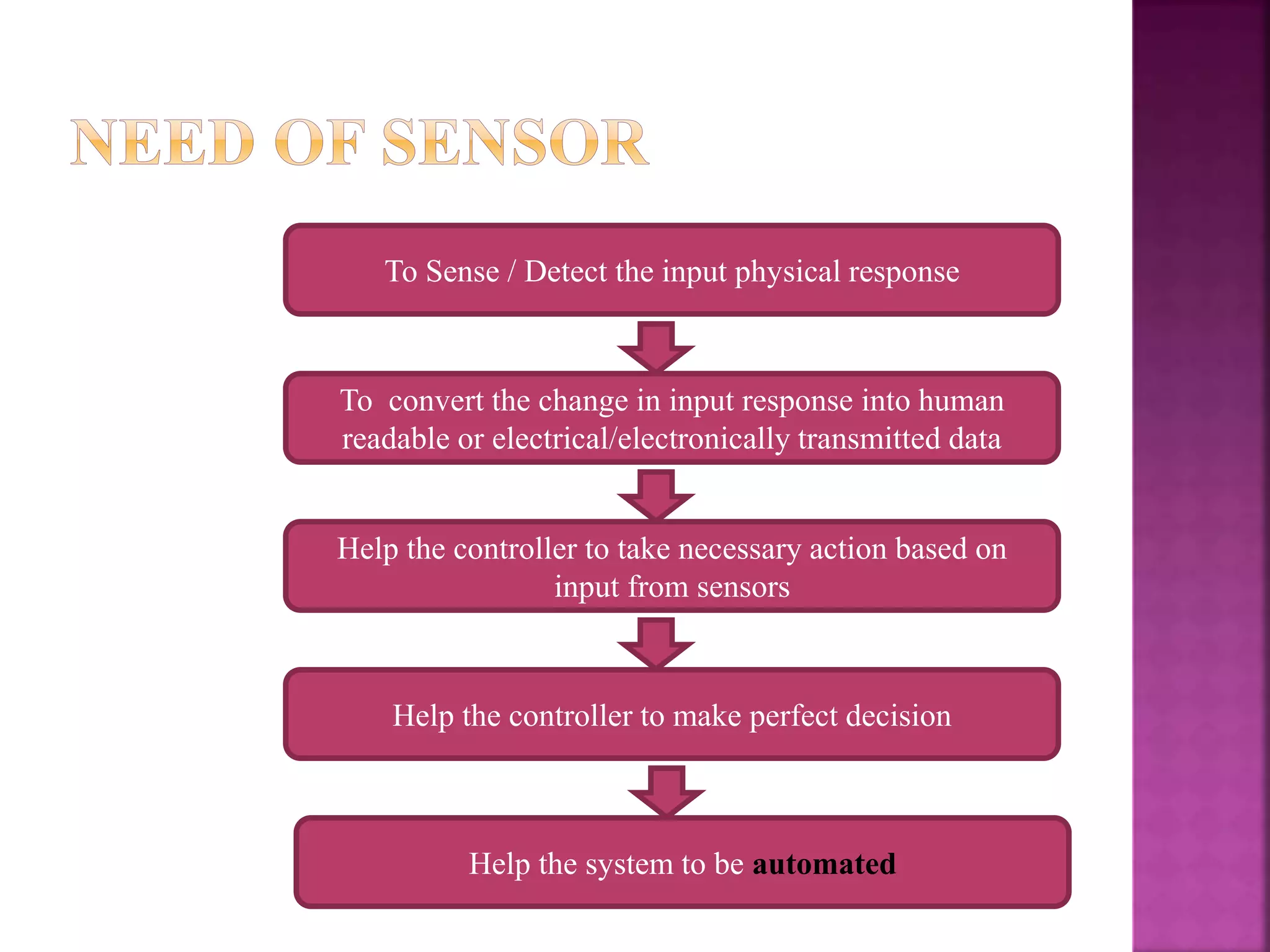
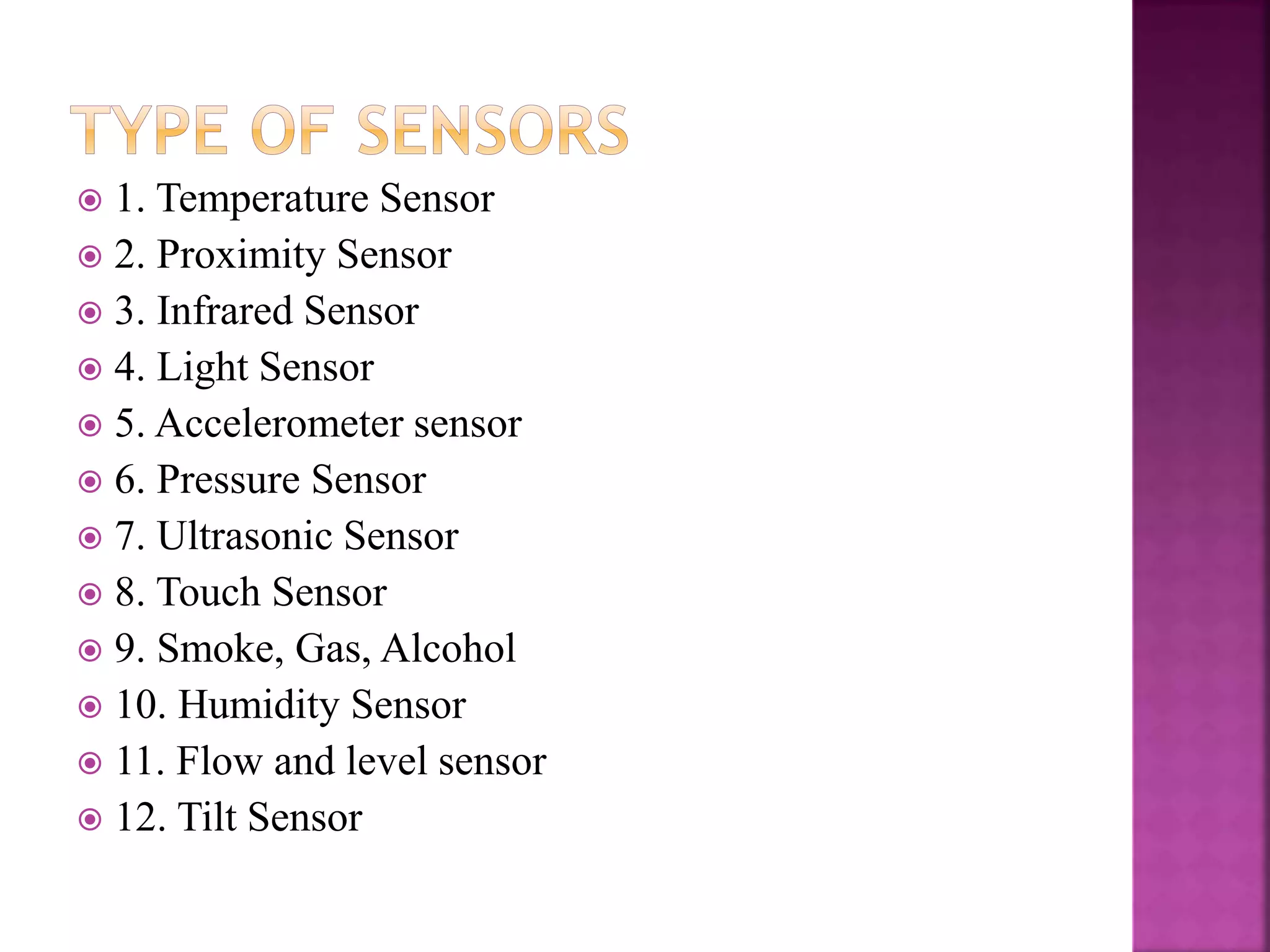
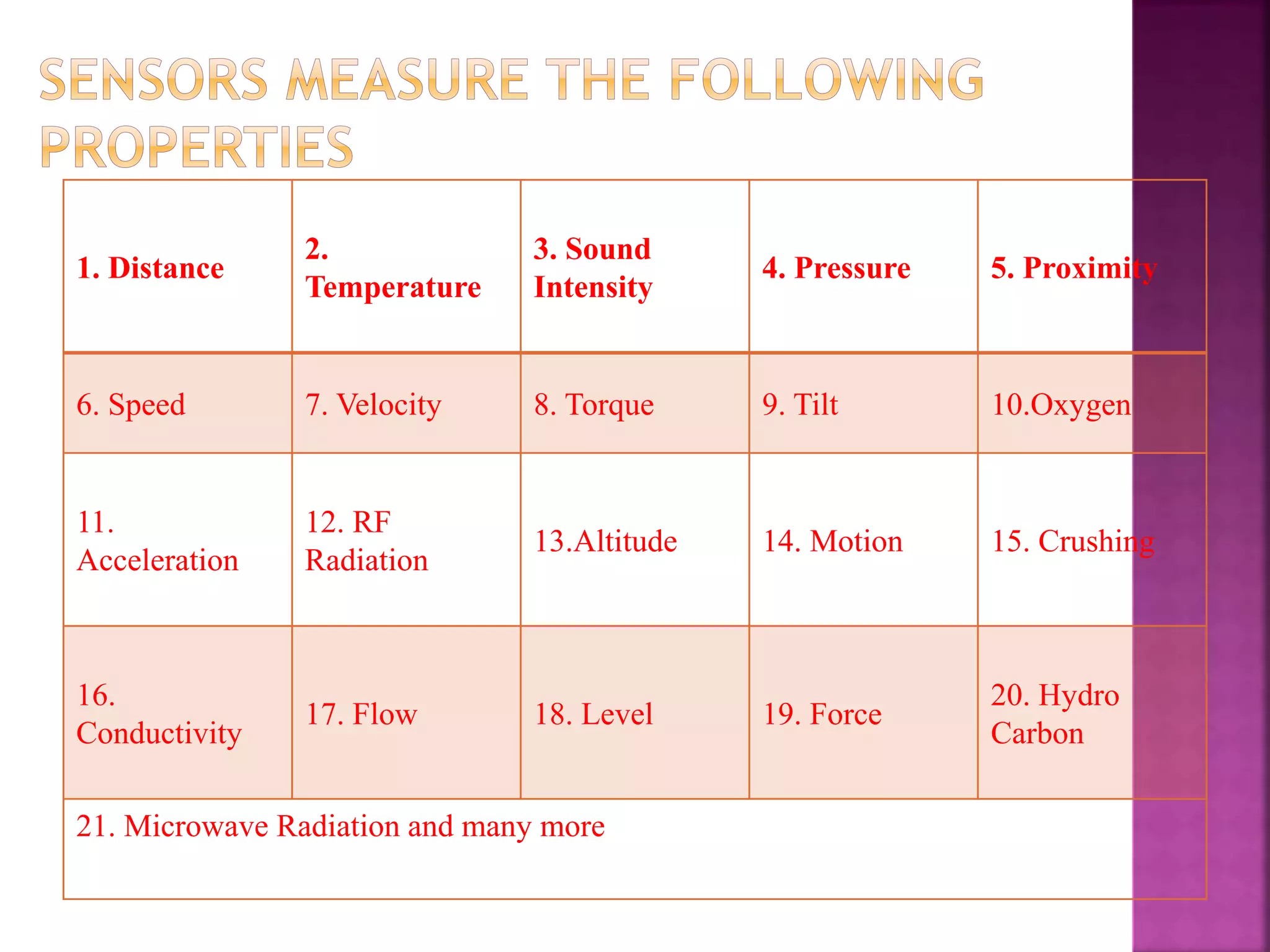
