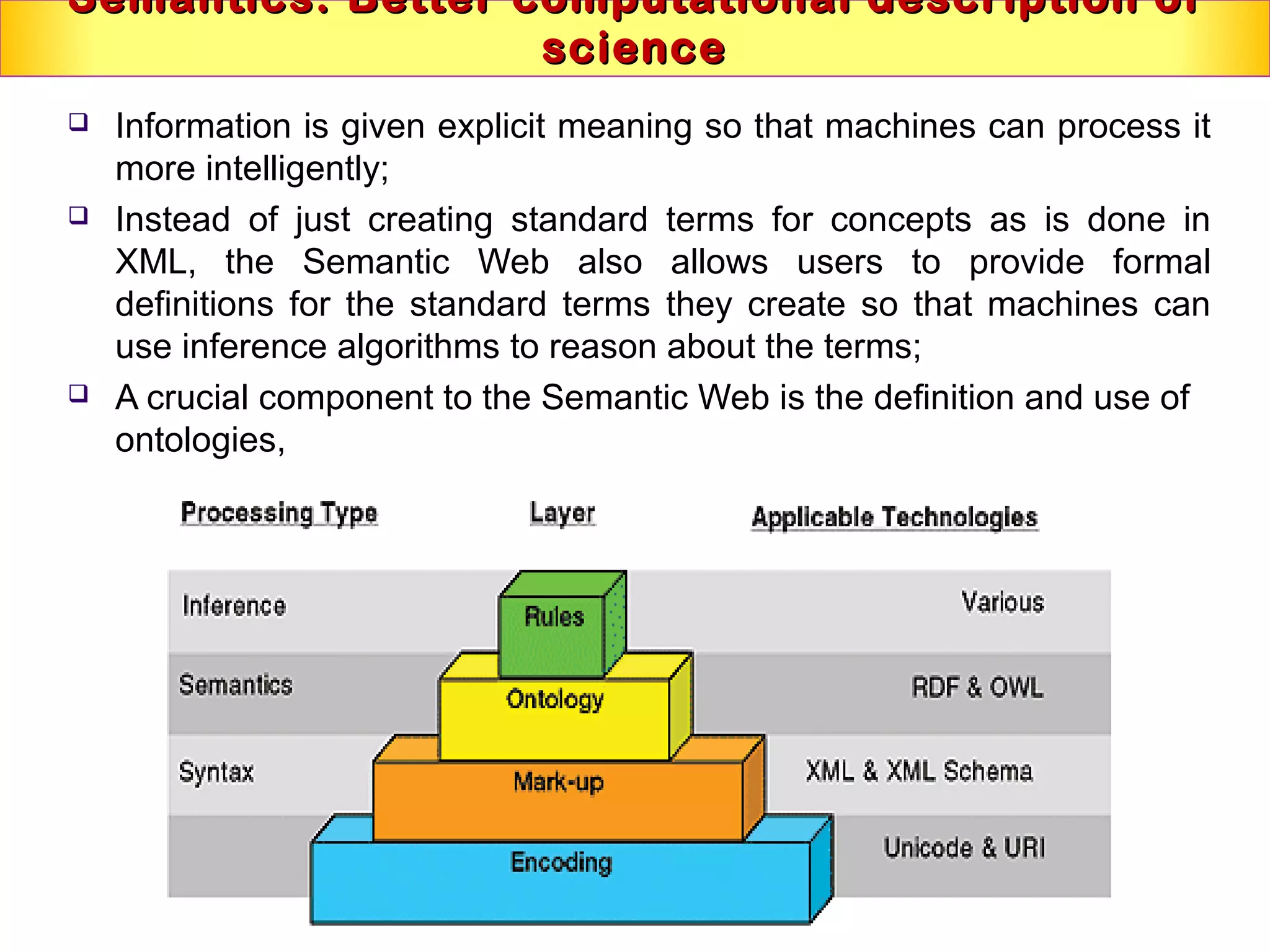
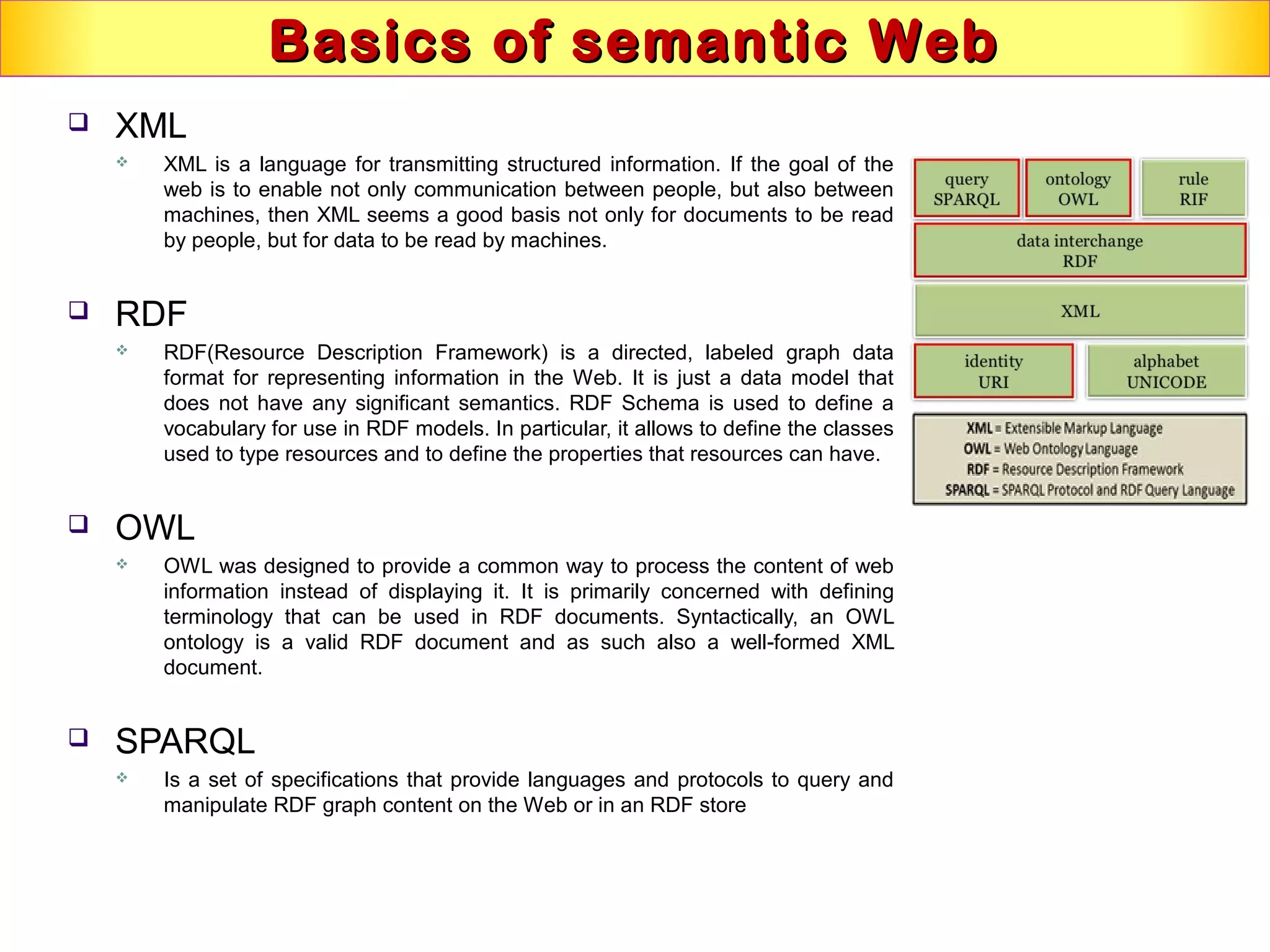
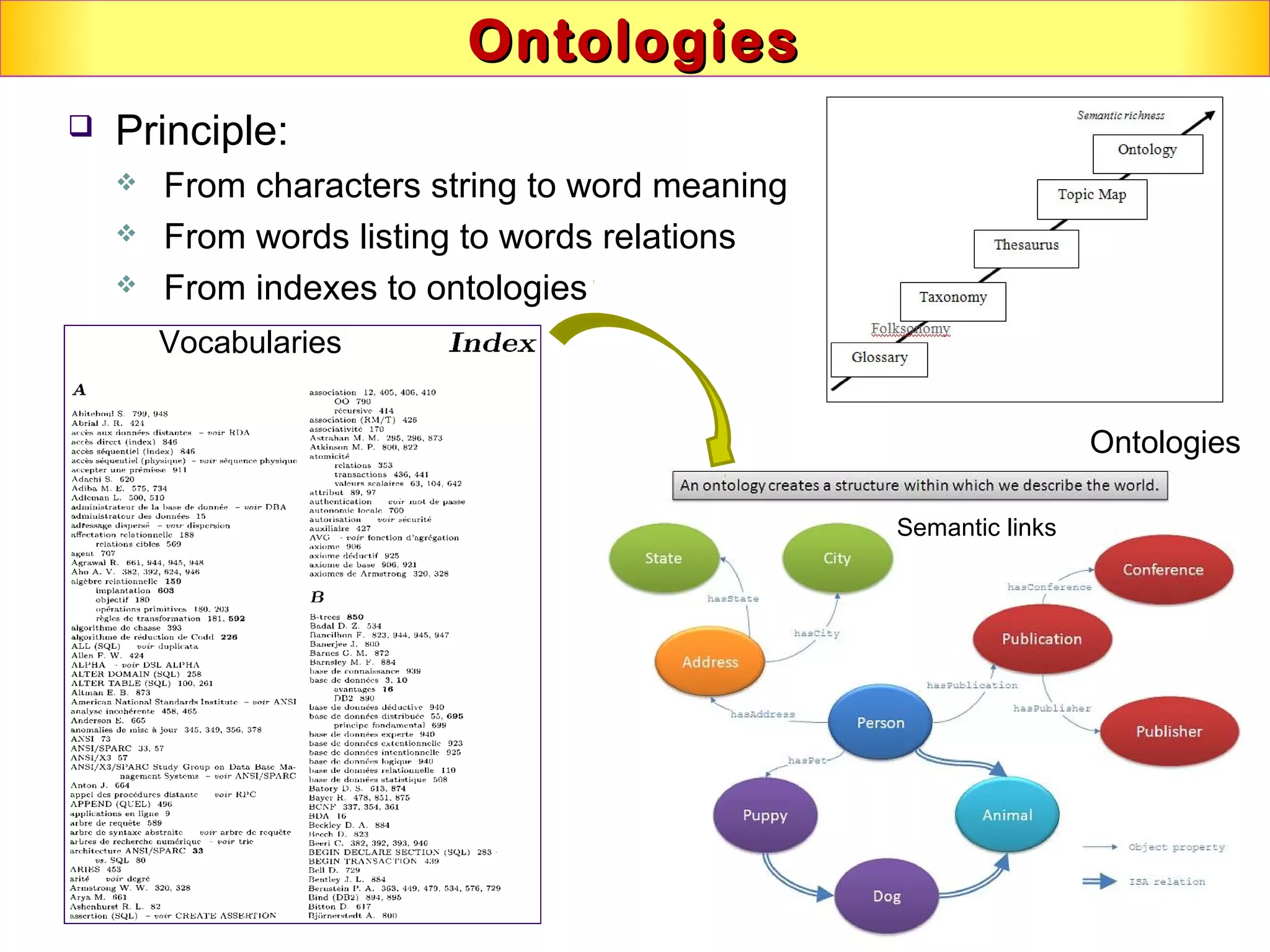
