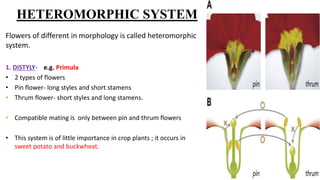
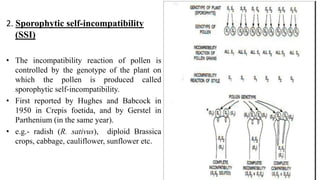
This document discusses self-incompatibility in plants. It begins by defining self-incompatibility as the prevention of fertilization after self-pollination. There are two main types of self-incompatibility systems - homomorphic and heteromorphic. Heteromorphic systems involve morphological differences between flowers like distyly seen in Primula, while homomorphic systems do not. Homomorphic systems include gametophytic and sporophytic self-incompatibility, which differ in how the incompatibility reaction is controlled. Self-incompatibility promotes outbreeding and maintains genetic diversity in plant species. It has applications for plant breeding through hybrid seed production.