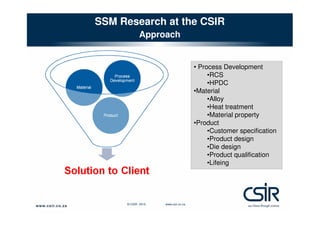
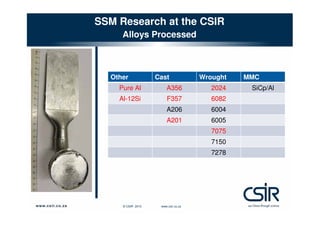
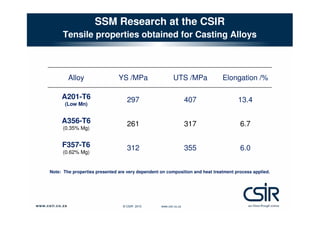
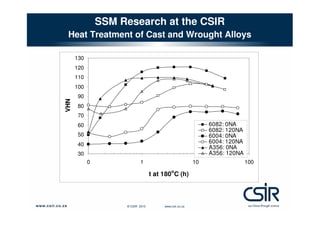
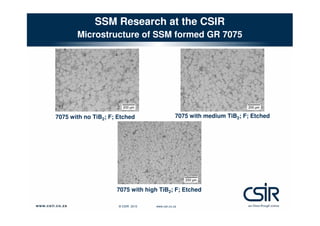
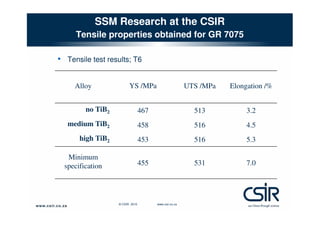
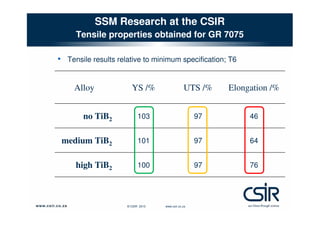
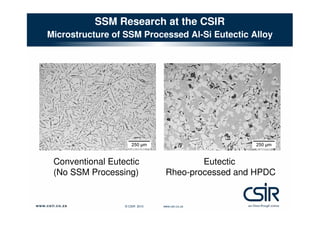
This document provides an overview of semi-solid metal forming research conducted by the CSIR in South Africa. It discusses the background of semi-solid metal forming including thixoforming and rheocasting. It describes the CSIR's approach to research, which involves developing the total product solution. Key research areas covered include processing cast and wrought aluminum alloys in semi-solid form, heat treatment, and product development. Infrastructure for research includes high pressure die casting and semi-solid billet production equipment. Research demonstrates microstructure and properties of semi-solid formed alloys can meet or exceed specifications.