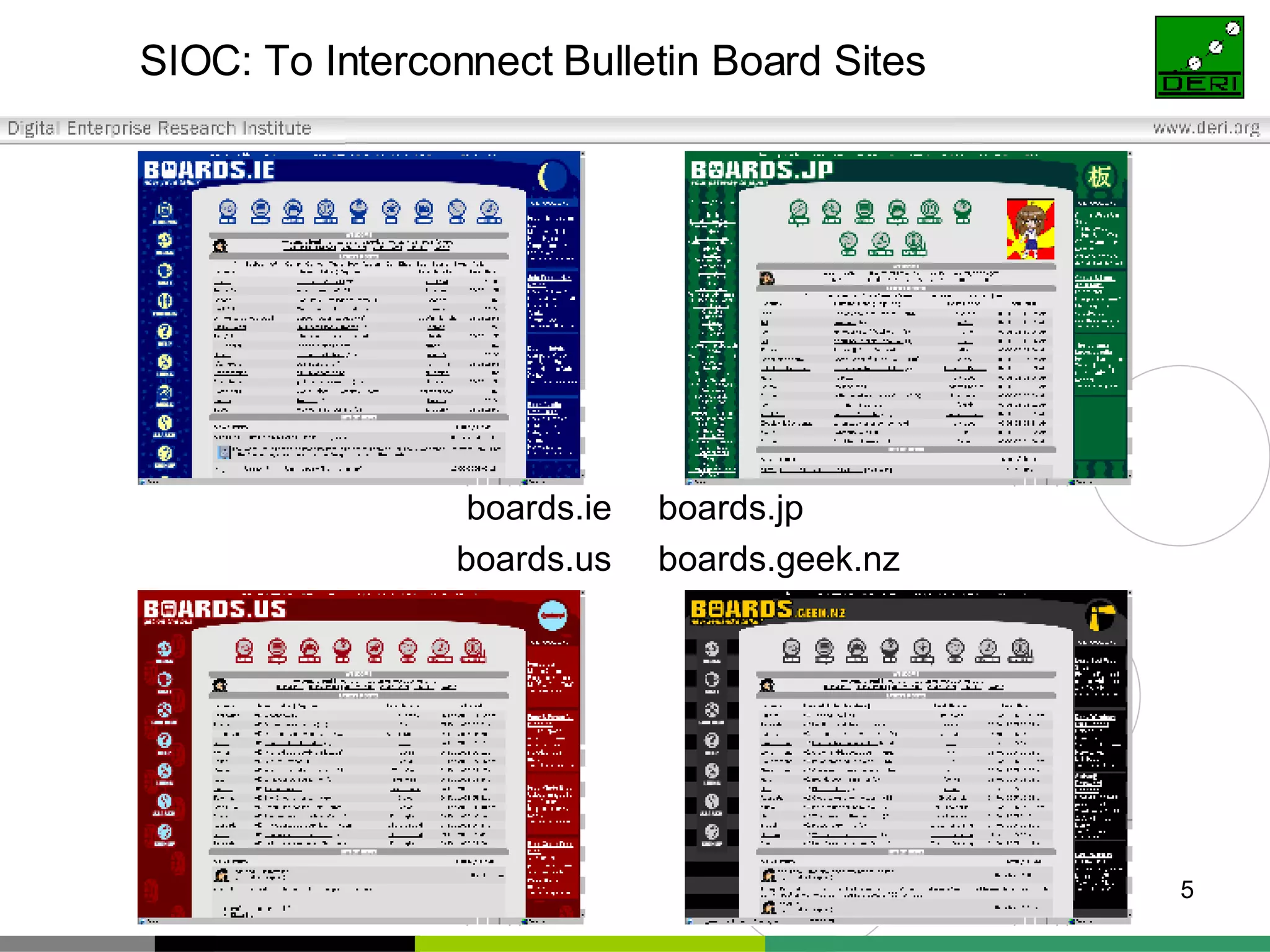
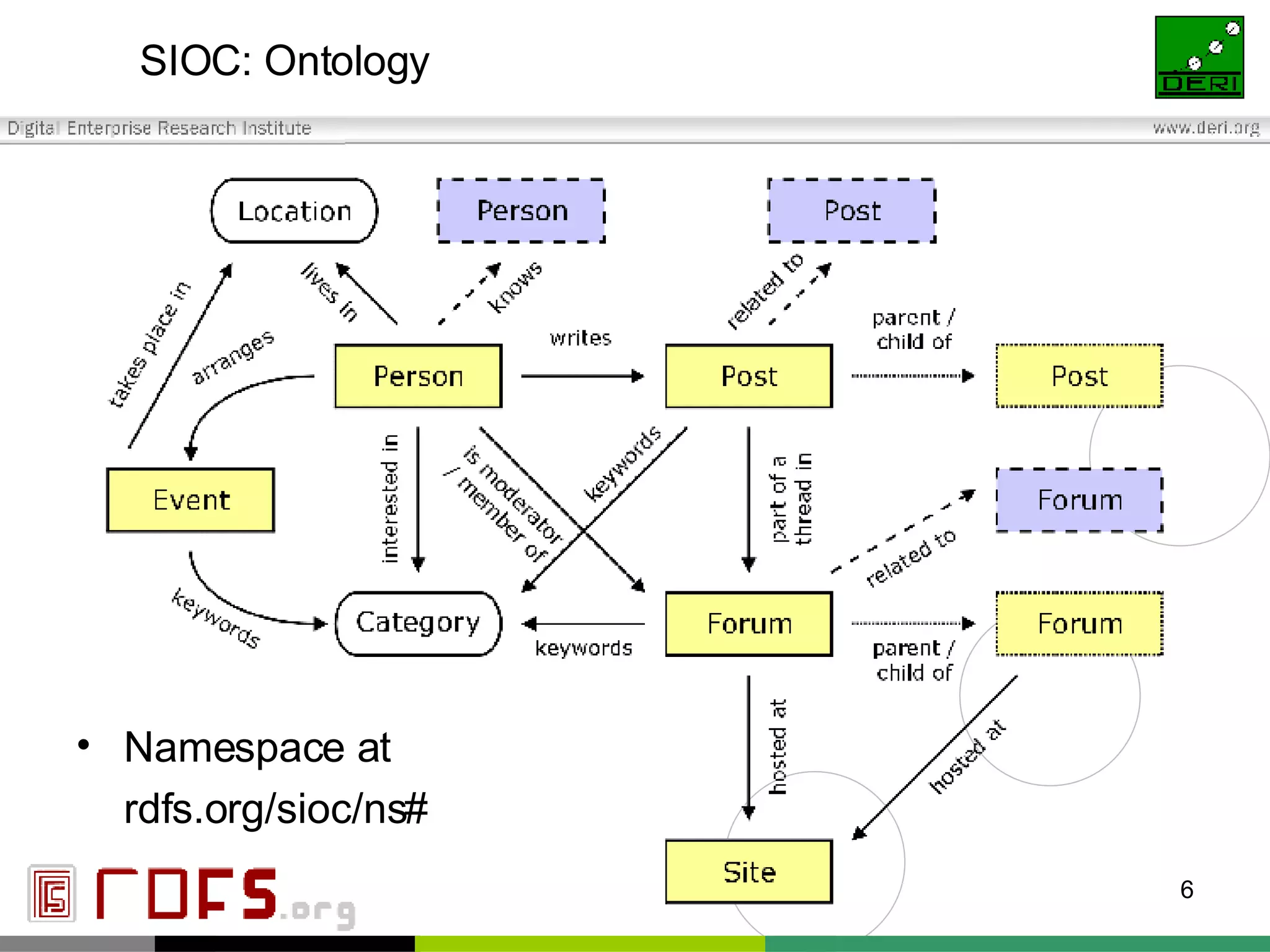
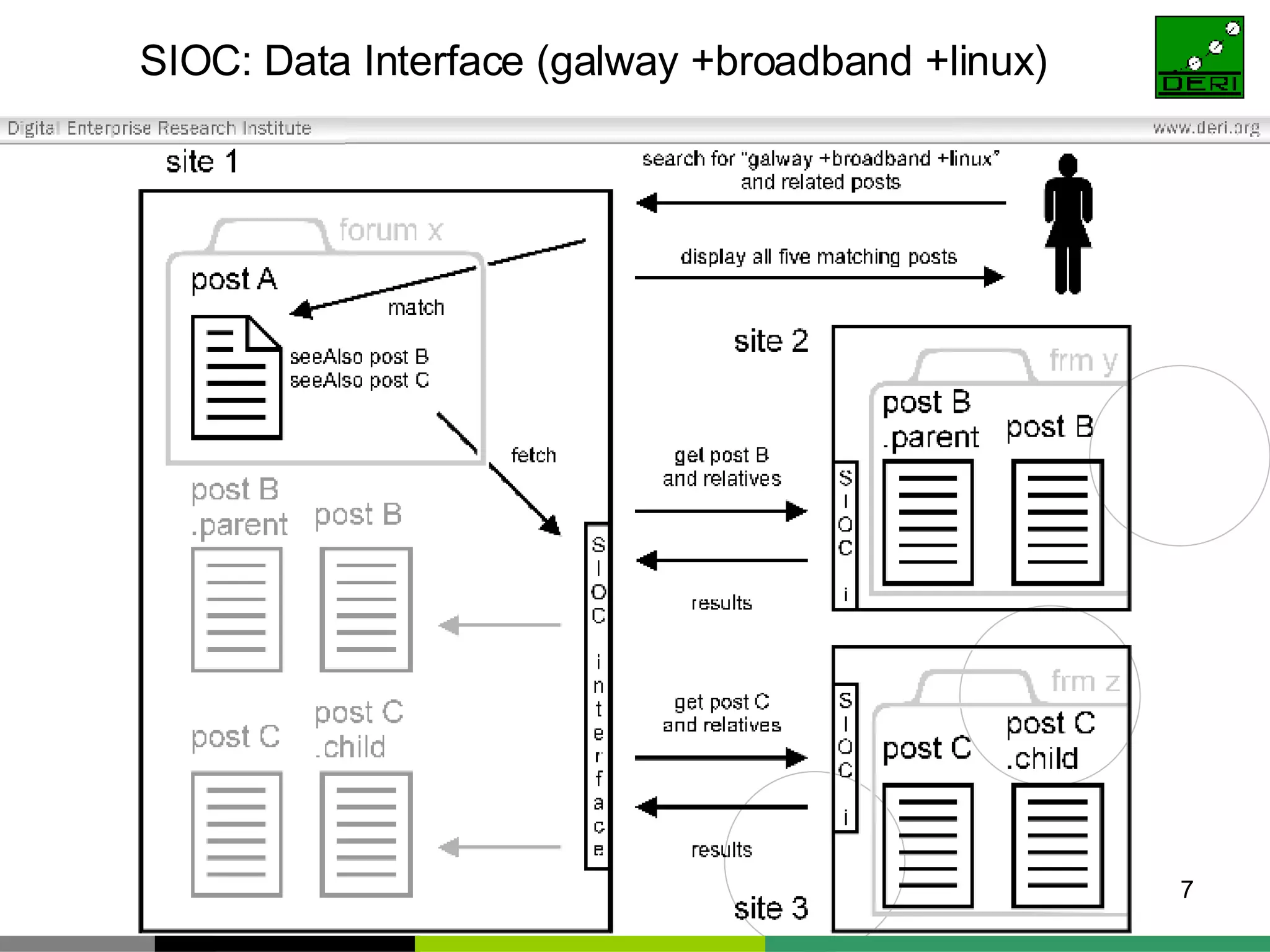
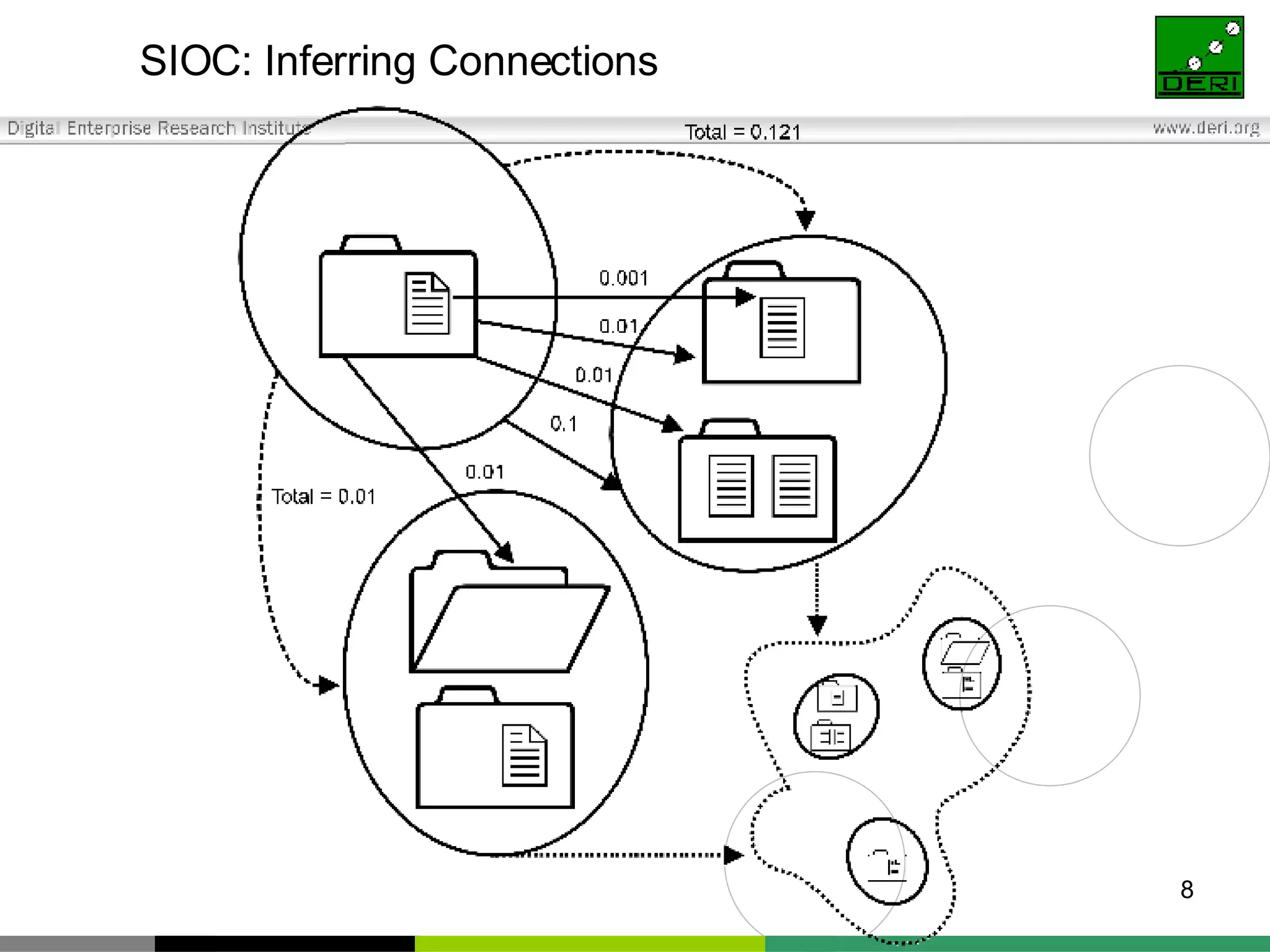
