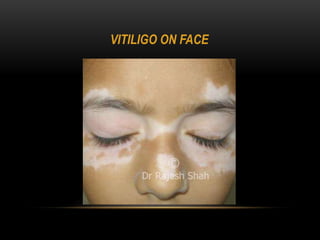
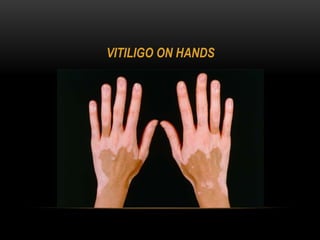
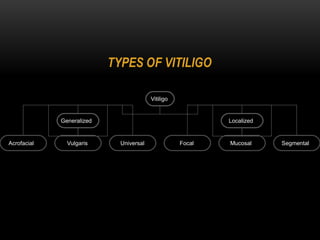
1) Vitiligo is a chronic skin disorder characterized by loss of skin pigmentation and the appearance of white patches on the skin.
2) It affects different parts of the body and can start progressing at any age. While it does not cause physical harm, it can cause psychological issues like low self-esteem.
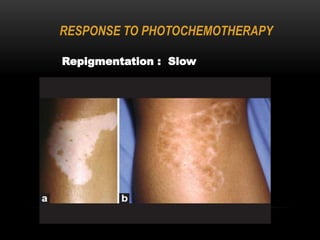
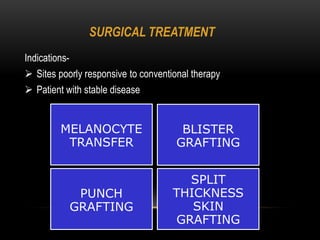
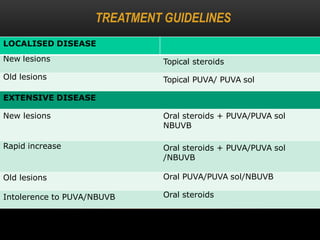
3) Treatments include topical corticosteroids, immune-modulators like tacrolimus, phototherapy using UV light, and cosmetic cover-ups. Many patients prefer traditional ayurvedic and homeopathic treatments as well.