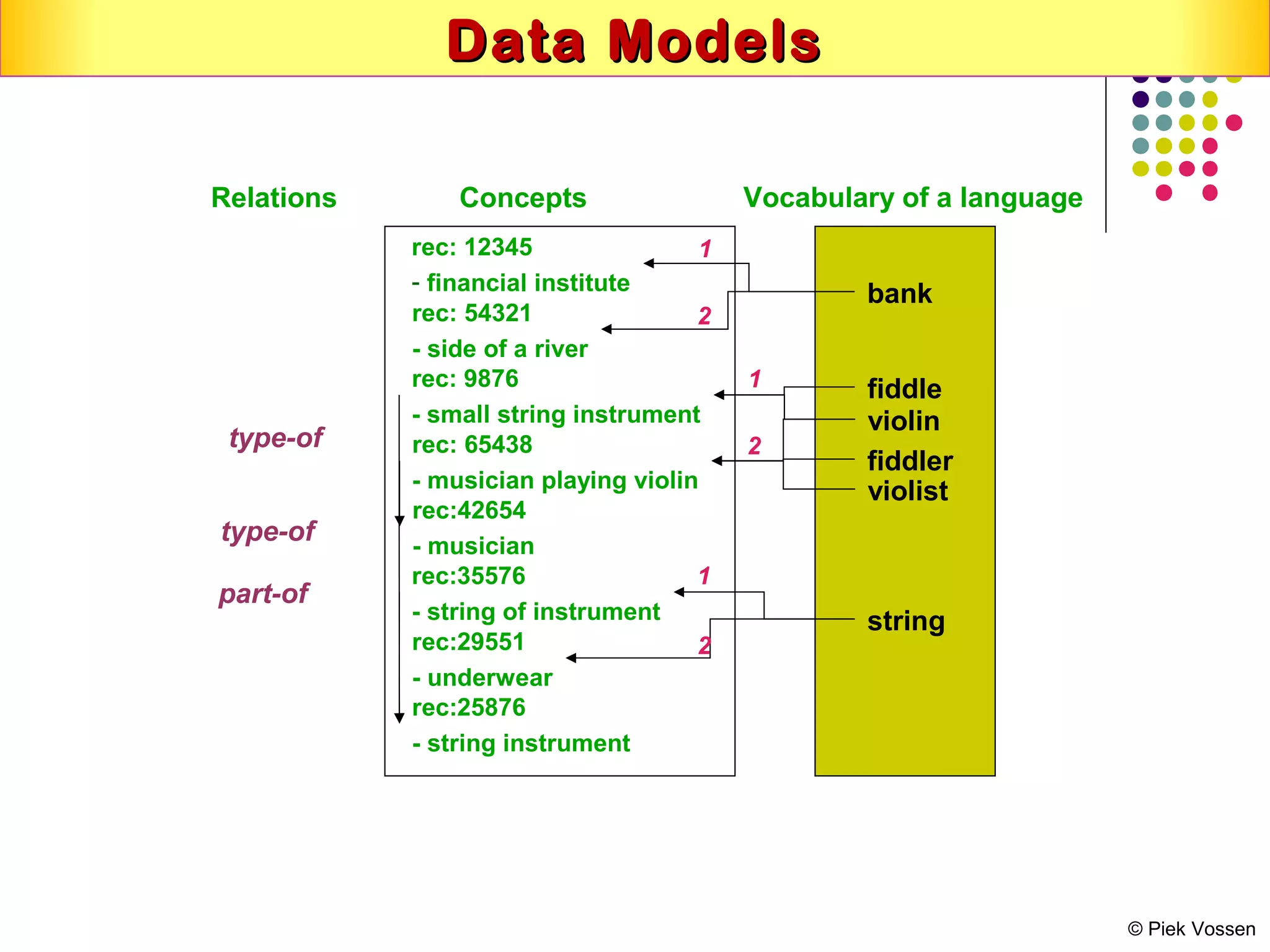
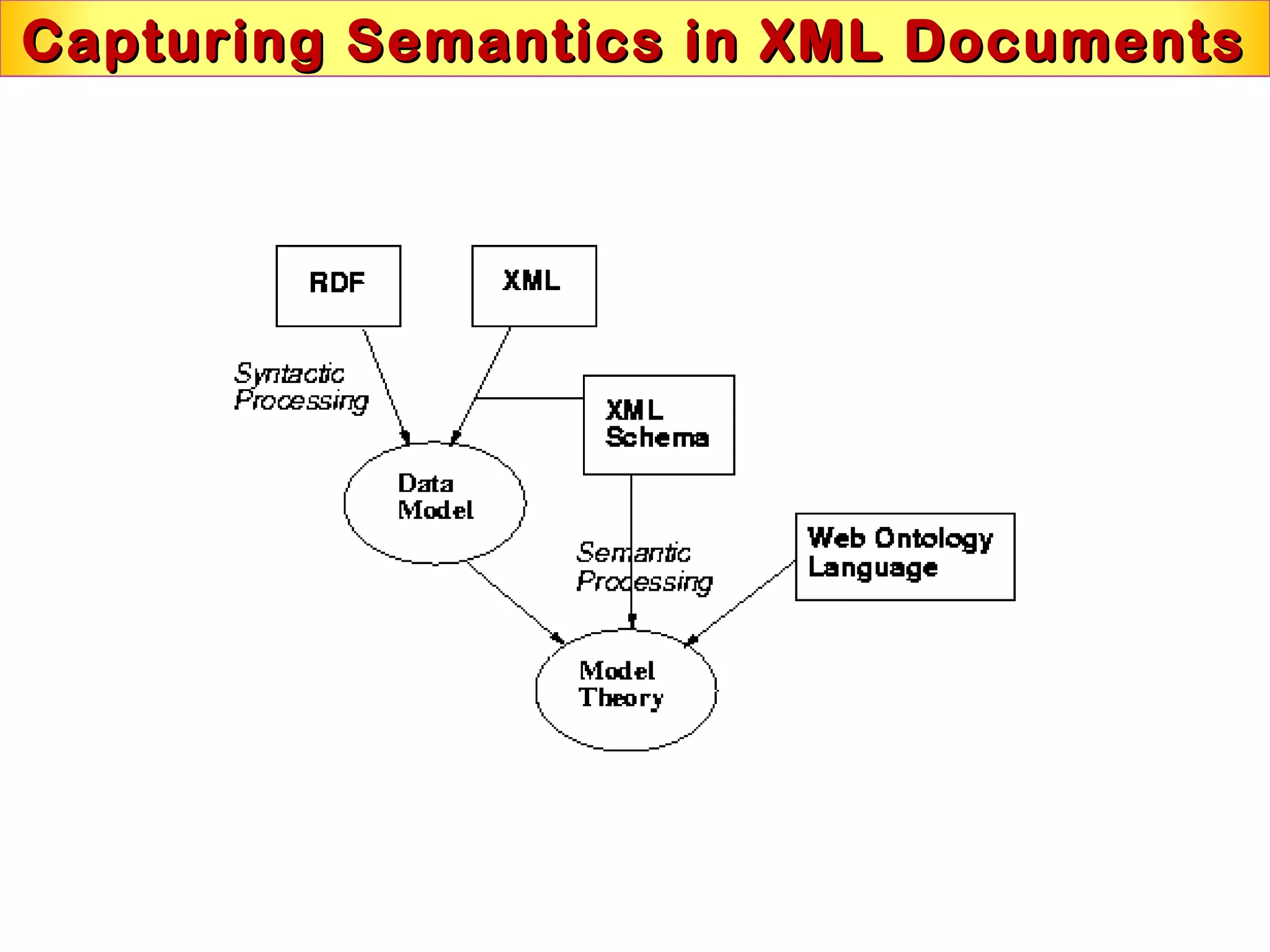
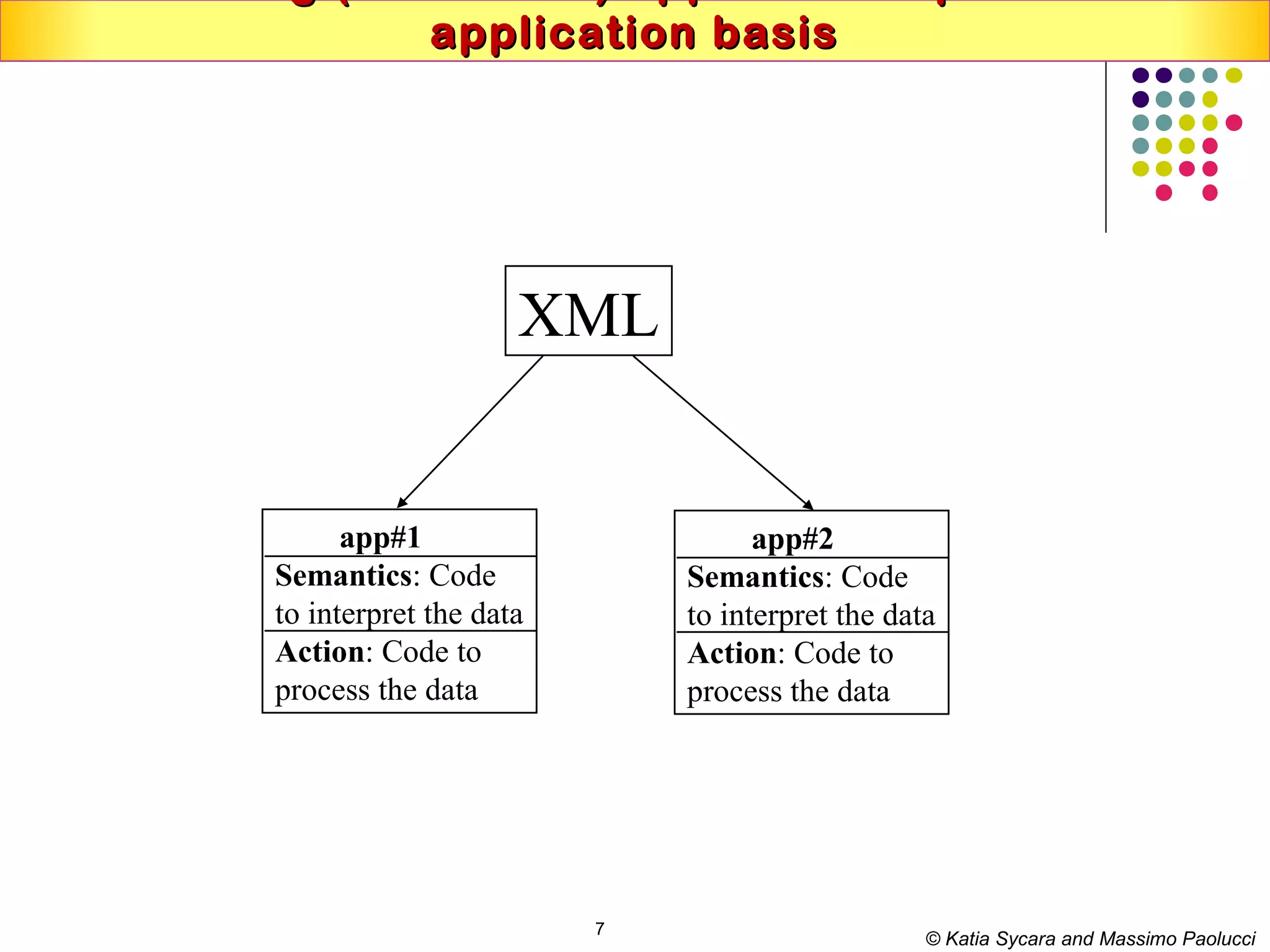