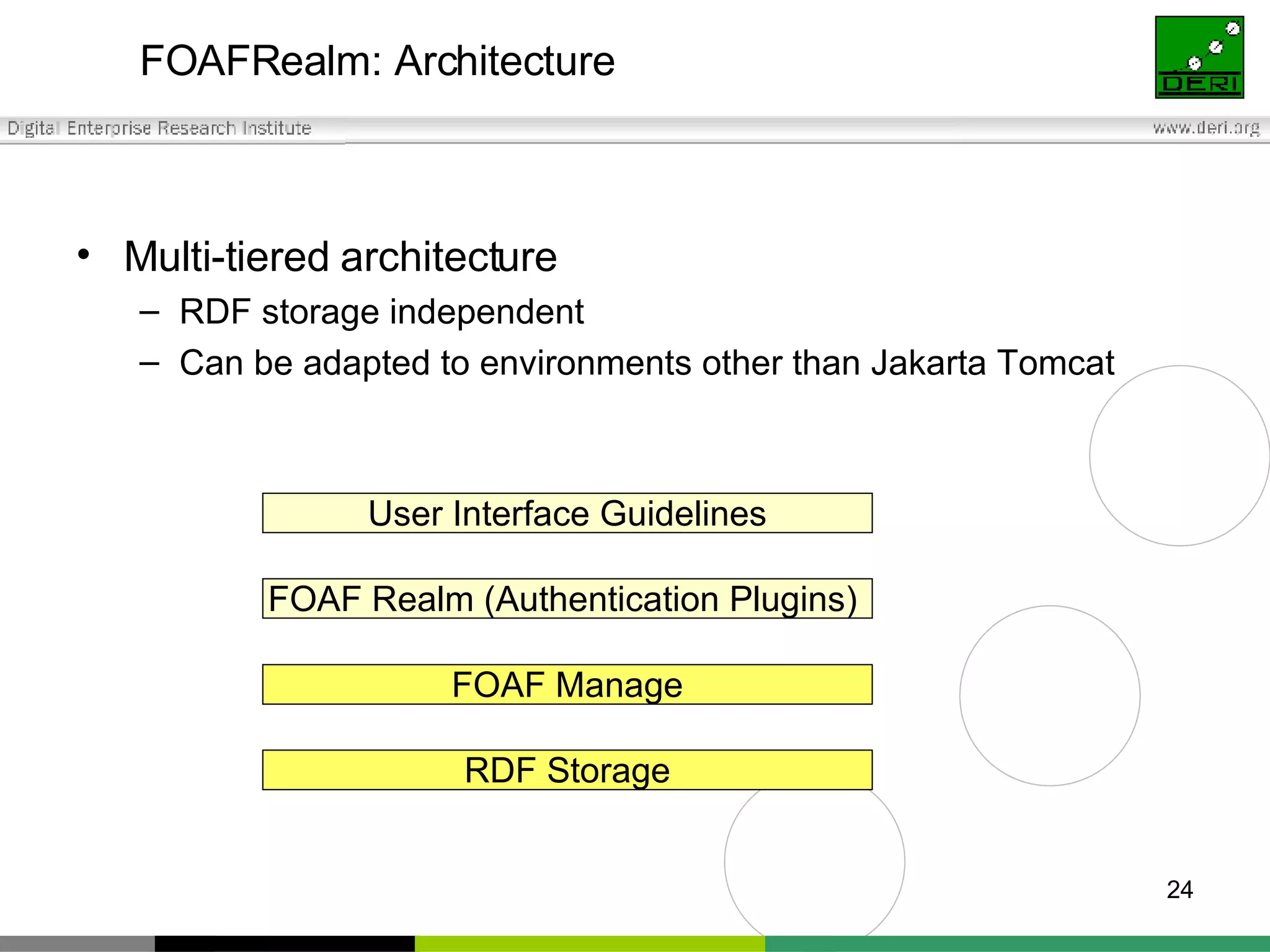
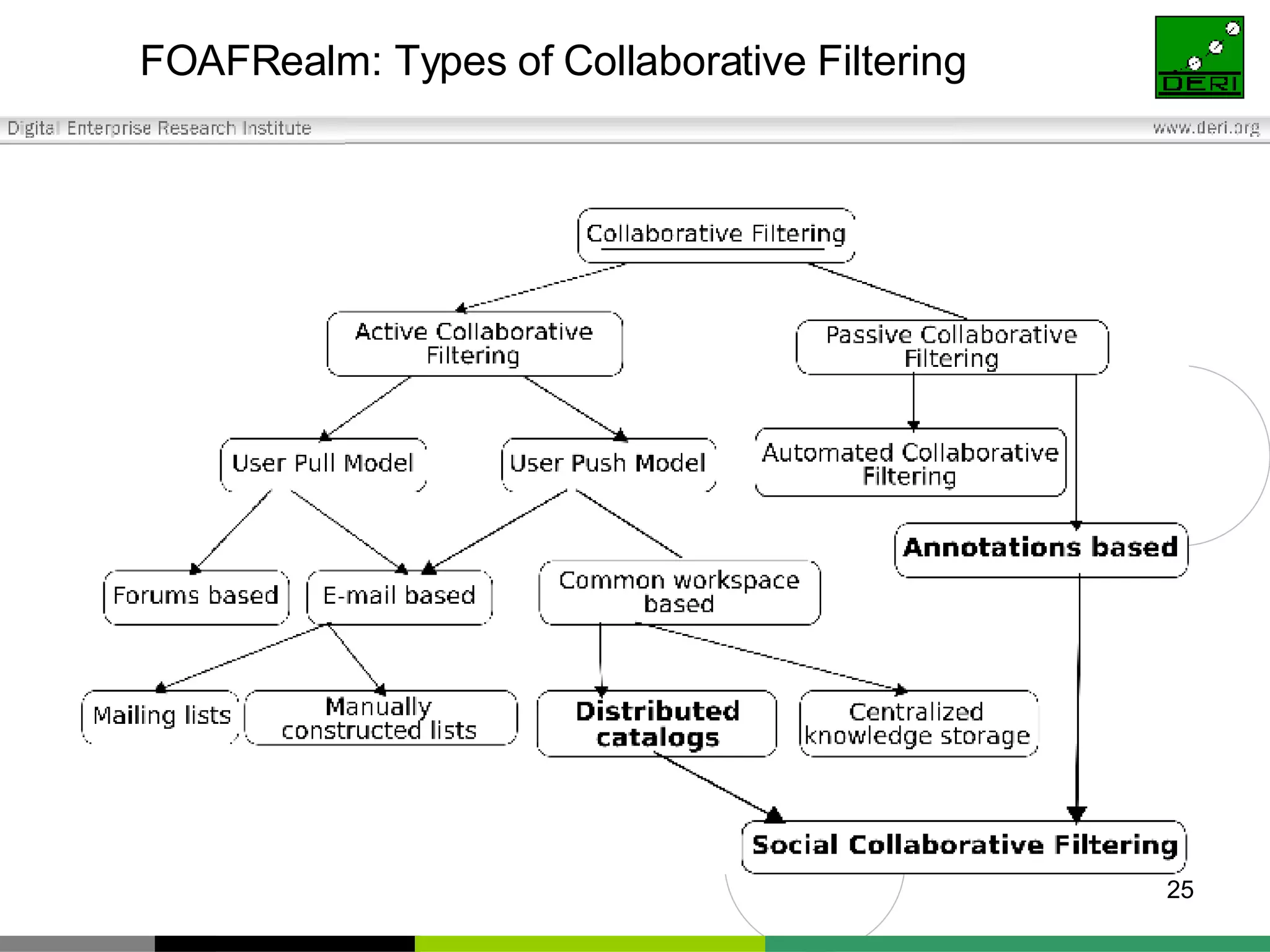
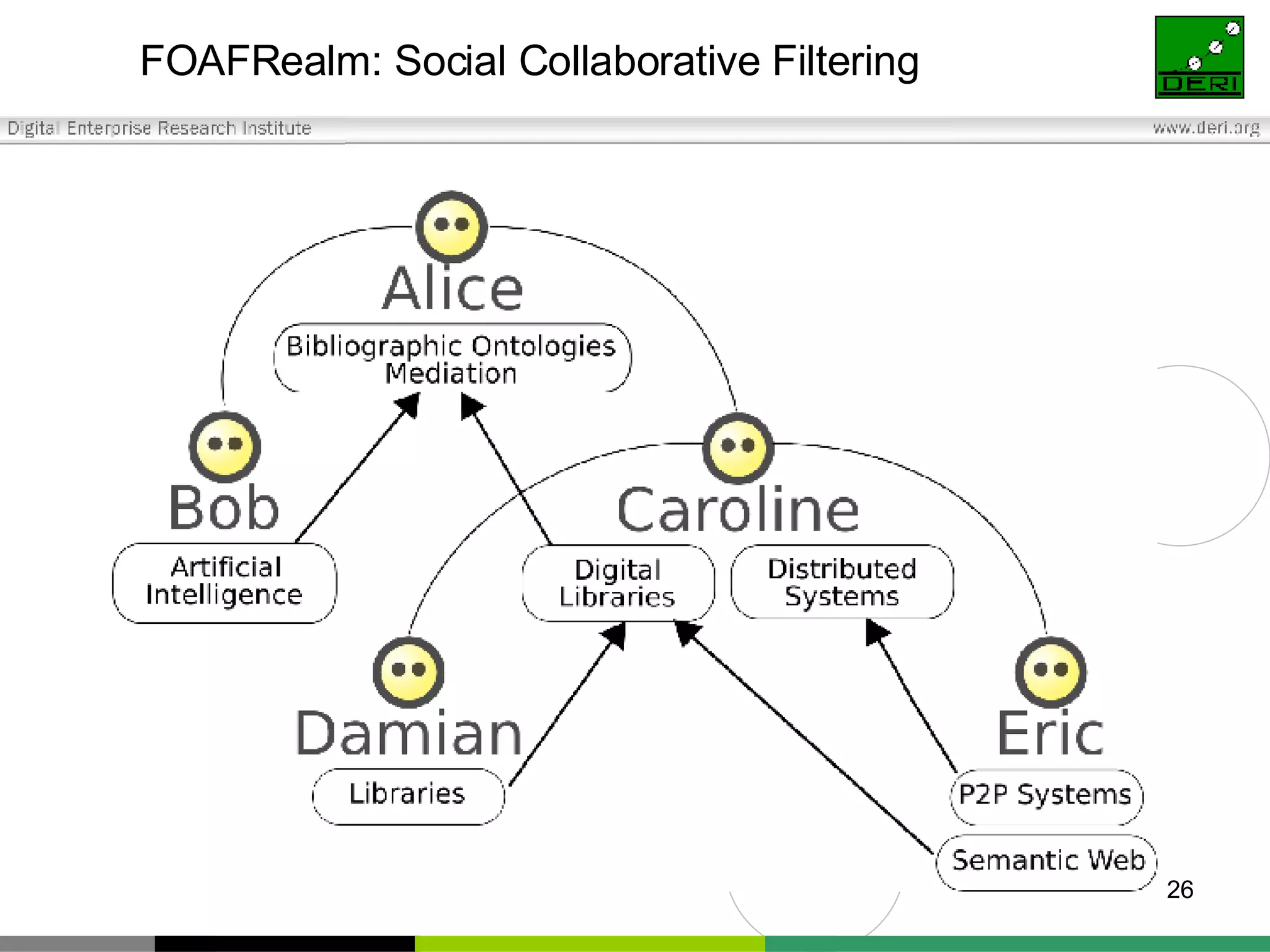
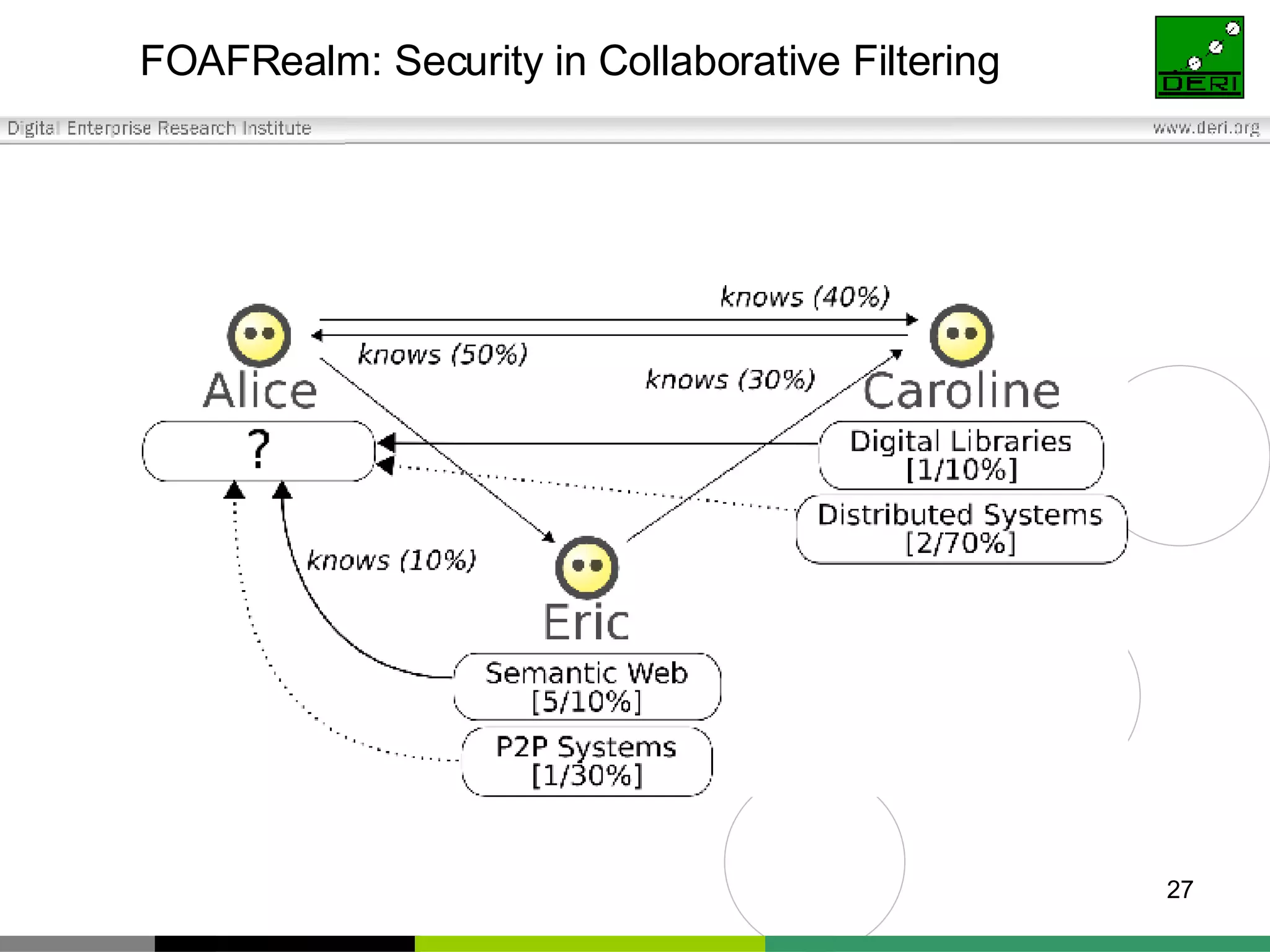
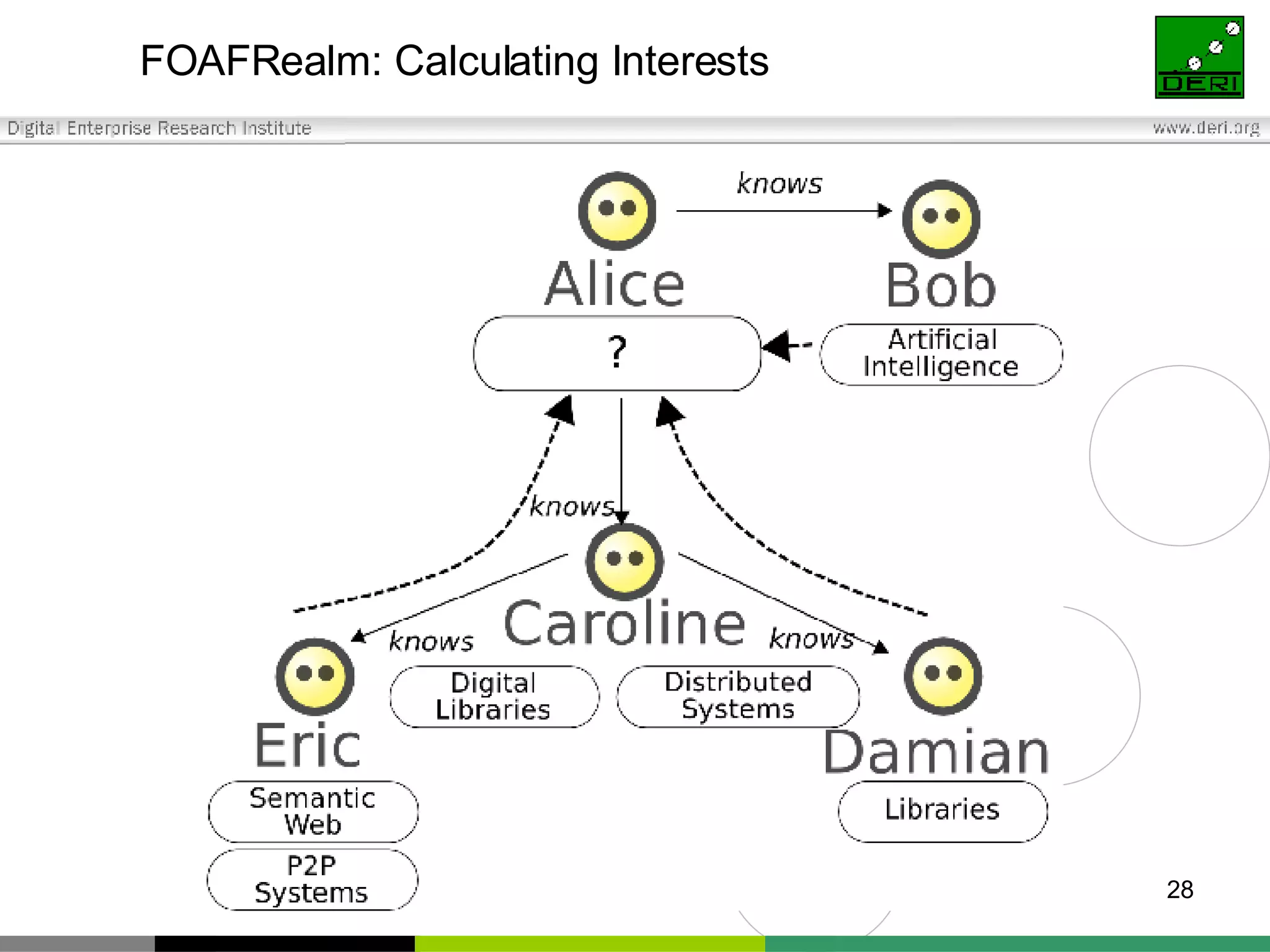
