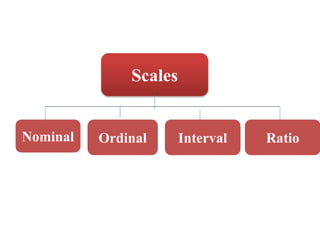
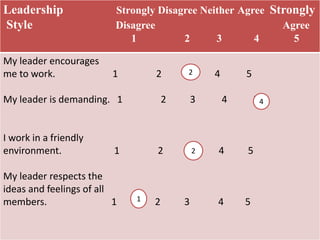
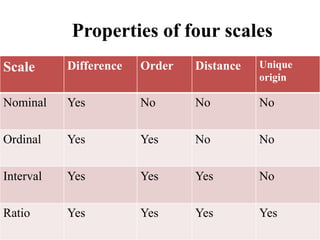
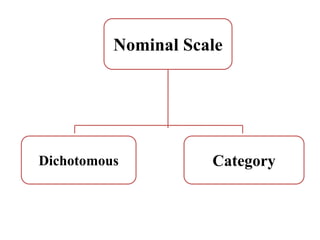
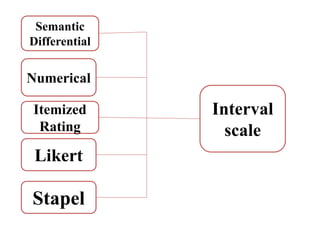
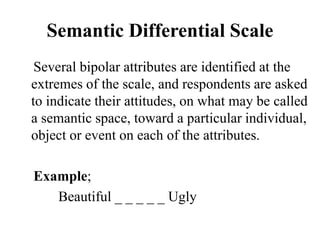
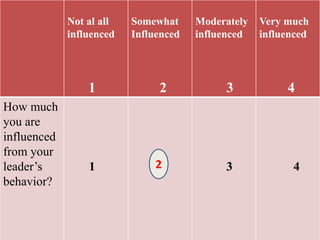
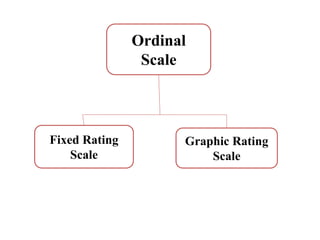
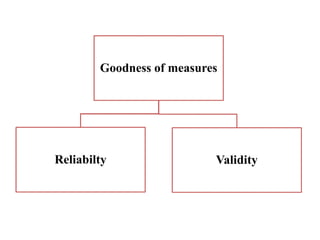
This document discusses different types of measurement scales used in research including nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio scales. It provides examples of each scale and describes their key properties. Nominal scales categorize variables but do not rank them, ordinal scales rank order categories, interval scales measure magnitude of differences, and ratio scales have a true zero point. The document also discusses different types of scales used to measure concepts like Likert scales, semantic differential scales, and fixed rating scales. It emphasizes the importance of reliability and validity in determining the quality of measurement scales.