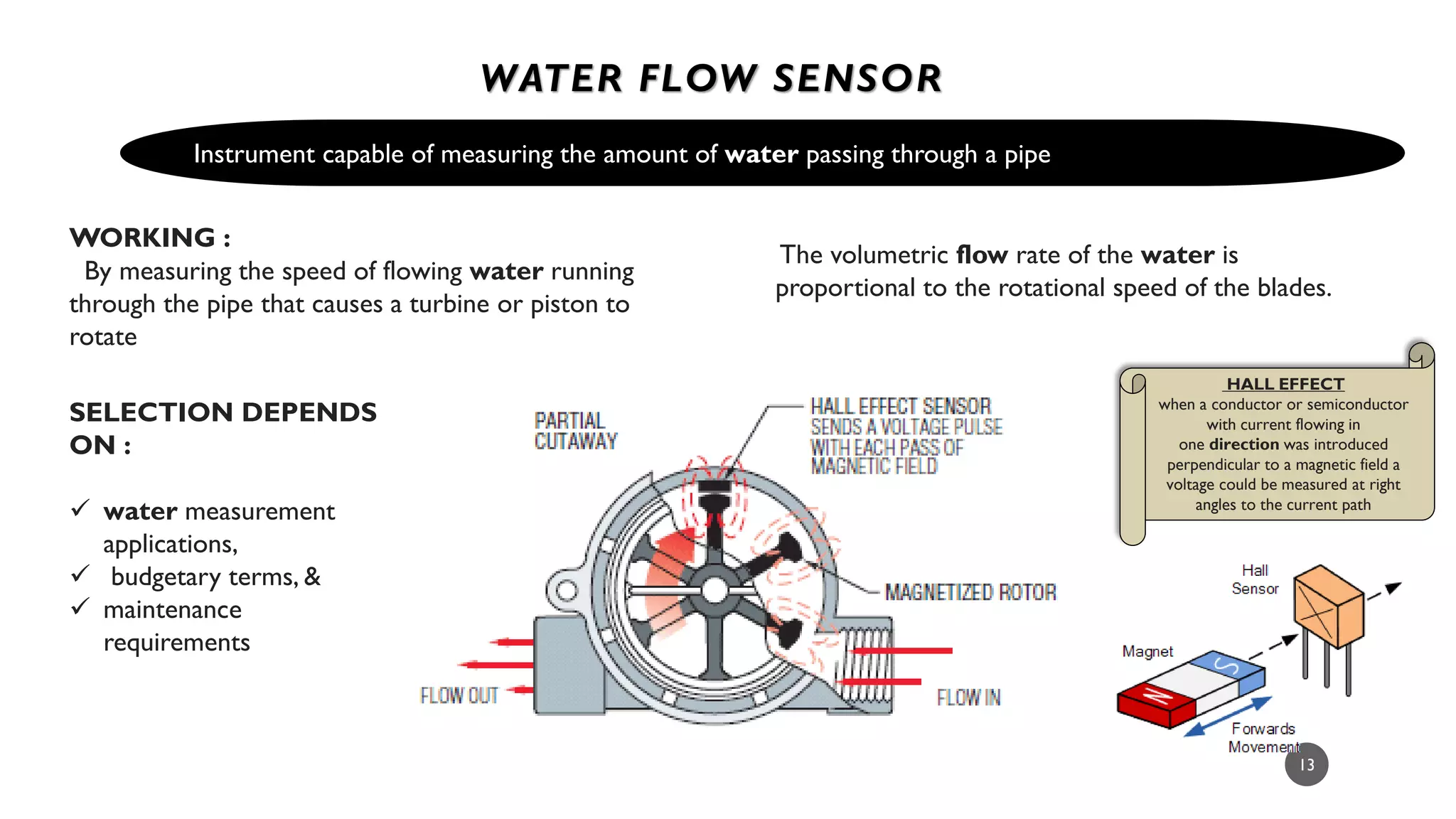
The document provides a comprehensive overview of various types of sensors used in the food industry, defining sensors as input devices that convert physical quantities into electrical signals. It classifies sensors into active and passive types and discusses specific examples such as ultrasound sensors, color sensors, light sensors, sound sensors, temperature sensors, water flow sensors, and humidity sensors, including their functions and applications. Additionally, the document emphasizes the importance of sensors for precise measurements and control in food processing and other environments.