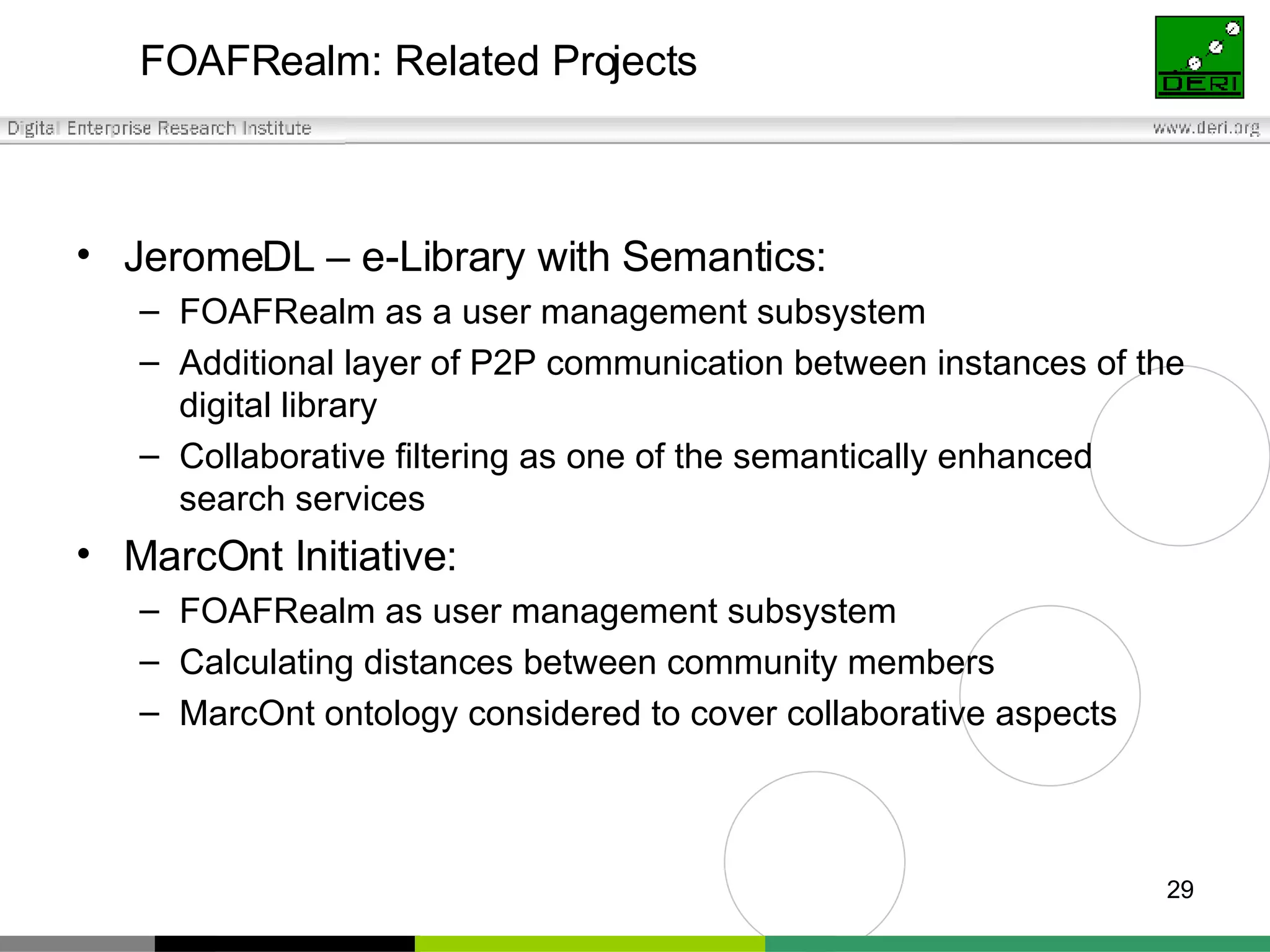
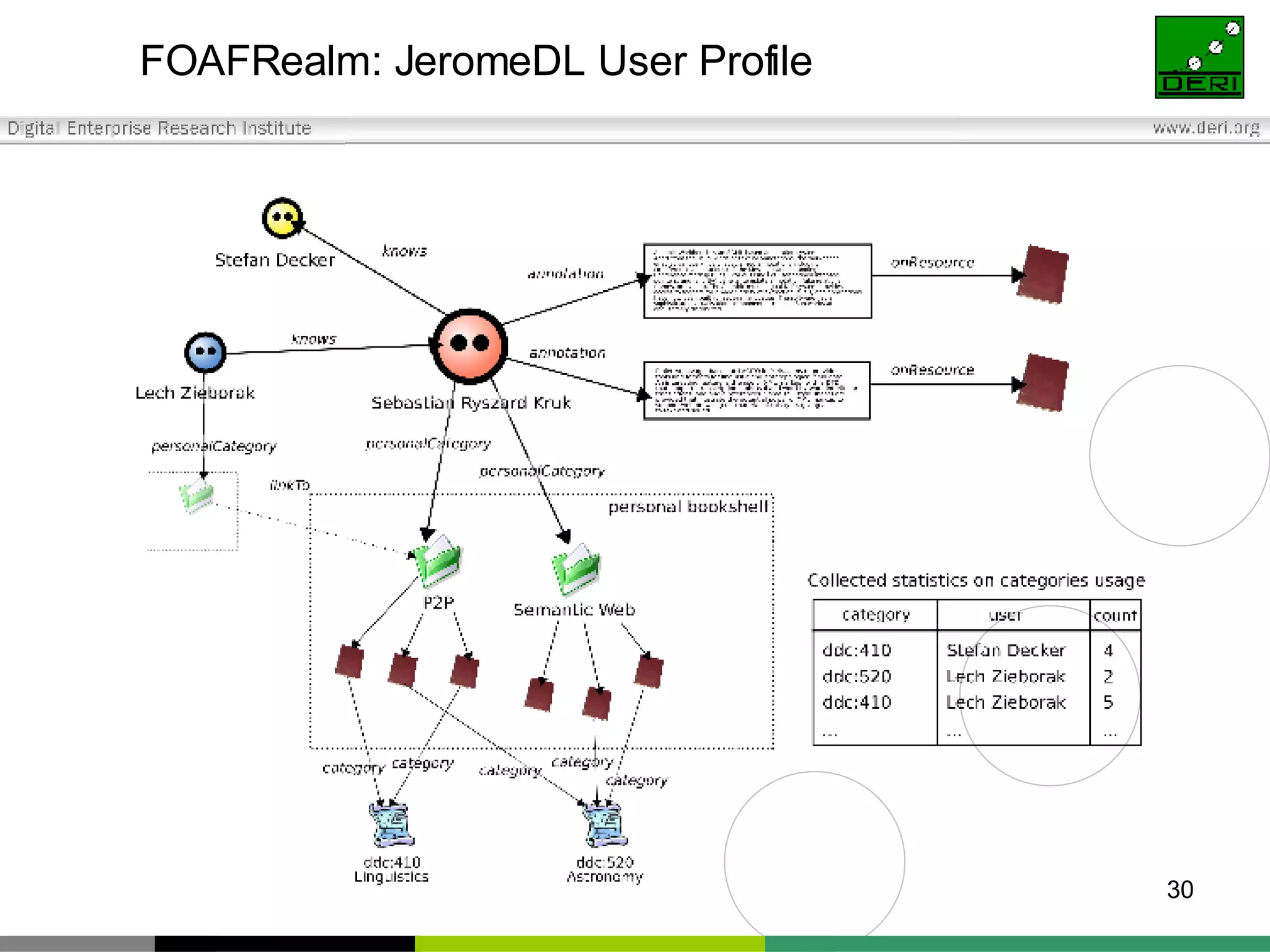
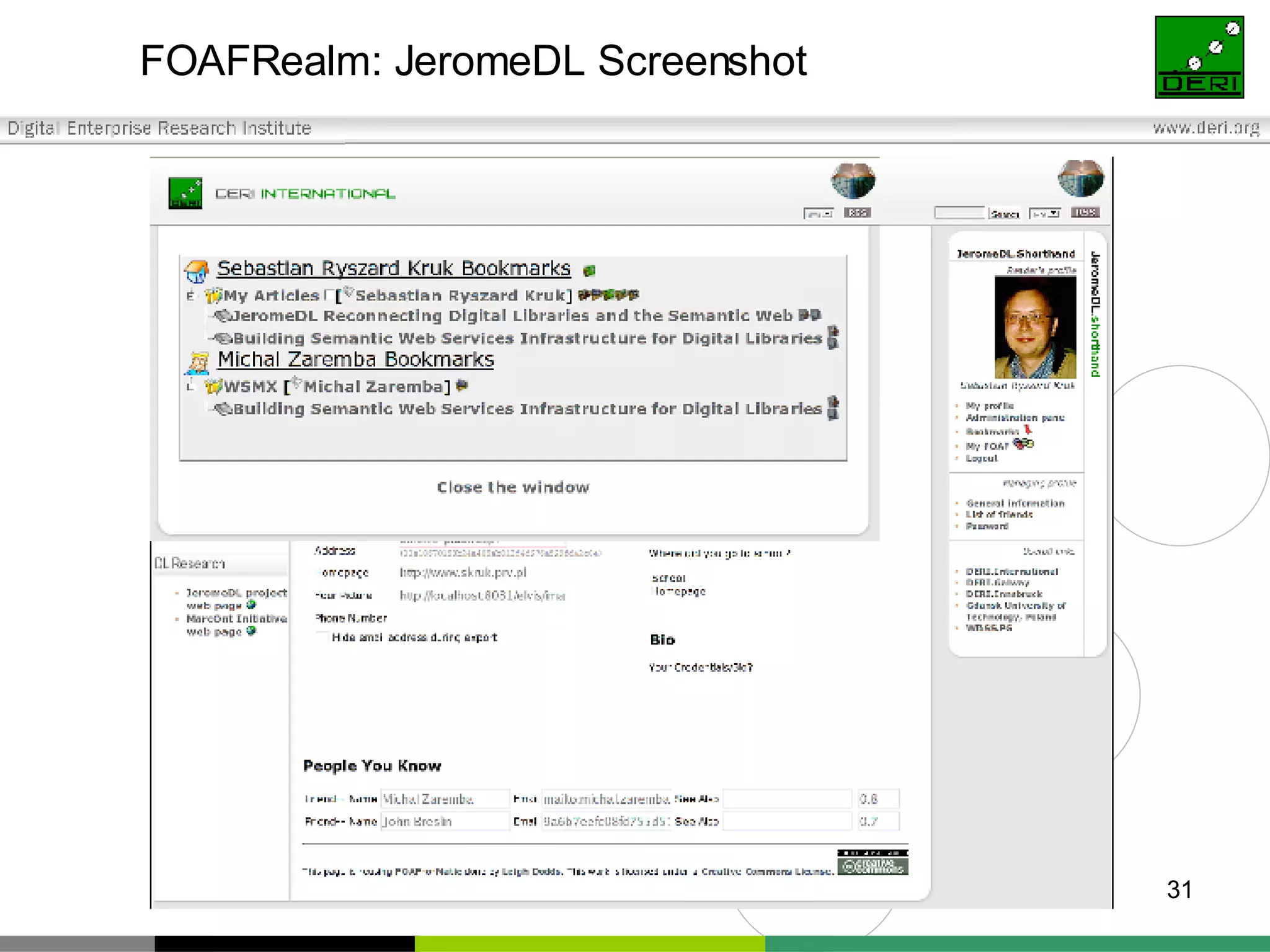
The document outlines interoperability issues and solutions for online communities, emphasizing the importance of the SIOC (Semantically Interlinked Online Communities) project. It discusses how semantic web technologies can facilitate data exchange and integration among various platforms, enhancing community interaction through ontologies and RDF datasets. Additionally, it presents the features and architecture of the FOAFRealm user management system and its role in collaborative filtering and social interactions within communities.
![John Breslin (for Stefan Decker) Site Interoperability Projects at DERI Galway‘s SW Cluster [email_address] www.johnbreslin.com Interop Issues in SW Sites 7 th February 2005](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/site-interoperability-projects-at-deri-galways-sw-cluster-1193235657929667-5/75/Site-Interoperability-Projects-at-DERI-Galway-s-SW-Cluster-1-2048.jpg)