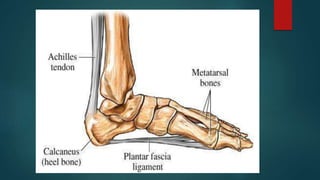
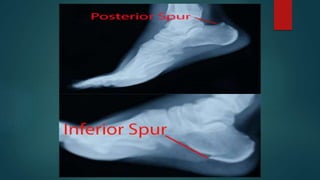
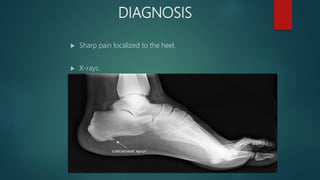
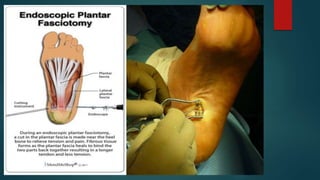
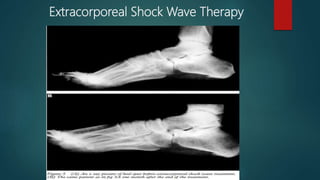
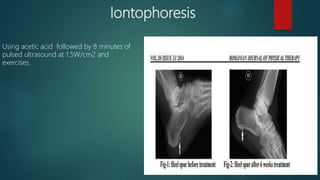
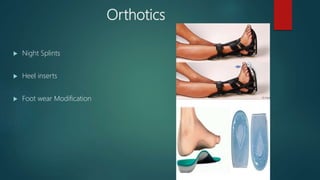
A heel spur is a bony growth that forms on the heel bone (calcaneus). Heel spurs are common and often do not cause pain, but can cause pain when contacting soft tissue. They may be caused by pressure on the heel and associated with plantar fasciitis or Achilles tendinopathy. Treatment options include medications like NSAIDs, corticosteroid injections, physiotherapy including stretching, ultrasound, shockwave therapy, and night splints or orthotics.