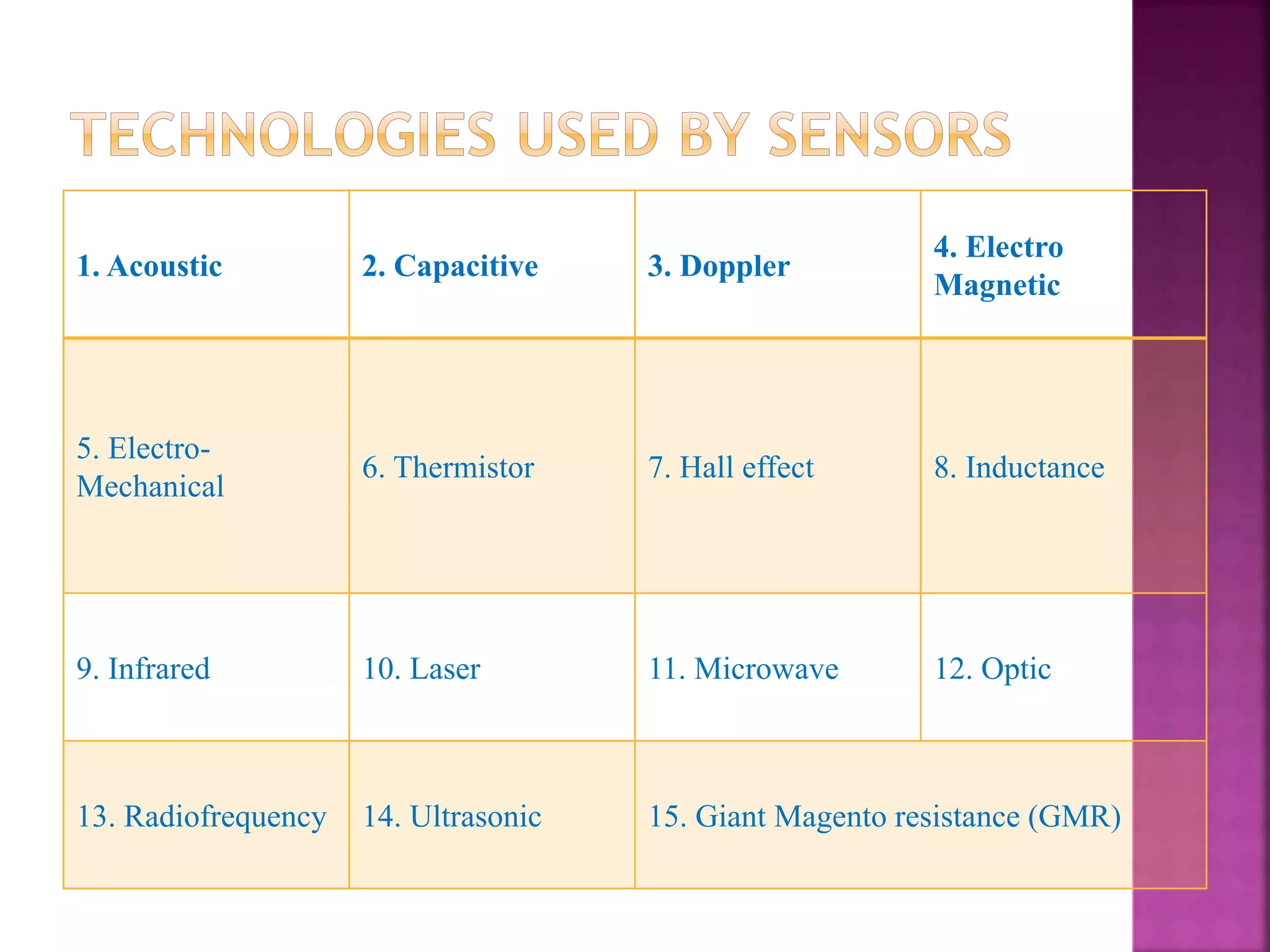
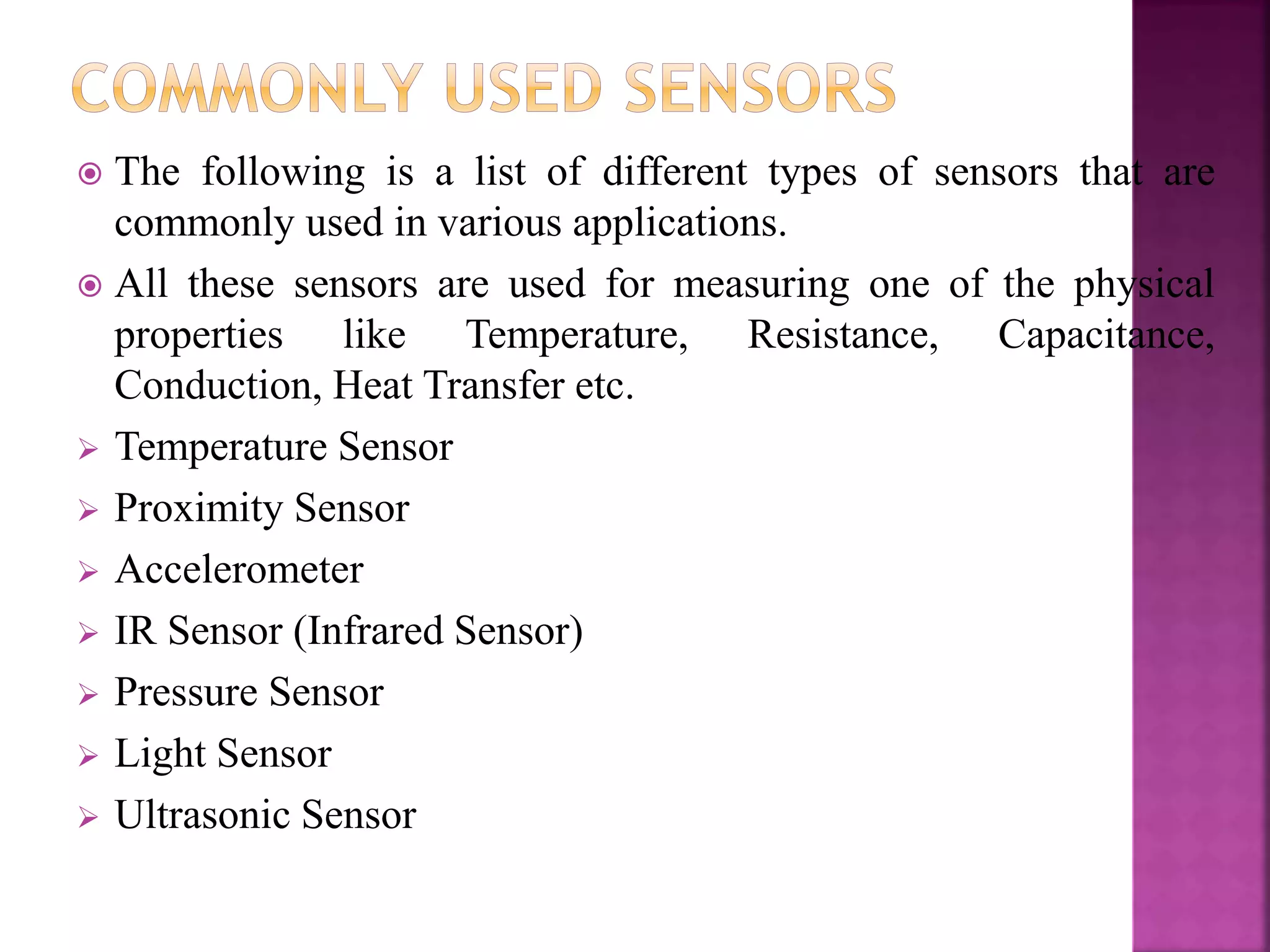
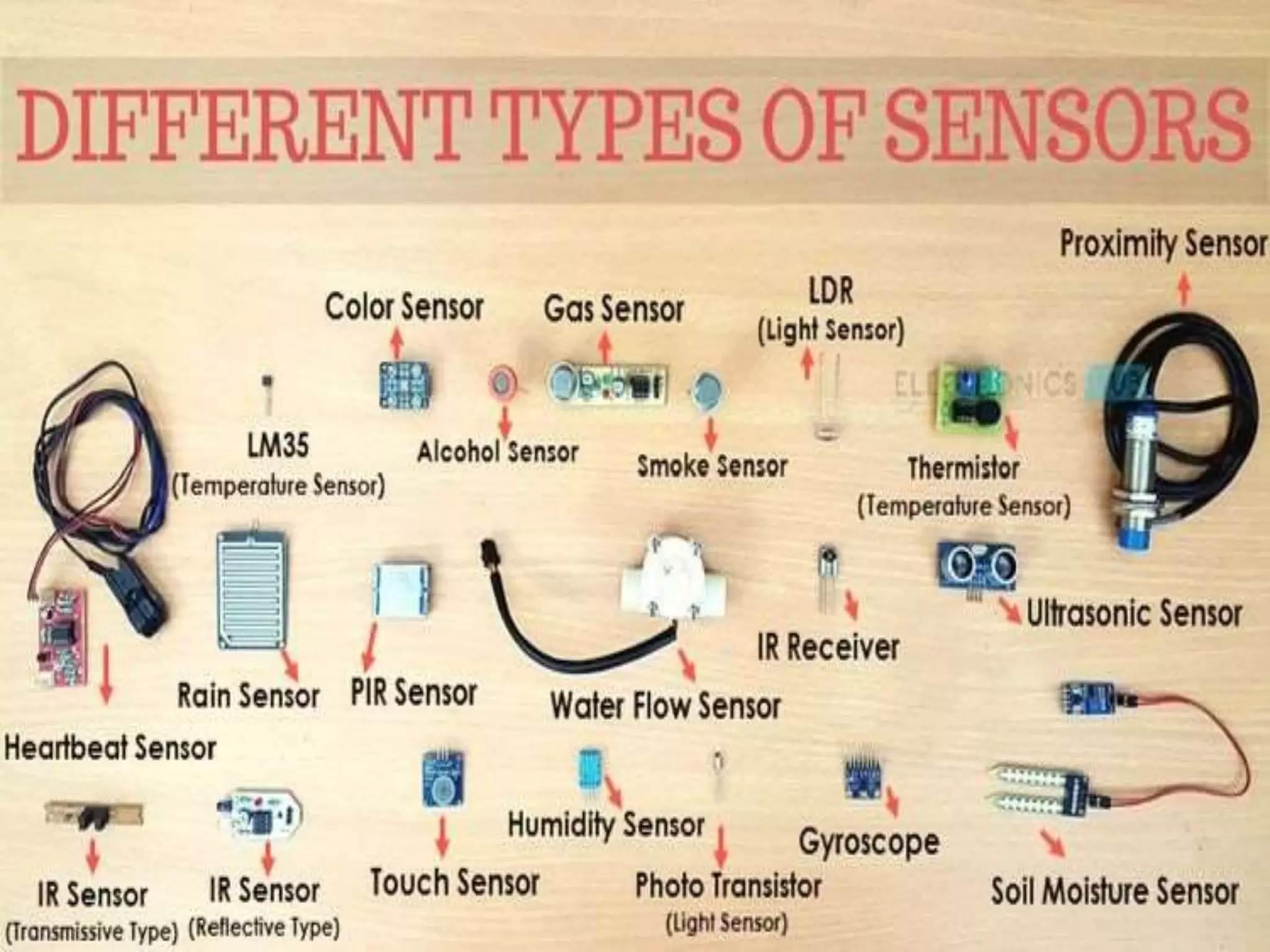
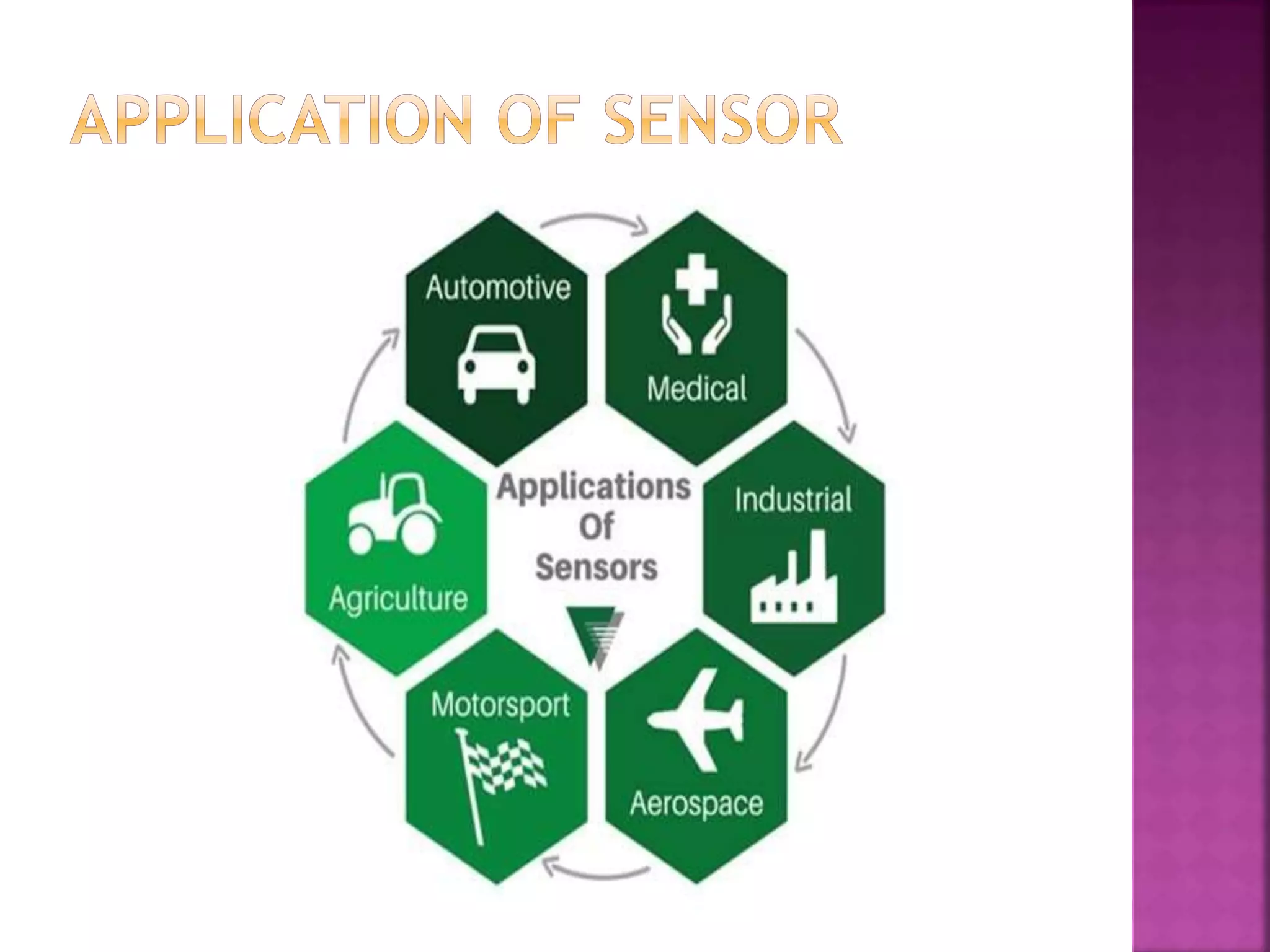
