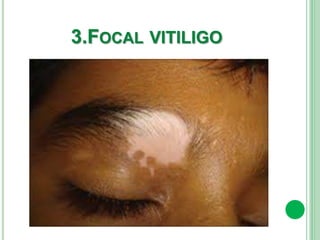
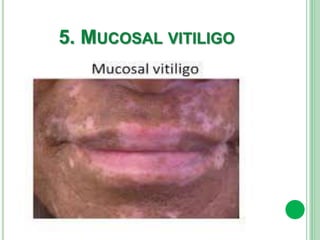
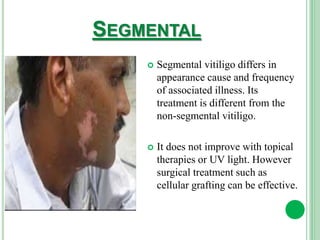
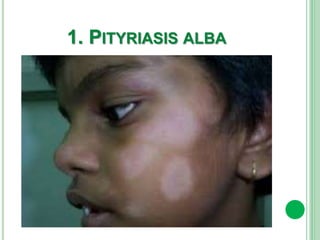
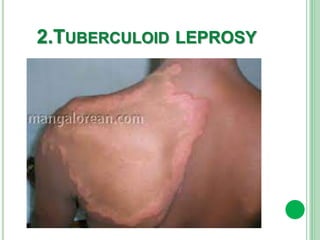
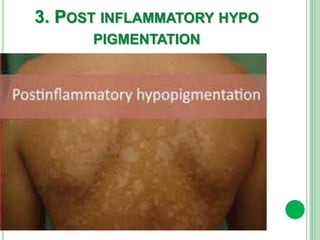
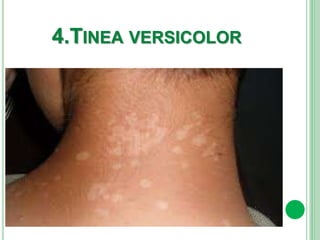
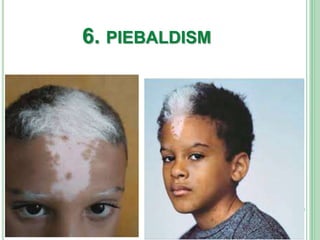
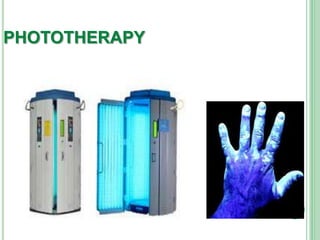
Vitiligo is a long-term skin condition characterized by patches of skin losing pigment, resulting in white patches with sharp borders. The cause is unknown but is believed to involve genetic susceptibility triggering an autoimmune response that destroys skin pigment cells. Risk factors include family history of autoimmune diseases. Treatment options aim to repigment the skin through topical steroids, phototherapy, or cellular grafting for segmental vitiligo. While there is no cure, combining treatments may provide improved management of symptoms and quality of life for patients.























![ Advances in Vitiligo: An Update on Medical and
Surgical Treatments
Alexander B. Dillon, MD, Andrew Sideris, MSC, [...],
and Nada Elbuluk, MD, MSC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminaronlecoderma-190912083802/85/Seminar-on-lecoderma-35-320.jpg)

