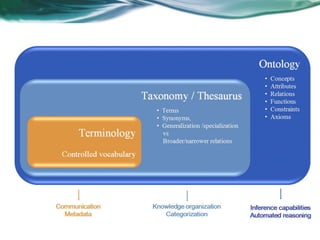
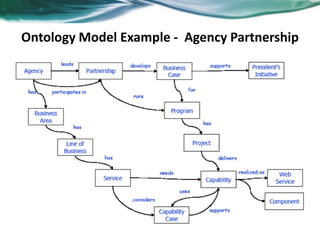
Ontologies provide a shared understanding of a domain by formally defining concepts, properties, and relationships. An ontology introduces vocabulary relevant to a domain and specifies the meaning of terms. Ontologies are machine-readable and enable overcoming differences in terminology across complex, distributed applications. Examples include gene ontologies, pharmaceutical drug ontologies, and customer profile ontologies. Semantic technologies use ontologies to provide semantic search, integration, reasoning, and analysis capabilities.