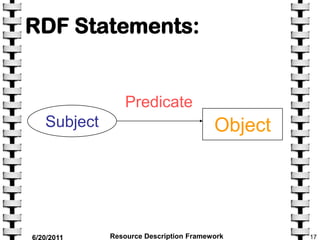
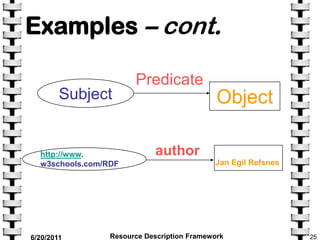
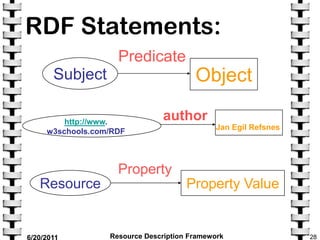
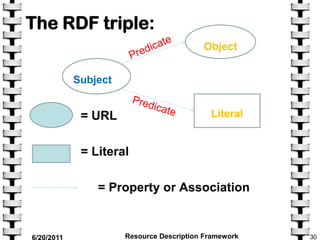
The document provides an overview of the Resource Description Framework (RDF). It describes RDF as a standard for describing web resources using metadata. RDF uses a simple data model based on making statements about resources in the form of subject-predicate-object expressions. This allows data to be shared across different applications. The document discusses key RDF concepts including resources, properties, and statements. It provides examples of RDF statements and illustrates the RDF triple format. The goal of RDF is to enable the encoding, exchange, and reuse of structured metadata about Web resources between applications.