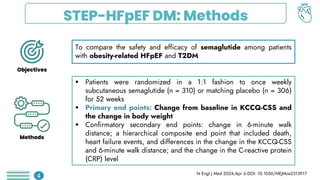
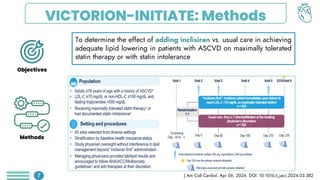
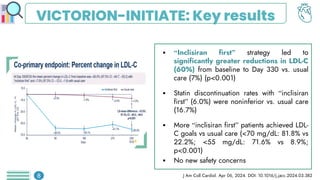
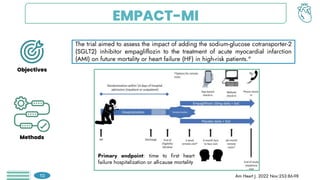
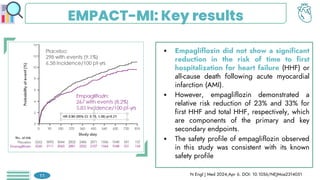
Among obese patients with HFpEF and type 2 DM, once weekly subcutaneous semaglutide was superior to placebo in improving body weight and patient-oriented QoL outcomes at 52 weeks. For patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease who hadn't achieved LDL-C levels below 70 mg/dL, the prompt addition of inclisiran resulted in significant reductions in LDL-C levels. Empagliflozin did not lower the risk of a first hospitalization for heart failure (HF) or death from any cause among patients with an increased risk for HF following acute myocardial infarction.







![PREVENT: Key results
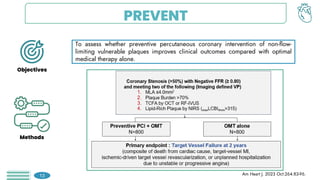
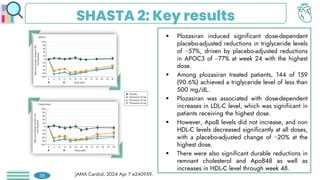
The primary endpoint of target vessel failure
at 2 years for PCI + OMT vs. OMT alone,
was: 0.4% vs. 3.4% (hazard ratio [HR] 0.11,
95% confidence interval [CI] 0.03-0.36, p =
0.0003).
Preventive PCI also reduced the composite
patient-oriented outcome of risk of all-cause
death, any MI, or any repeat
revascularization.
This benefit was sustained throughout the 7-
year follow-up period.
Lancet 2024;Apr 8. DOI:0.1016/S0140-6736(24)00413-6
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acc2024chronicles-240418084524-5ed5bc4d/85/ACC-2024-Chronicles-Cardiology-Exam-pdf-16-320.jpg)










![AEGIS II CSL 112: Key results
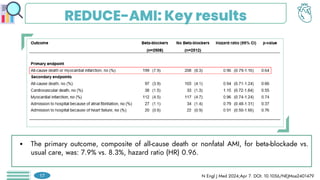
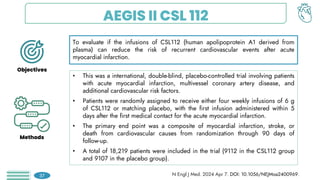
There was no significant difference between the
groups in the risk of a primary end-point event at
90 days of follow-up (439 patients [4.8%] in the
CSL112 group vs. 472 patients [5.2%] in the
placebo group; hazard ratio, 0.93 (P=0.24)
At the end of 180 days of follow-up (622 patients
[6.9%] vs. 683 patients [7.6%]; hazard ratio,
0.91), or at 365 days of follow-up (885 patients
[9.8%] vs. 944 patients [10.5%]; hazard ratio,
0.93).
N Engl J Med. 2024 Apr 7. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2400969.
38](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acc2024chronicles-240418084524-5ed5bc4d/85/ACC-2024-Chronicles-Cardiology-Exam-pdf-40-320.jpg)