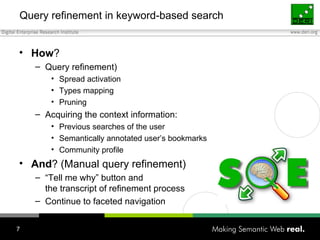
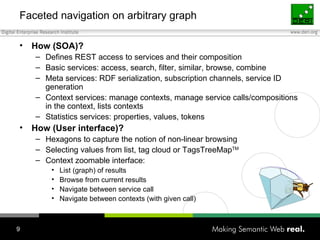
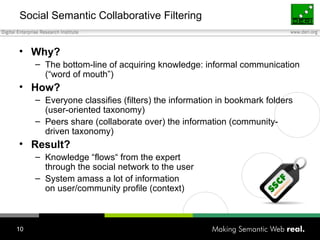
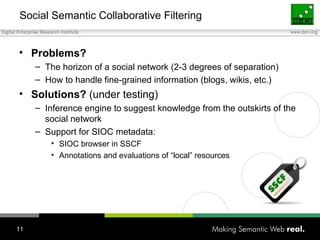
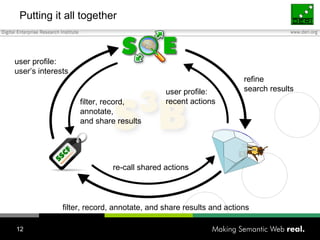
The document discusses how individuals search for information through various means, emphasizing that keyword search alone is insufficient for diverse user goals such as resource seeking, navigational, and informational searches. It introduces concepts like query refinement, faceted navigation, and collaborative filtering, and suggests that integrating semantic web technologies and social networks can enhance search processes. The author concludes by exploring user profiles and community dynamics as essential for improving knowledge flow and search relevance.
![Social Semantic Search and Browsing Sebastian Ryszard Kruk Digital Enterprise Research Institute National University of Ireland, Galway [email_address] http://corrib.deri.ie/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/social-semantic-search-and-browsing-16548/75/Social-Semantic-Search-and-Browsing-1-2048.jpg)



![Search and browsing lifecycle Why ? Information can be useful Information can be a garbage How ? (Search and browsing actions) [REUSE] keyword-based search (resource seeking) [REDUCE] faceted navigation (navigational) [RECYCLE] collaborative filtering (informational) Can this process be improved with Semantic Web and Social Networking technologies?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/social-semantic-search-and-browsing-16548/85/Social-Semantic-Search-and-Browsing-5-320.jpg)