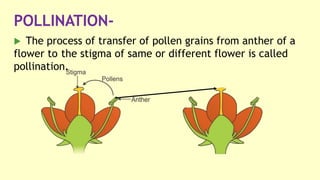
This document discusses self-pollination in plants. It defines self-pollination as the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same flower or a different flower on the same plant. There are two types of self-pollination: autogamy, where the pollen is transferred to the stigma of the same flower; and geitonogamy, where the pollen is transferred between different flowers on the same plant. Autogamy occurs through homogamy and cleistogamy and has the advantages of not depending on external pollinators and ensuring genetic purity, but has the disadvantages of not producing variation and weaker progeny.