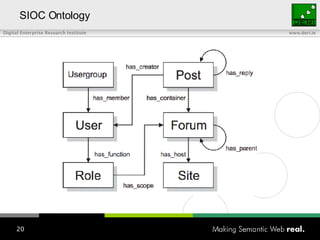
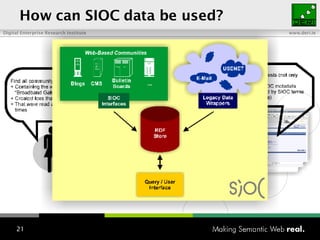
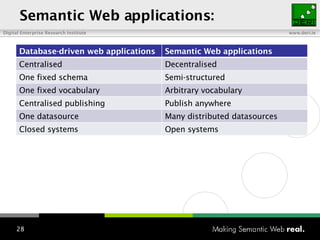
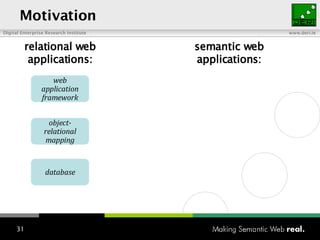
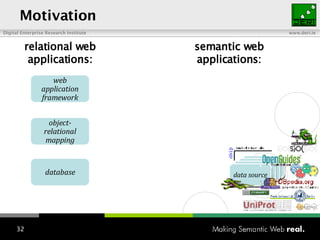
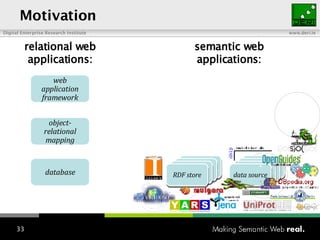
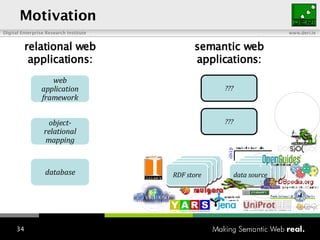
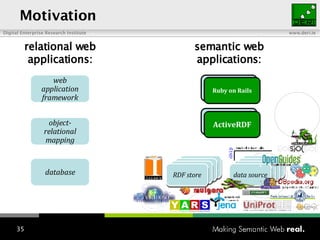
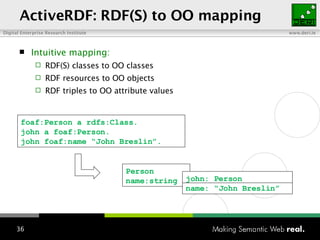
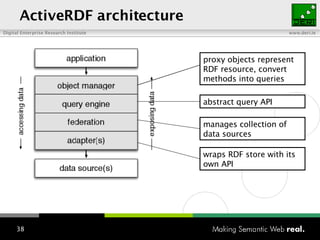
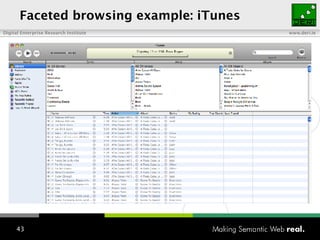
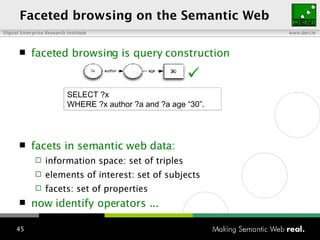
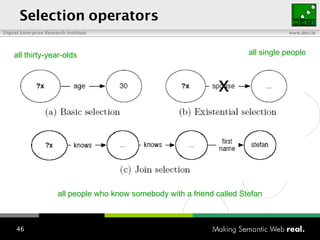
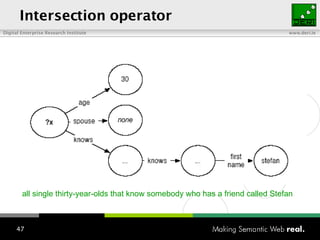
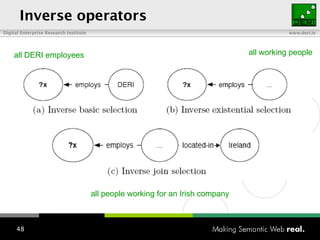
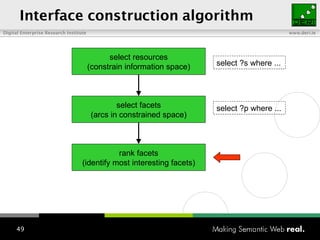
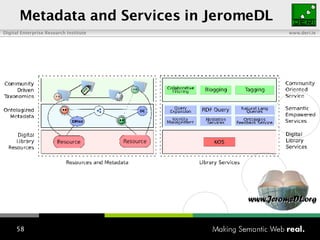
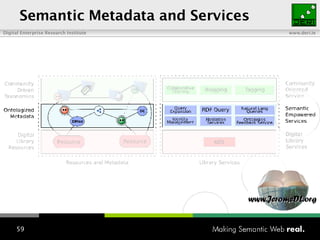
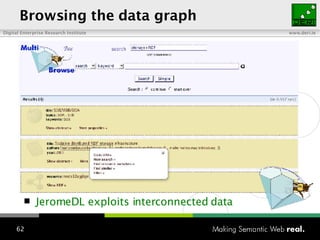
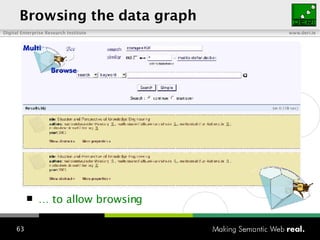
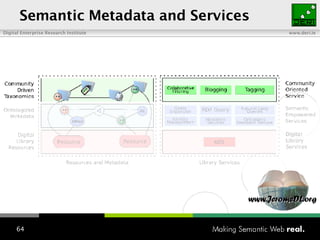
The document provides an overview of the work done at DERI Galway, including developing technologies like SIOC, ActiveRDF, and BrowseRDF to interconnect online communities and enable