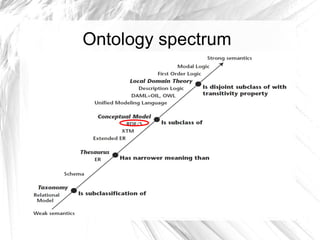
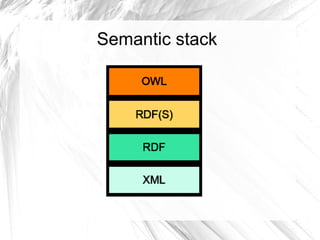
The document discusses the need for semantic technologies like ontologies to help address information overload by allowing machines to extract knowledge. It describes the evolution of semantic technologies, starting with XML providing syntactic interoperability, RDF providing a semantic grammar through assertions and relationships, and RDFS providing semantic interoperability through hierarchies and taxonomies for defining vocabulary. However, RDFS is not expressive enough to model all ontologies, so OWL was created by W3C to further extend RDFS while addressing complexity through different profiles like OWL Lite, DL, and Full.