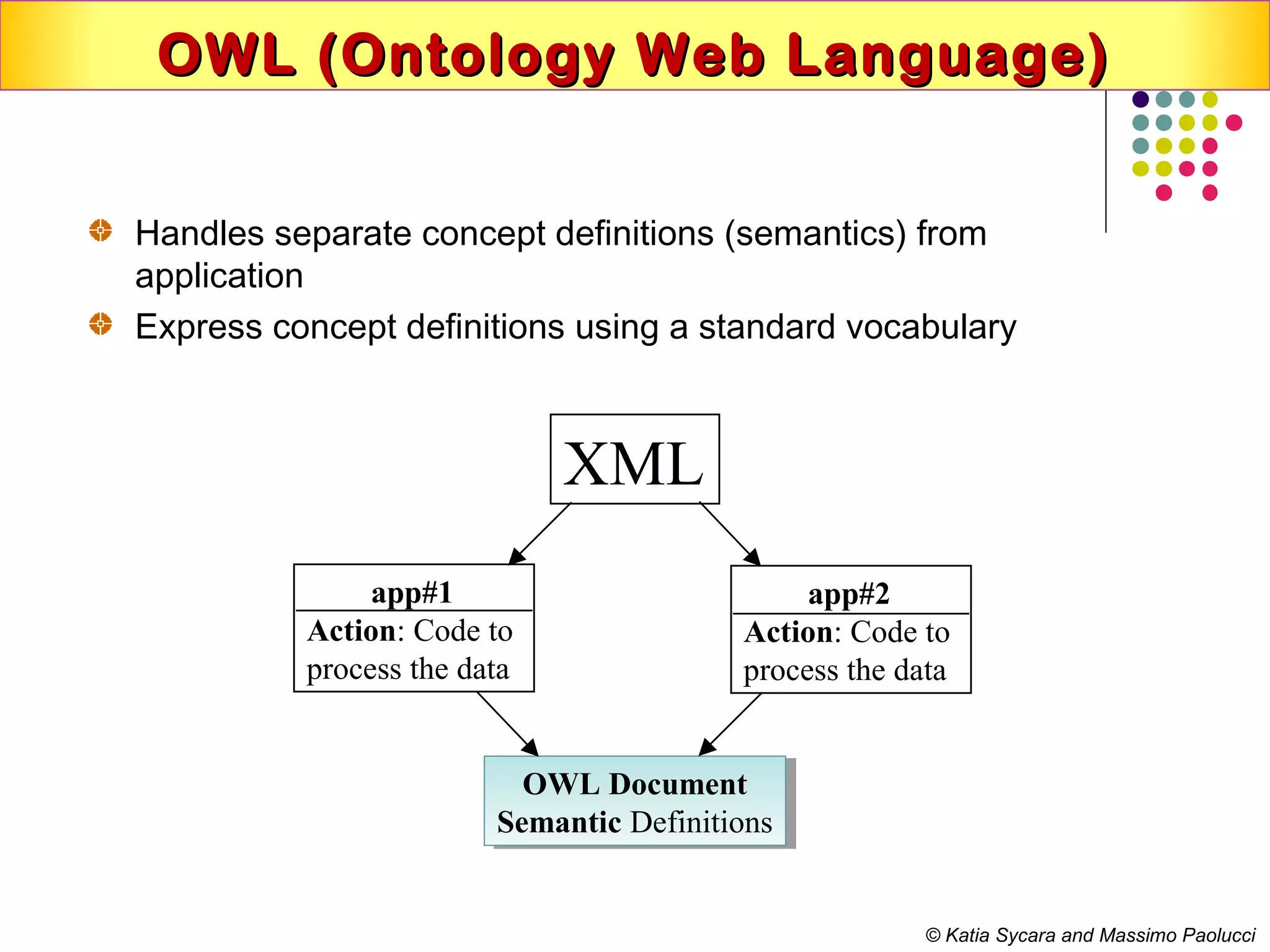
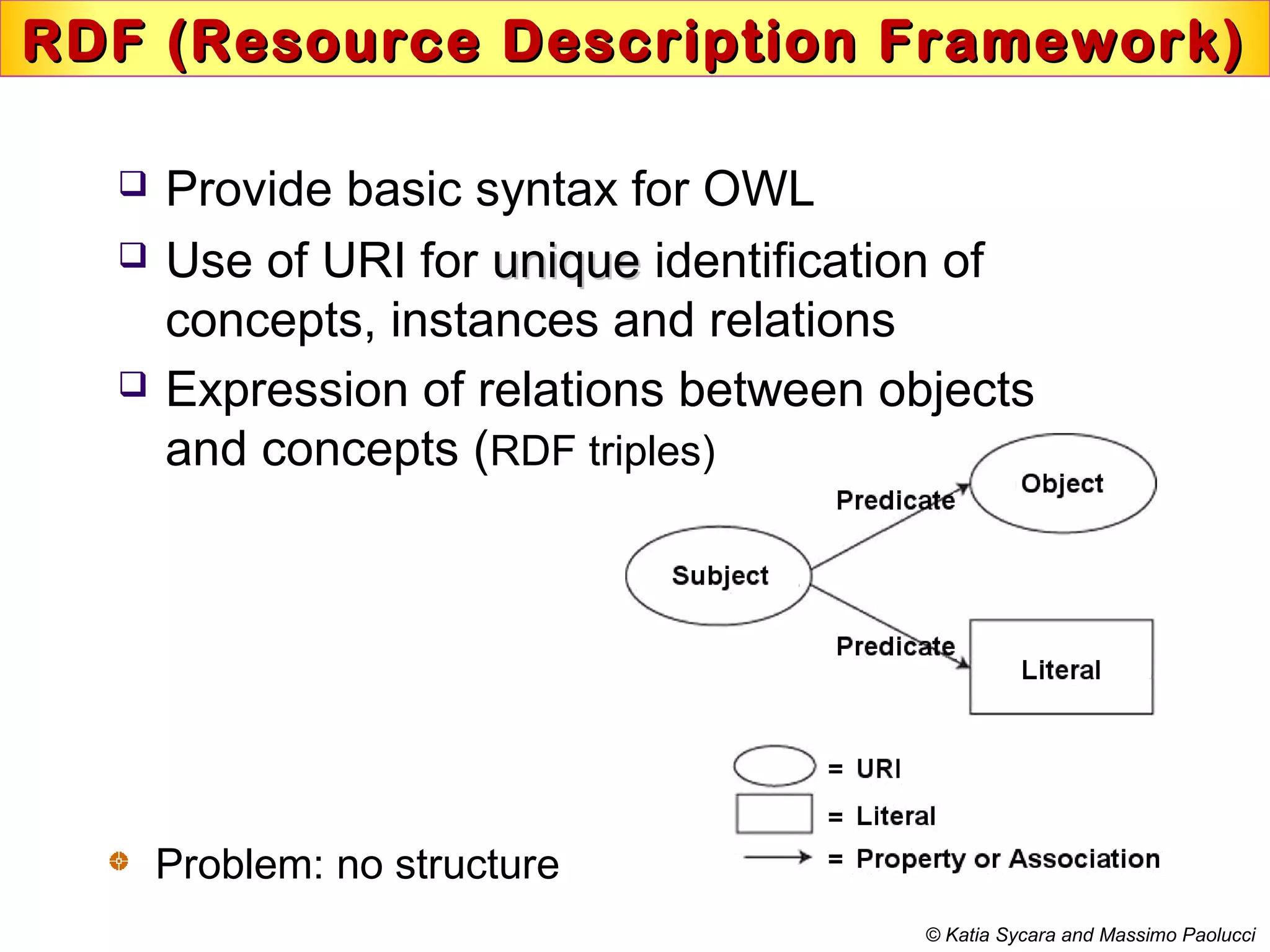
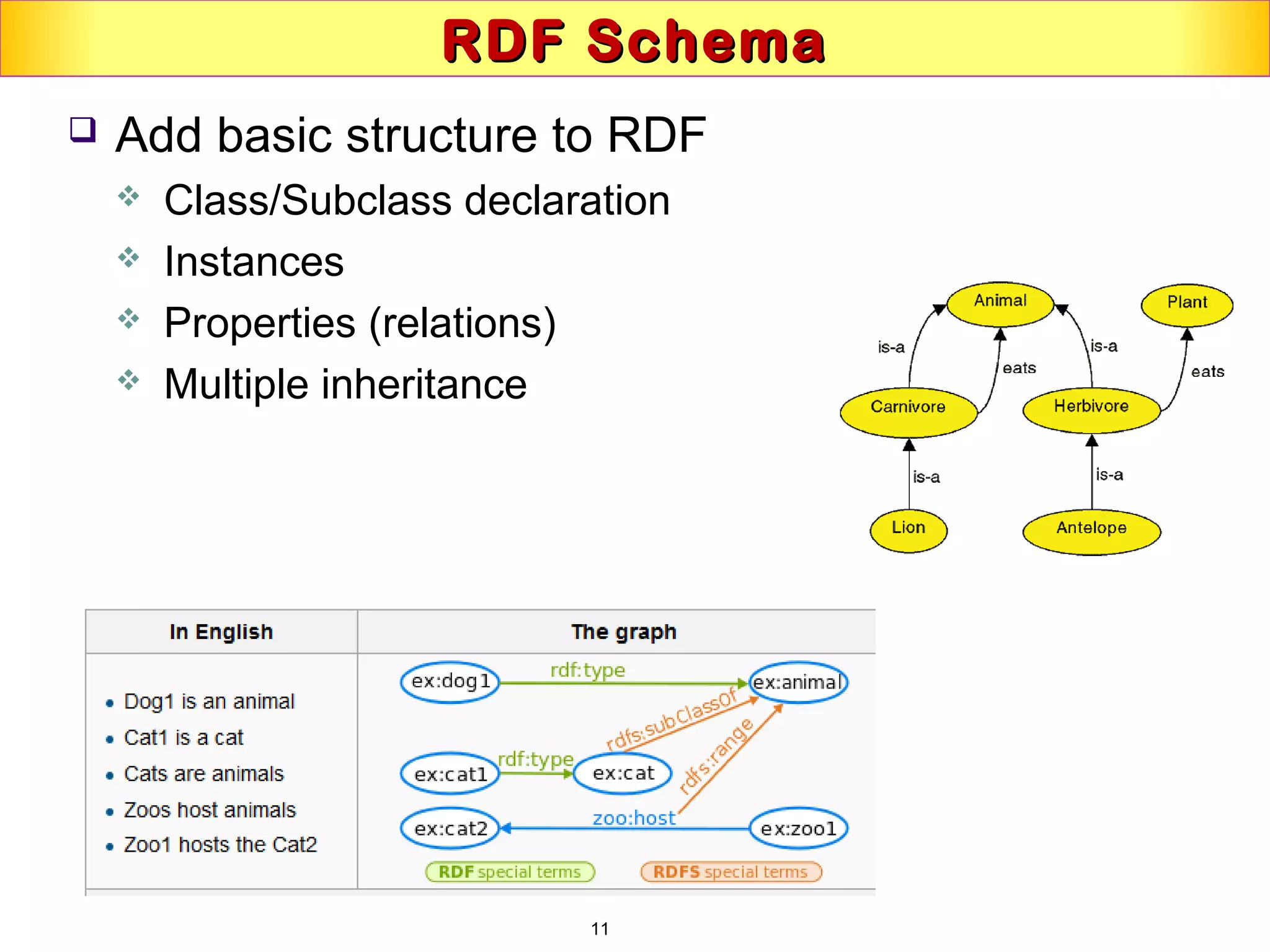