semantic applications. It also describes JeromeDL, a digital library system that uses semantic metadata and services to allow users to collaboratively browse and share knowledge.






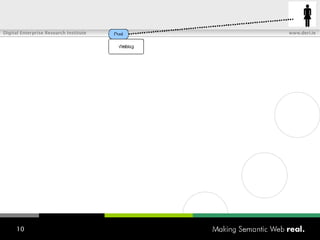
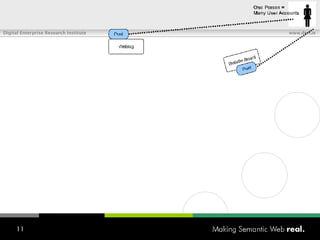
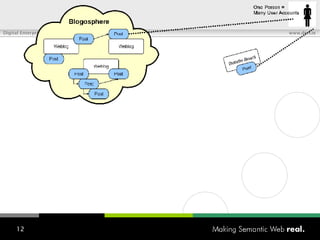
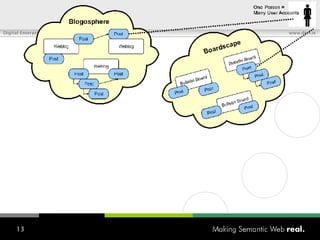
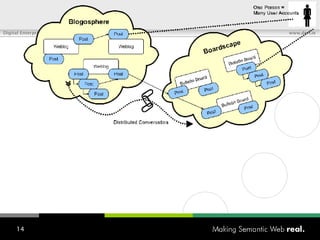
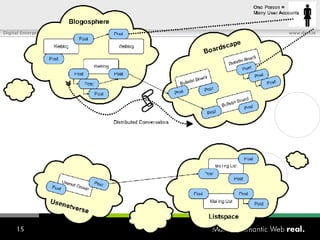
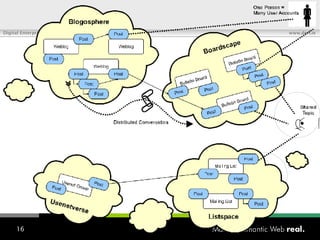
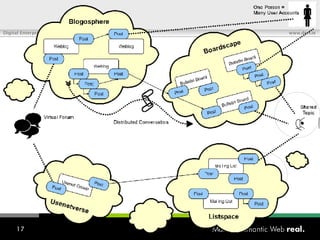
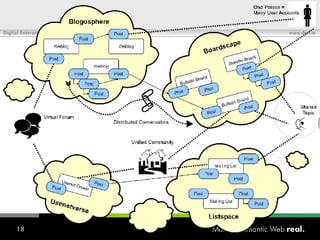
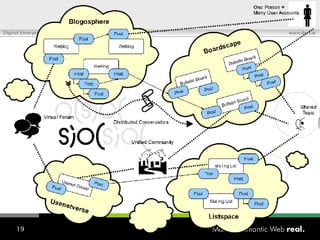
![What is SIOC? Semantically-Interlinked Online Communities (SIOC) Connecting many types of online communities (blogs, forums, mailing lists, etc.) Interesting possibilities: Distributed linked conversations Decentralised discussion channels and communities “ I […] think the concept is HOT” – Robert Douglass, Drupal Developer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/semantic-web-in-action-22267/85/Semantic-Web-in-Action-9-320.jpg)