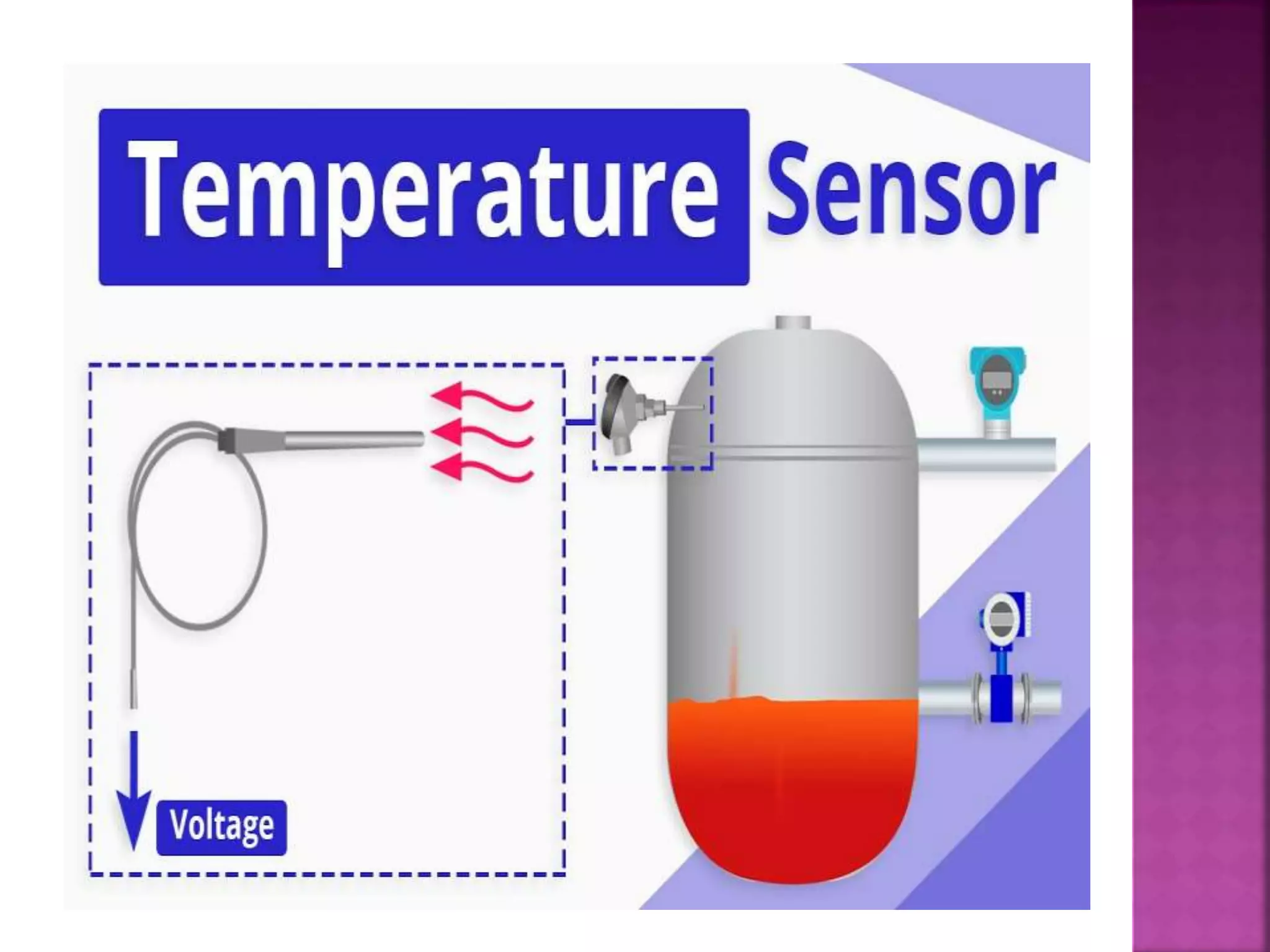
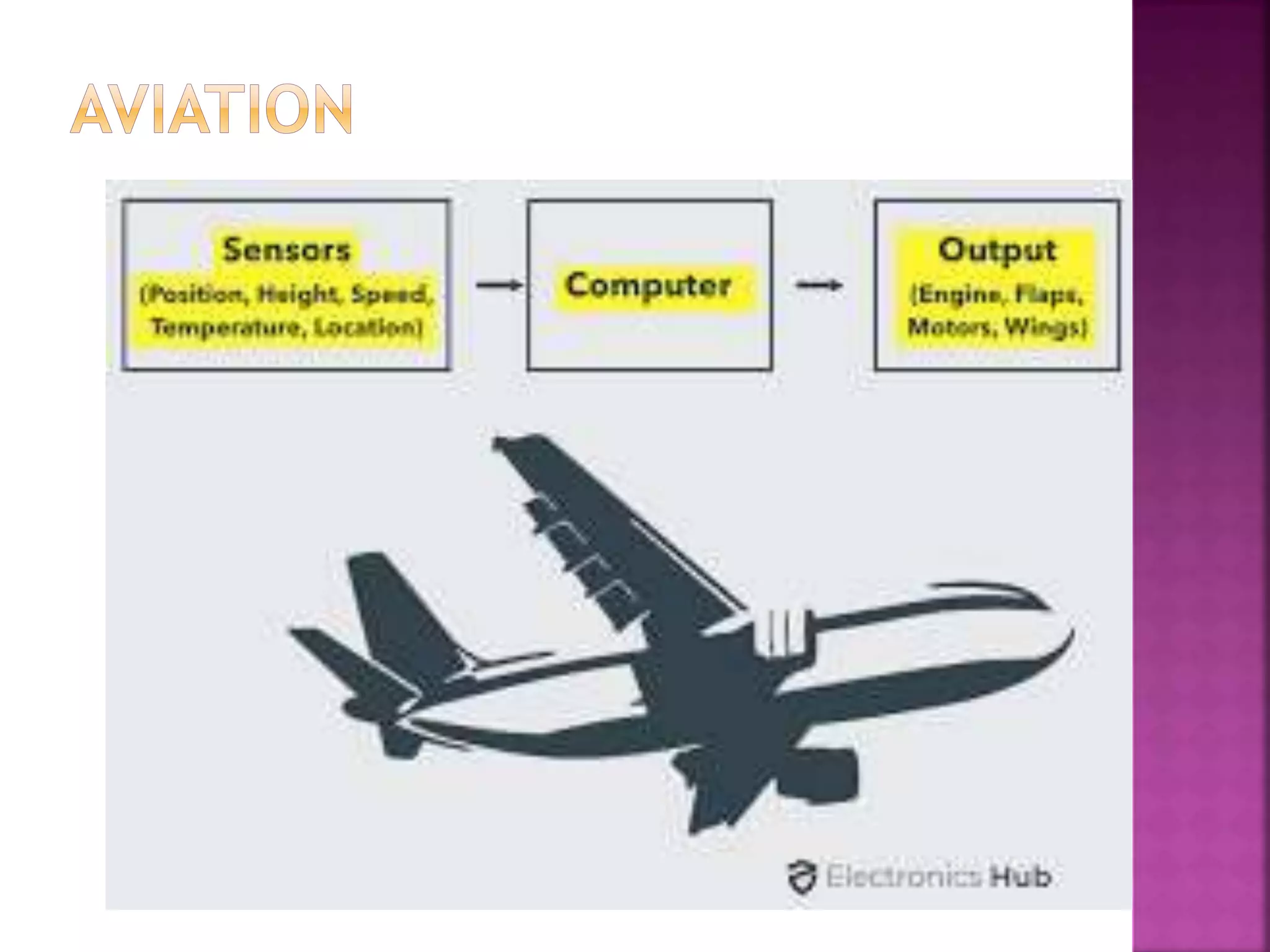
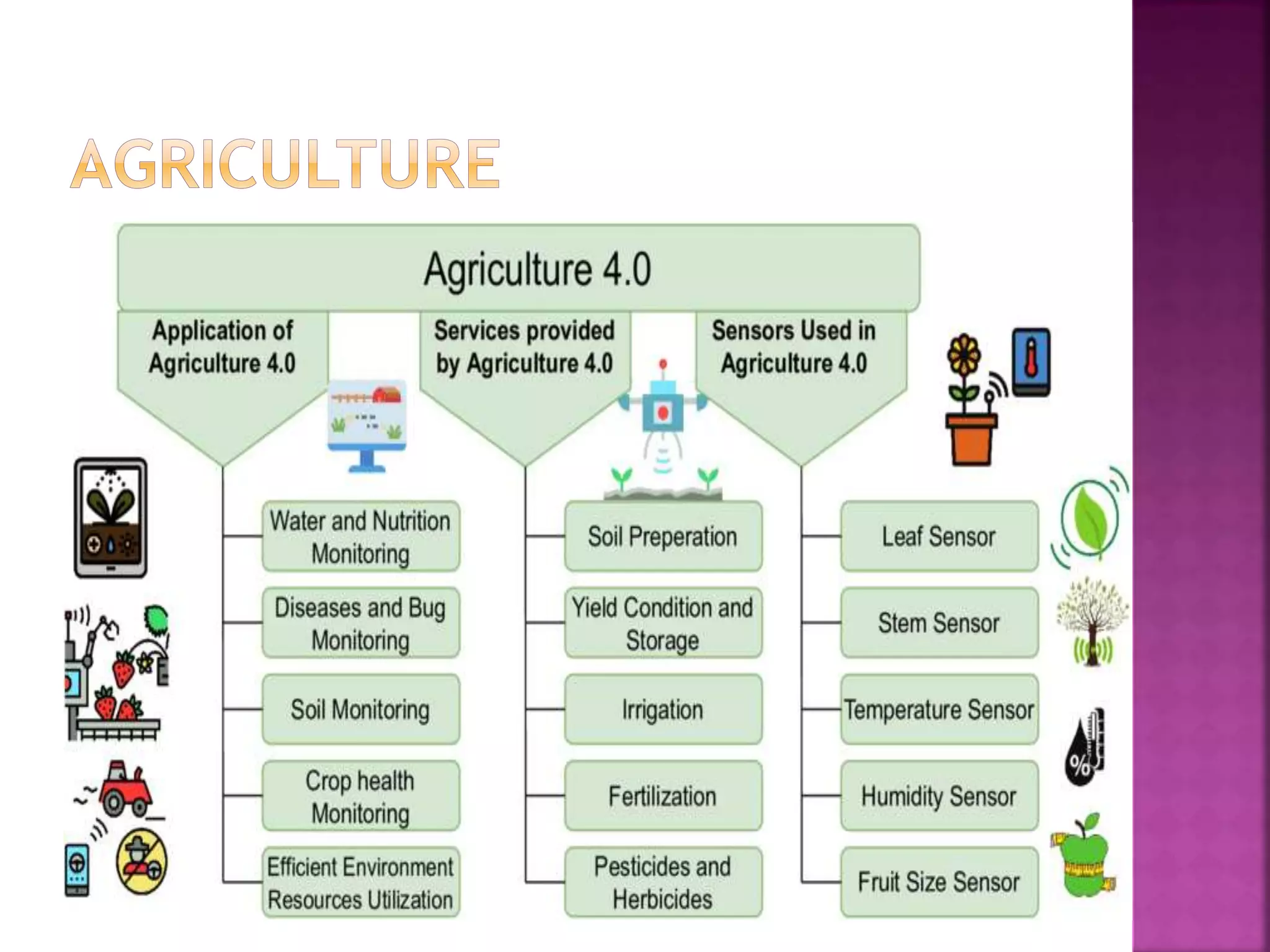