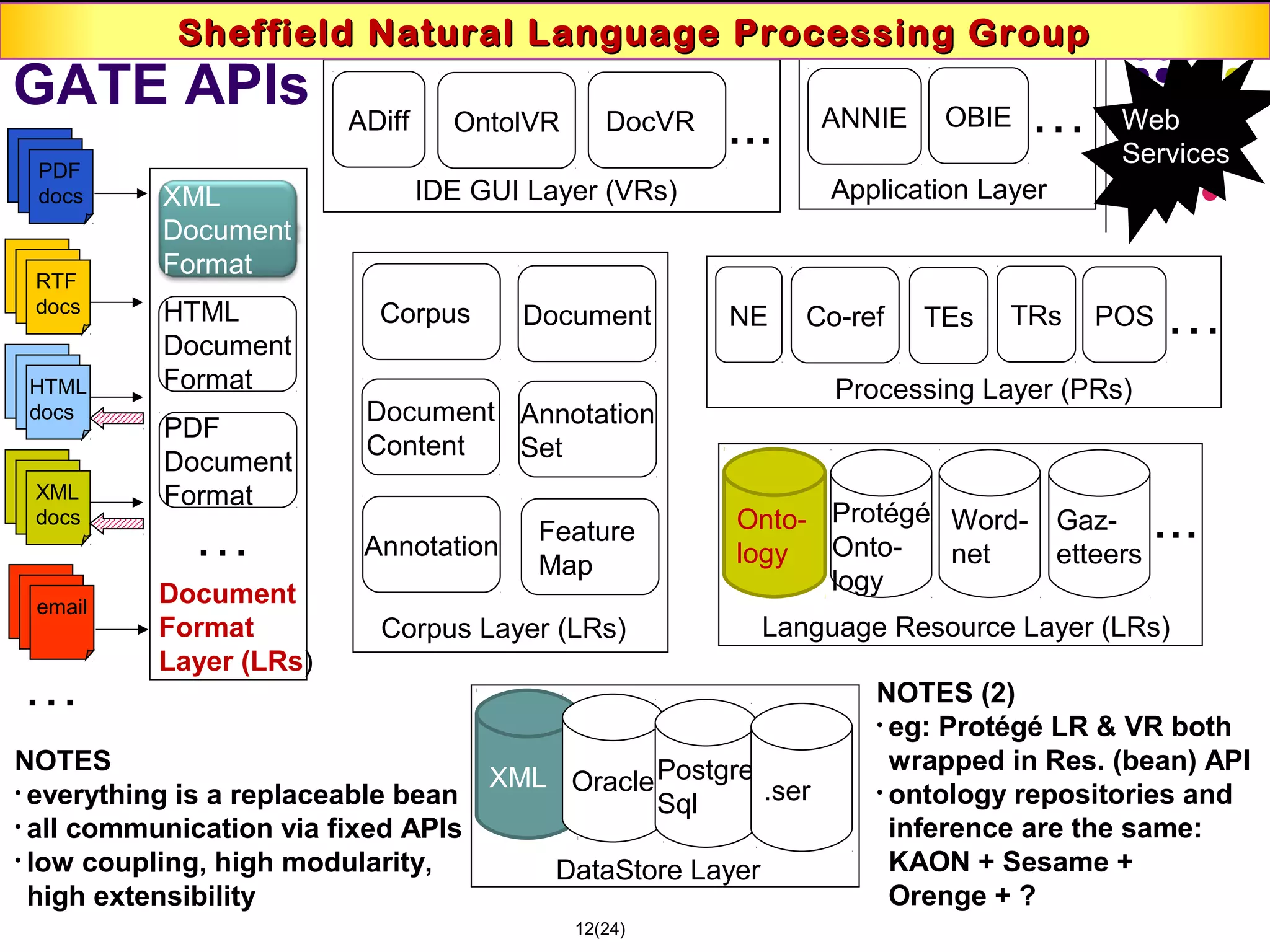
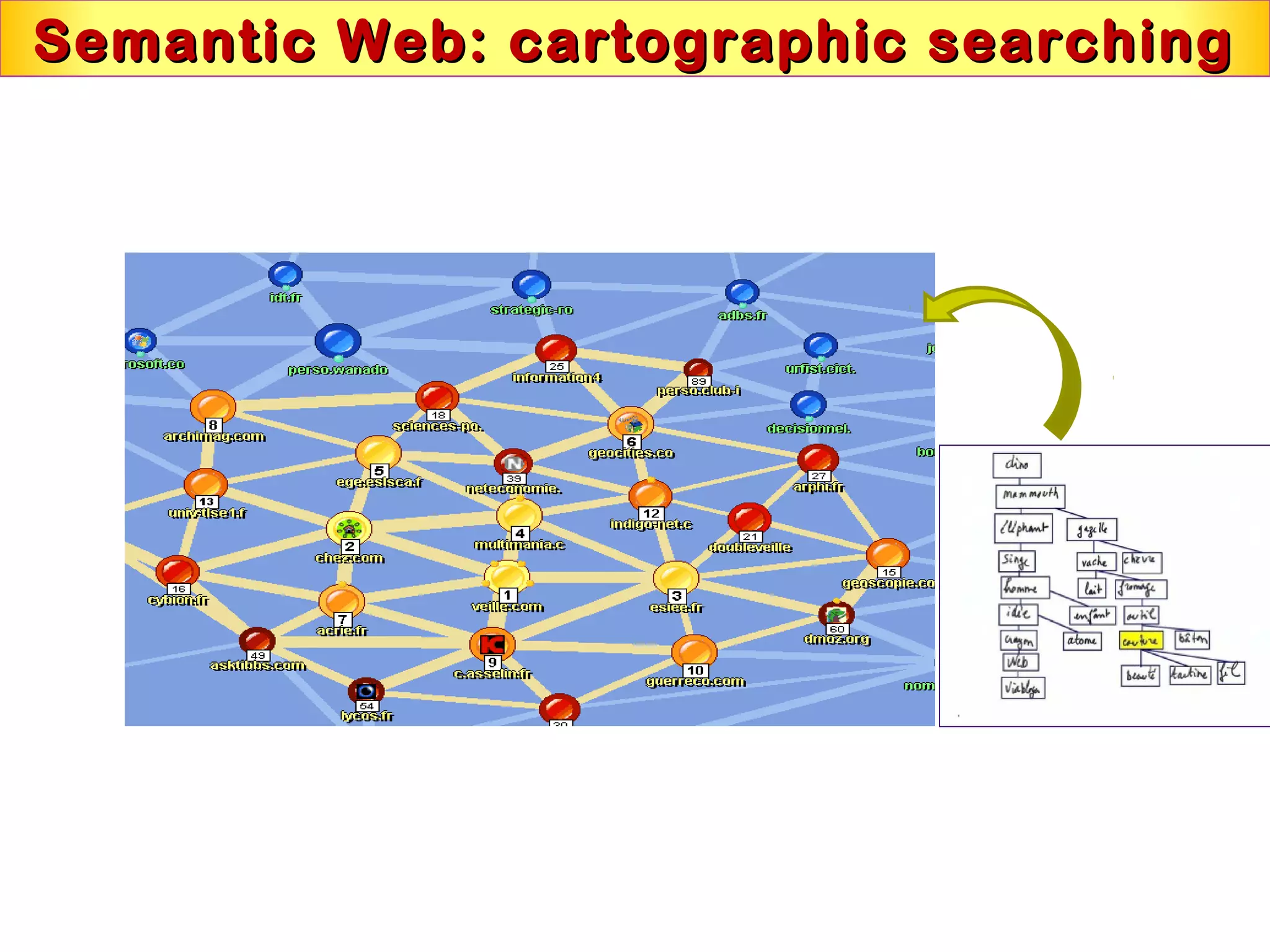
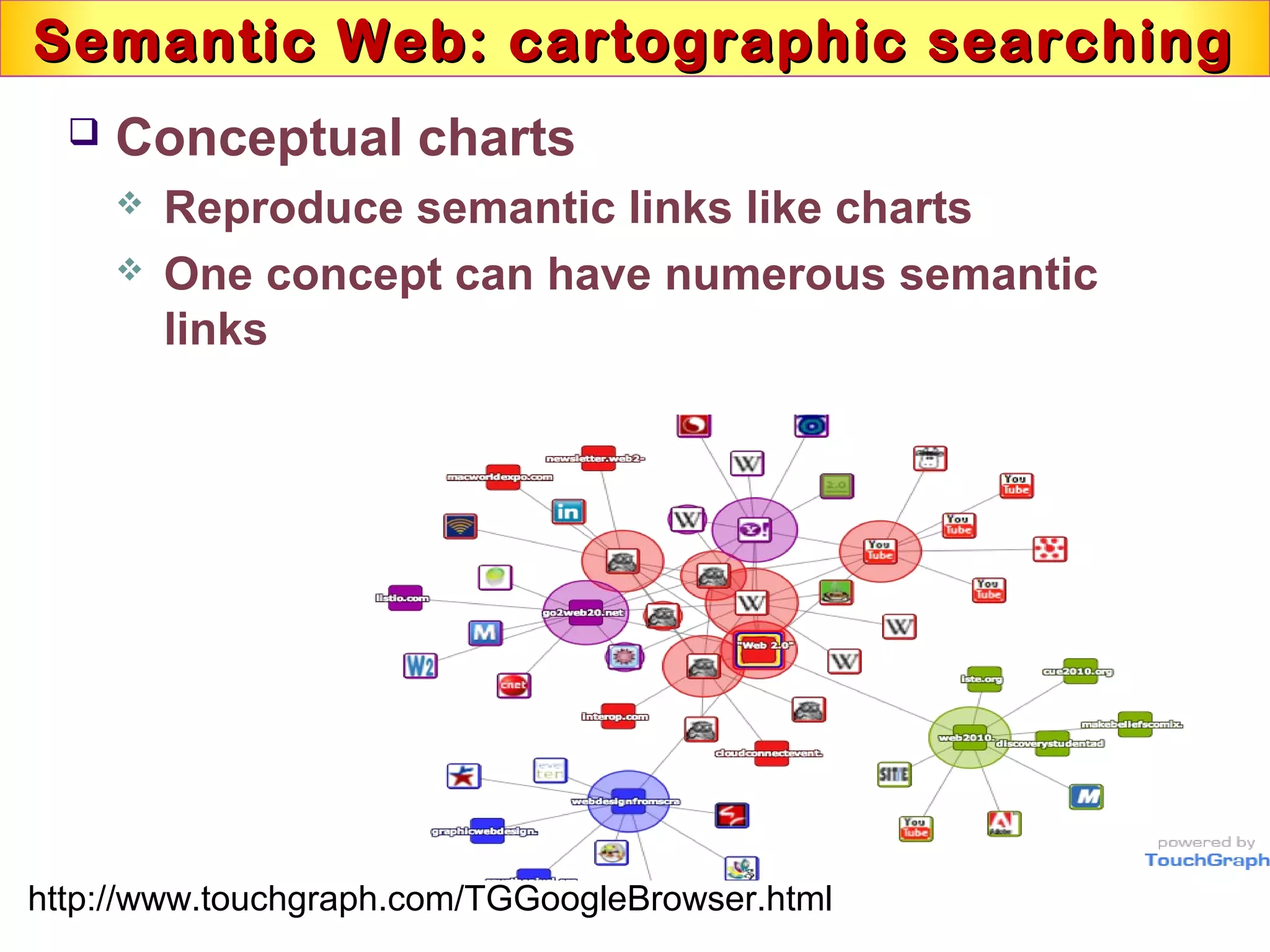
