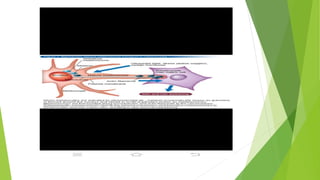
Vitiligo is a long-lasting skin disorder where white patches appear on the skin due to the loss of pigment-producing cells. The exact cause is unknown but genetic and autoimmune factors may play a role. Vitiligo lesions typically appear on sun-exposed areas and around body orifices. Treatment options include phototherapy, photochemotherapy using psoralens and UVA light, topical steroids for small lesions, and surgical techniques for resistant areas. Preventive measures involve a health diet rich in antioxidants, minerals and avoiding skin trauma.