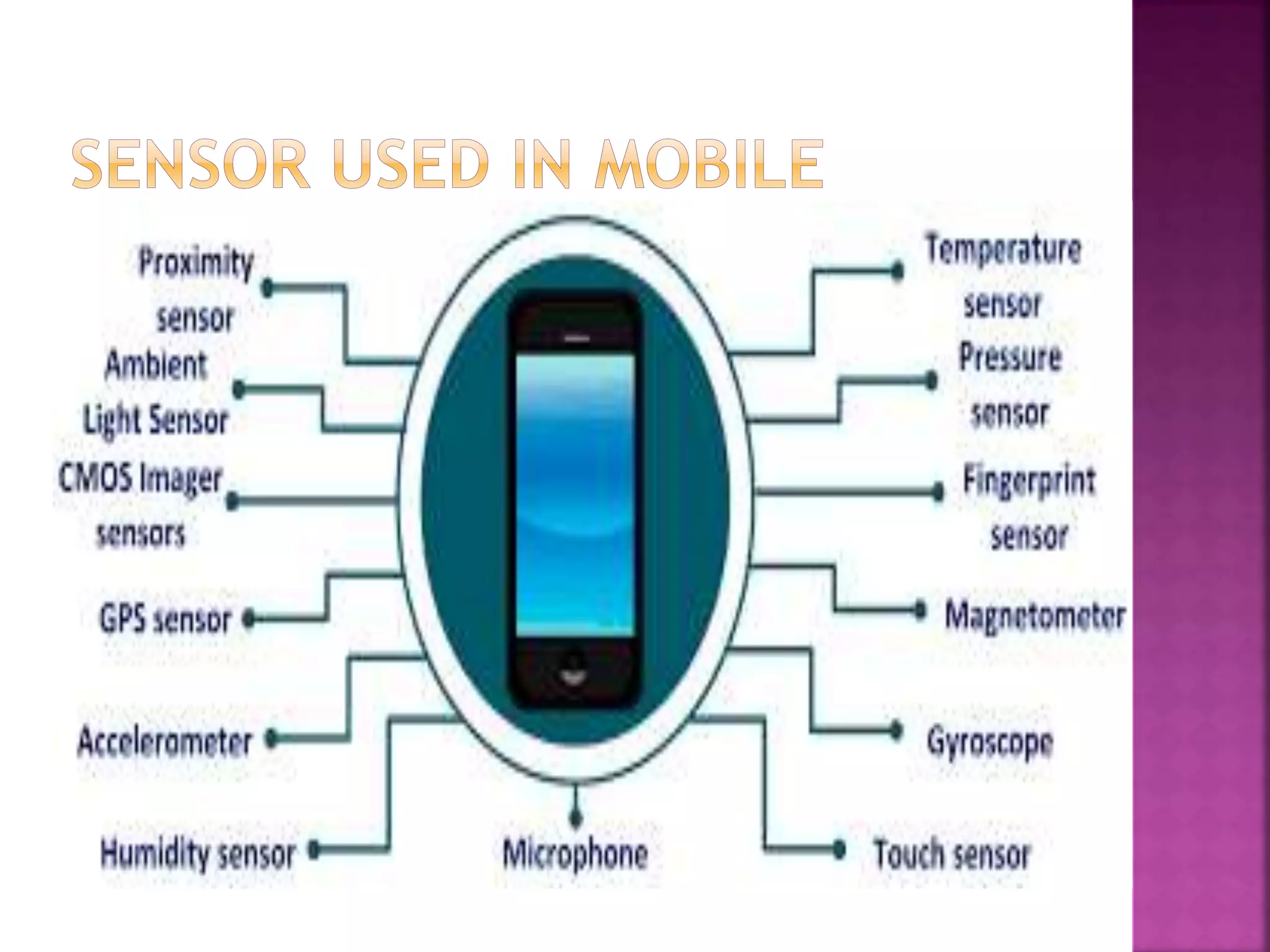
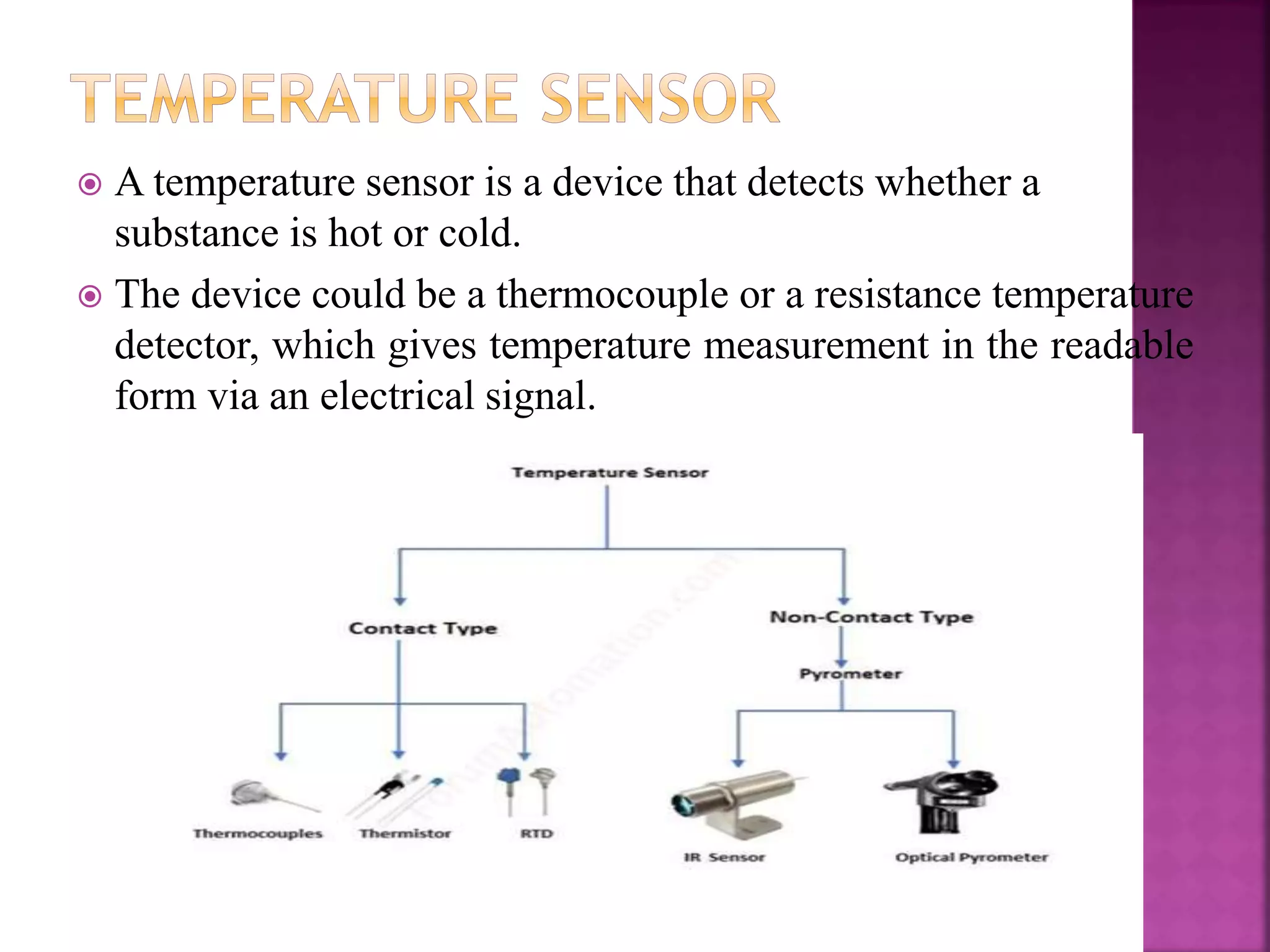
The document discusses sensors and temperature sensors. It defines a sensor as a device that detects and responds to physical input from the environment and converts it into a readable signal. It then discusses different types of temperature sensors like thermocouples, thermistors, and RTDs that detect temperature changes by measuring properties like voltage, resistance, or current. Finally, it provides examples of infrared temperature sensors and optical pyrometers that can measure the temperature of moving or hot objects non-contactly and discusses common temperature sensor uses.