1. The document discusses cross pollination, which is the transfer of pollen from the anther of one plant to the stigma of a different plant.
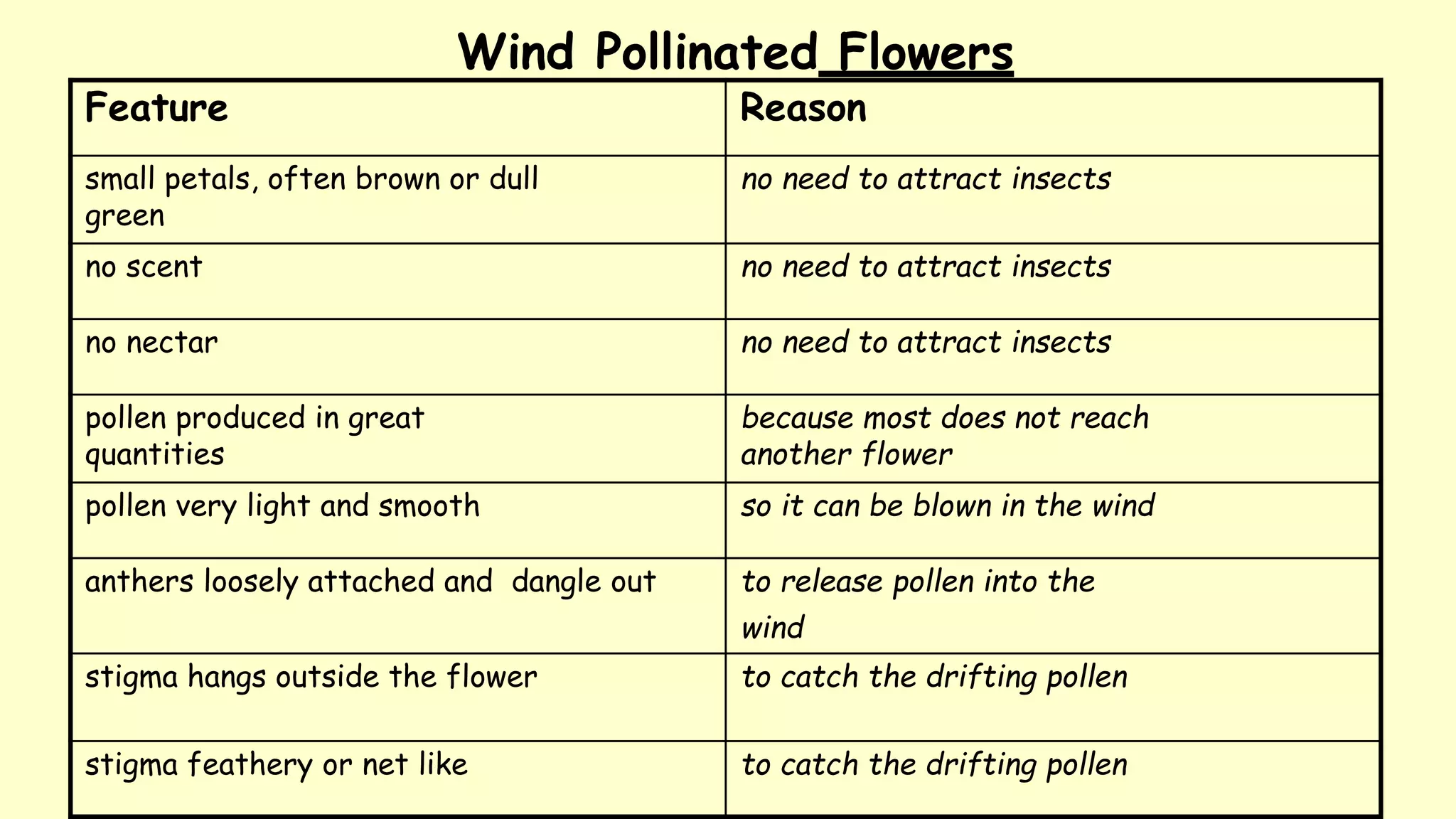
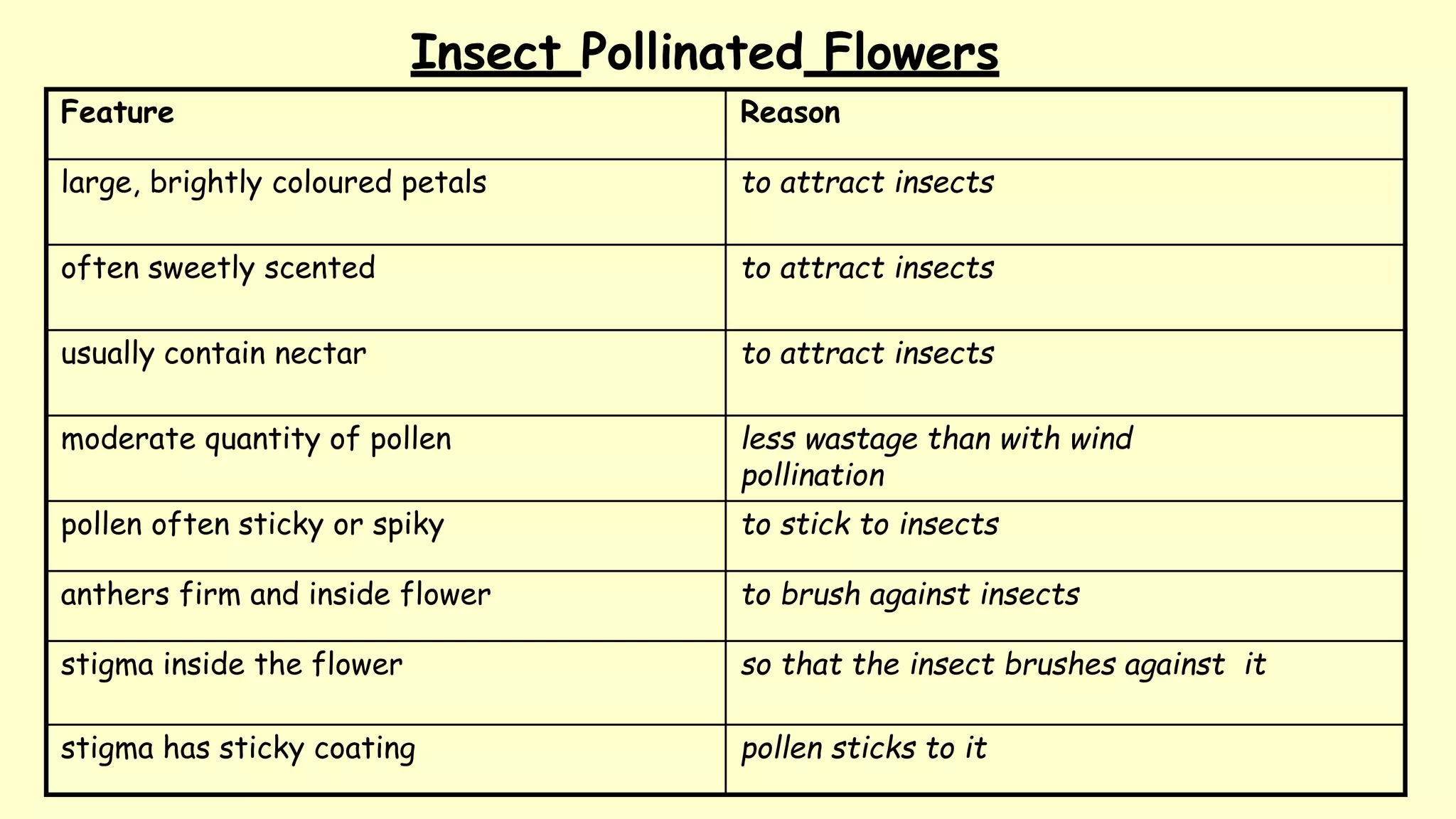
2. There are two main types of pollination - wind pollination and insect pollination. Wind pollinated flowers have adaptations like small dull flowers and lightweight pollen for wind dispersal, while insect pollinated flowers offer rewards like nectar and scent to attract pollinators.