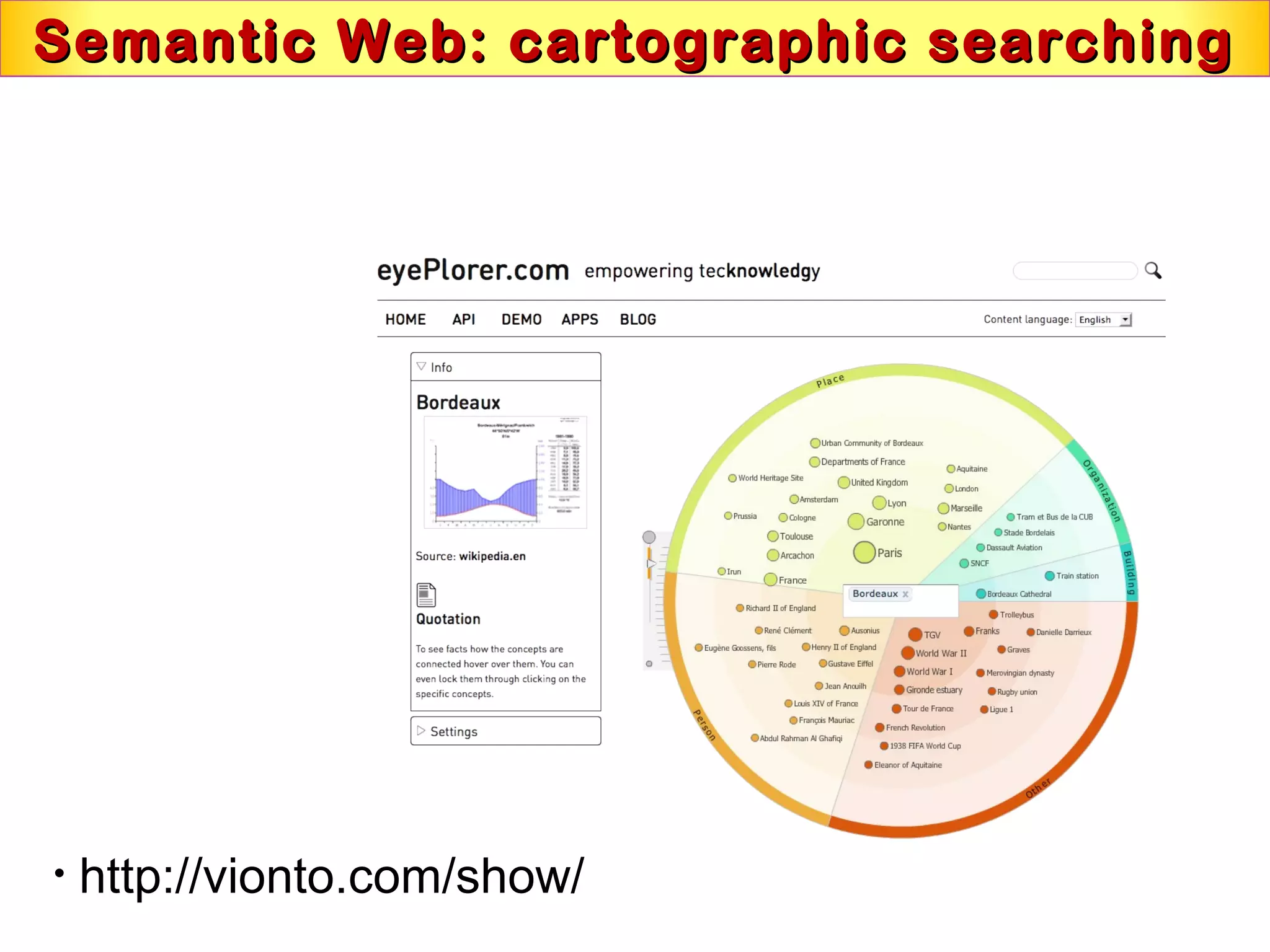
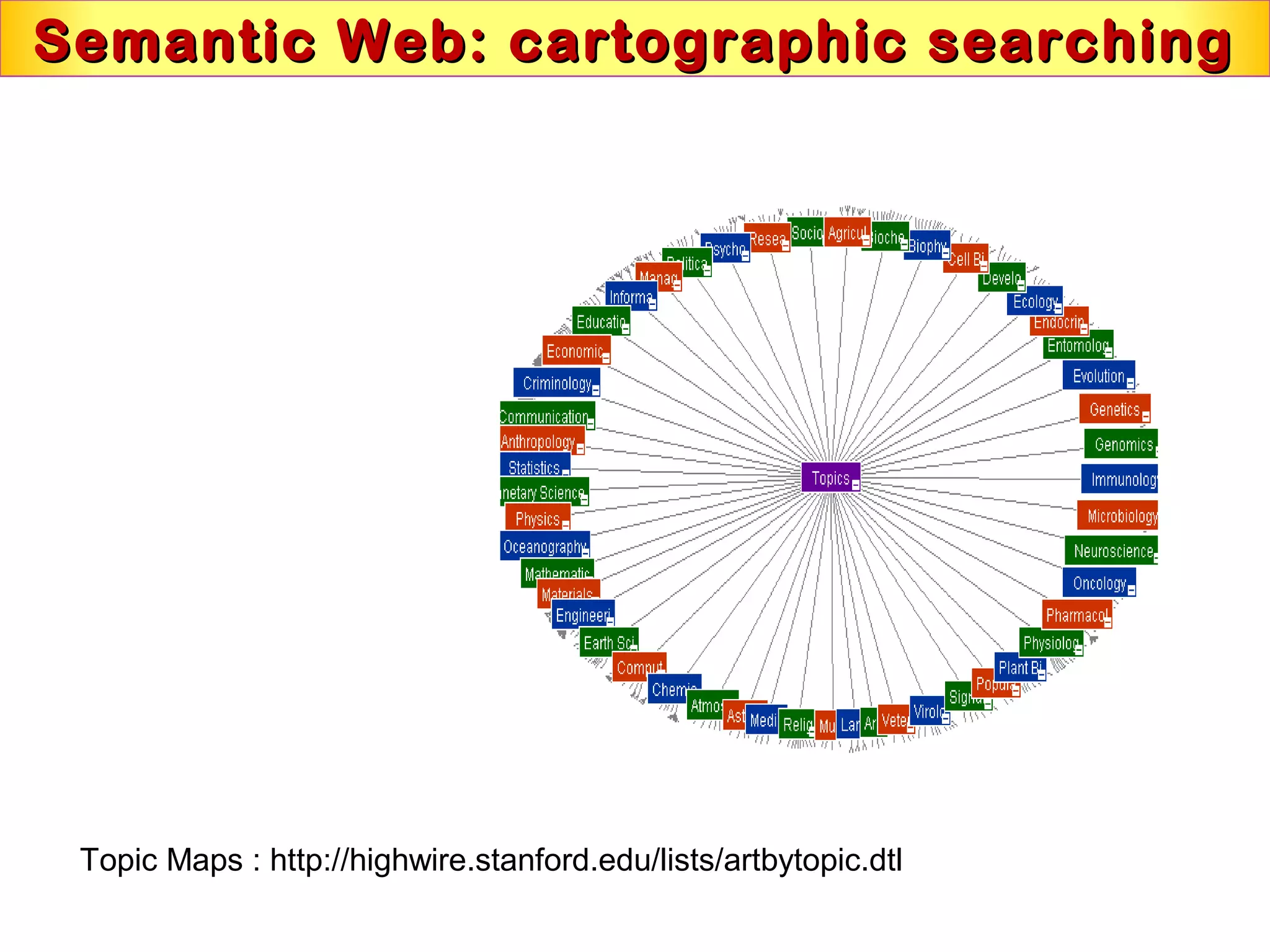
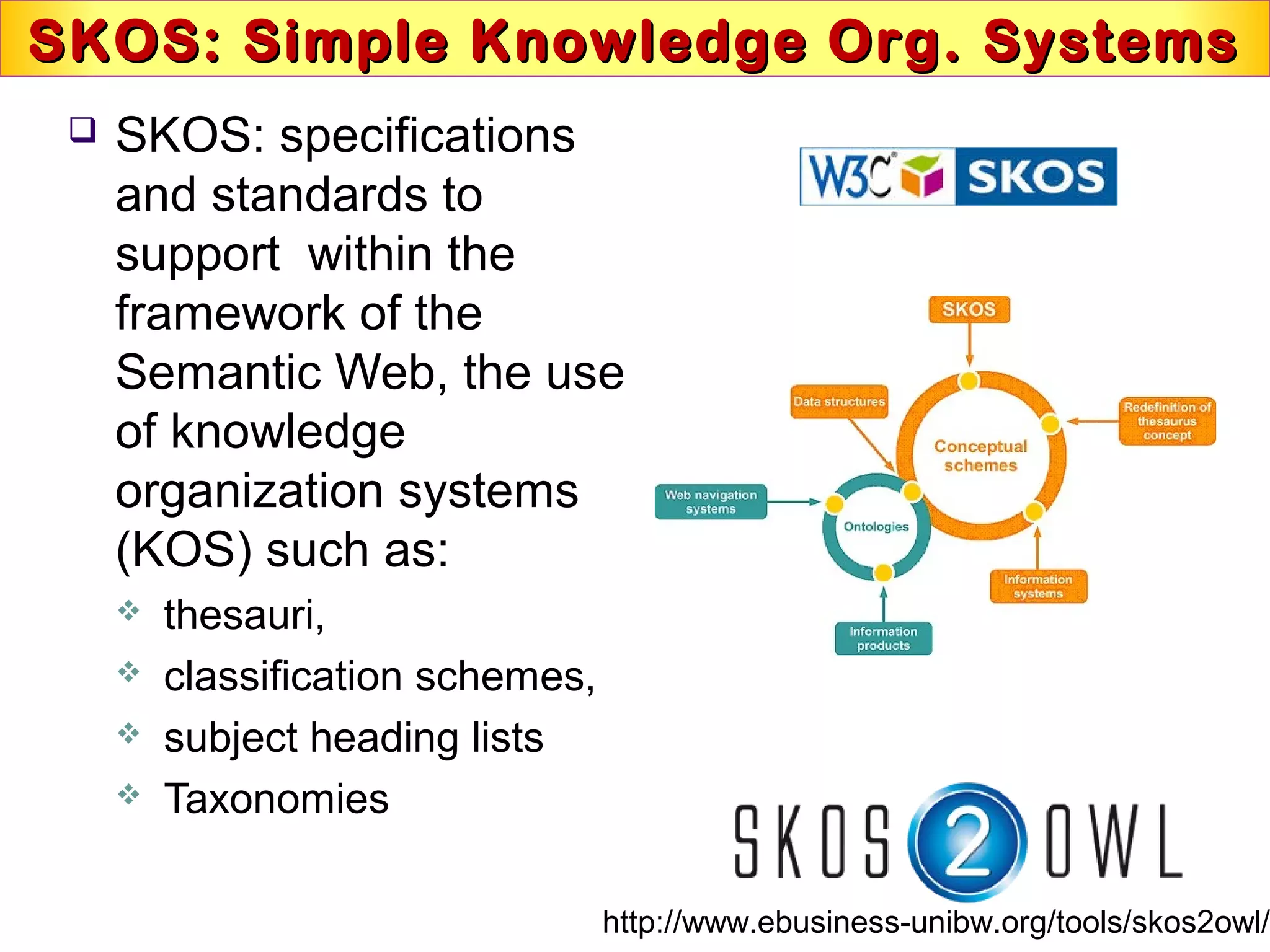
This document discusses semantic technologies and digital data processing. It provides an overview of semantics and the semantic web, including XML, RDF, OWL, SPARQL, ontologies, and data models. It also discusses capturing semantics in XML documents, OWL, RDF schema, semantic web applications like cartographic searching, SKOS for knowledge organization systems, and the SKOS Play visualization tool.