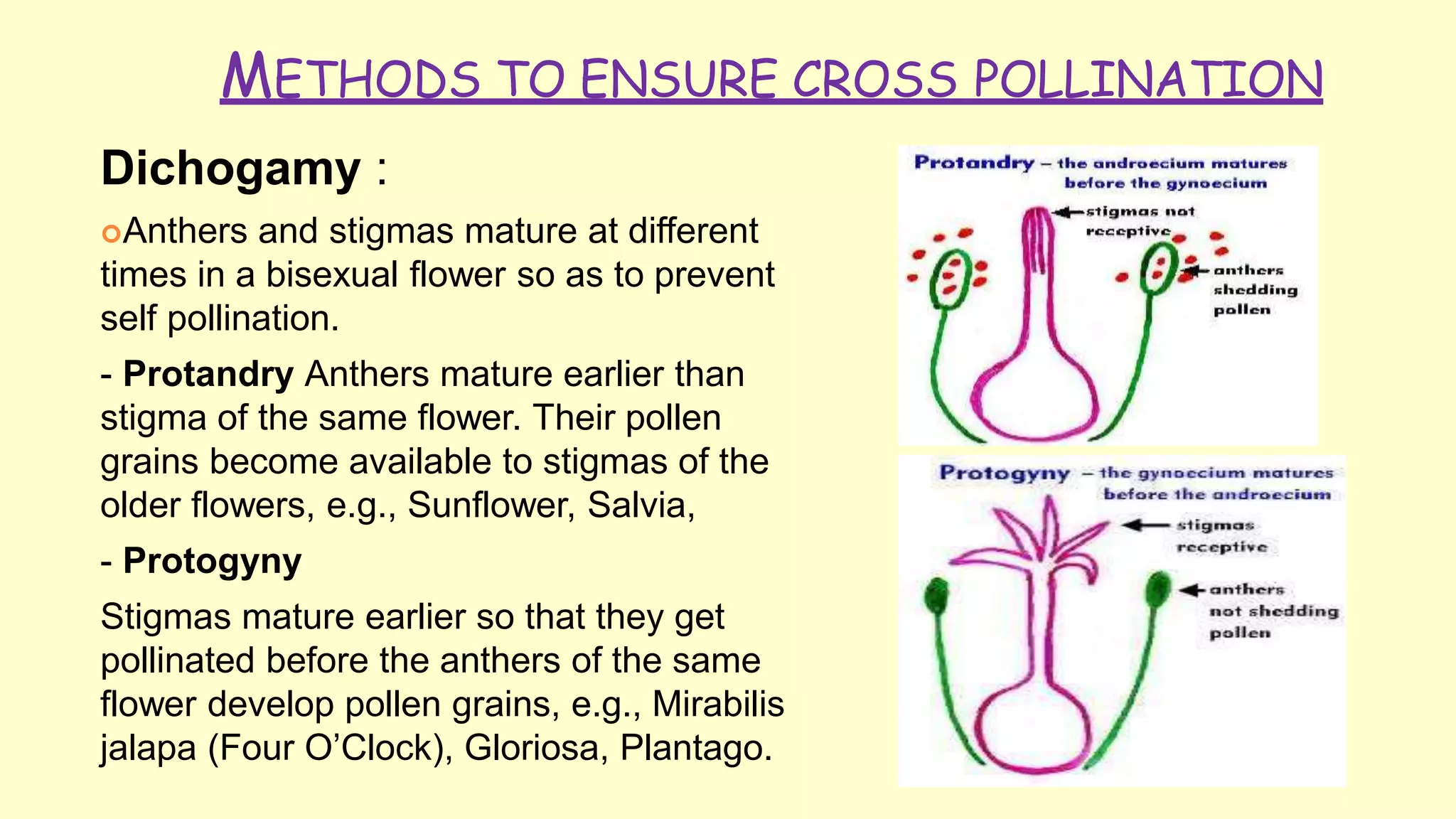
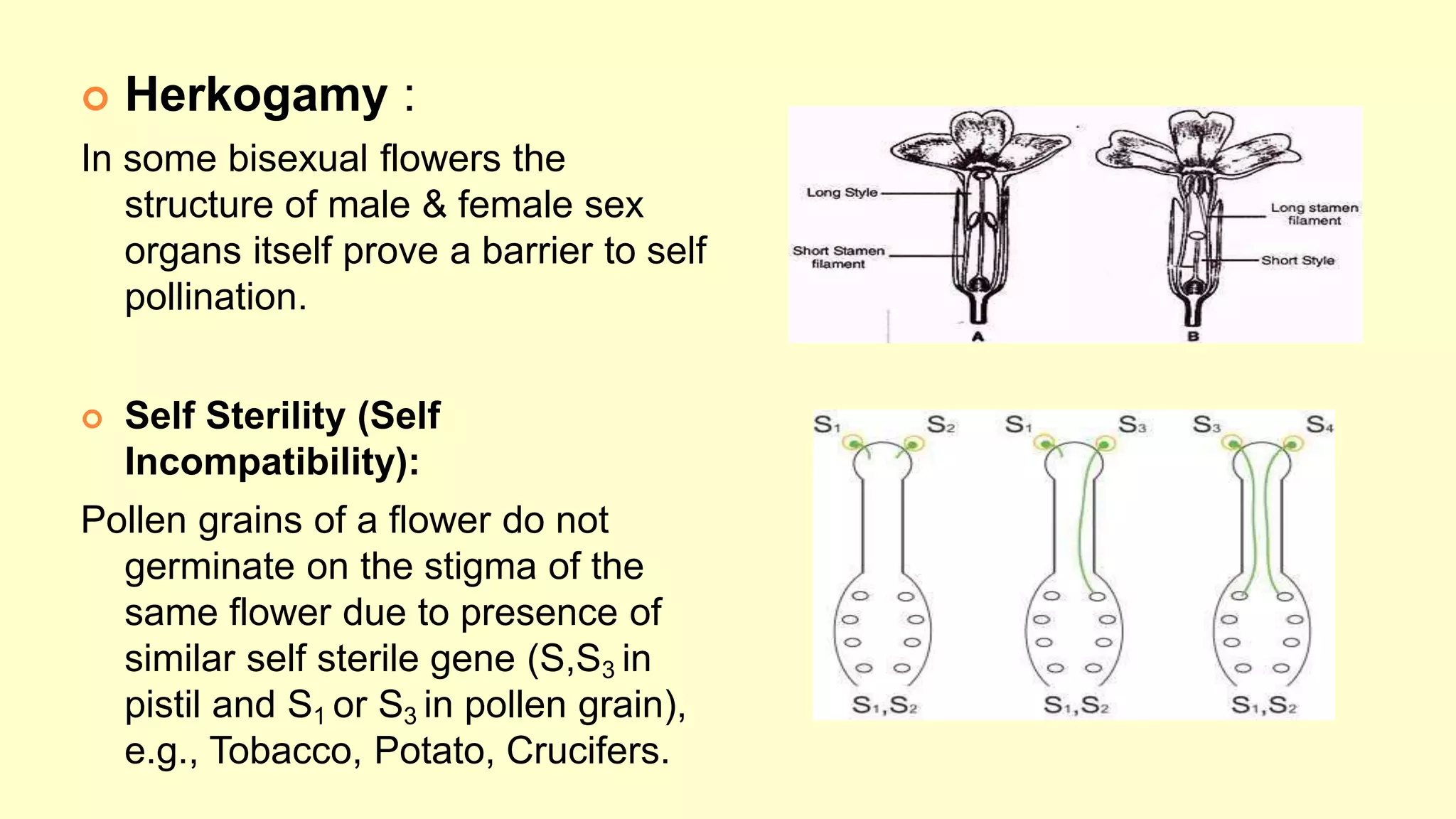
3. Cross pollination provides advantages like more viable and resistant offspring through genetic recombination, but also disadvantages like less genetic purity and reliance on pollinating agents. Plants use mechanisms like dichogamy and self-sterility to encourage out