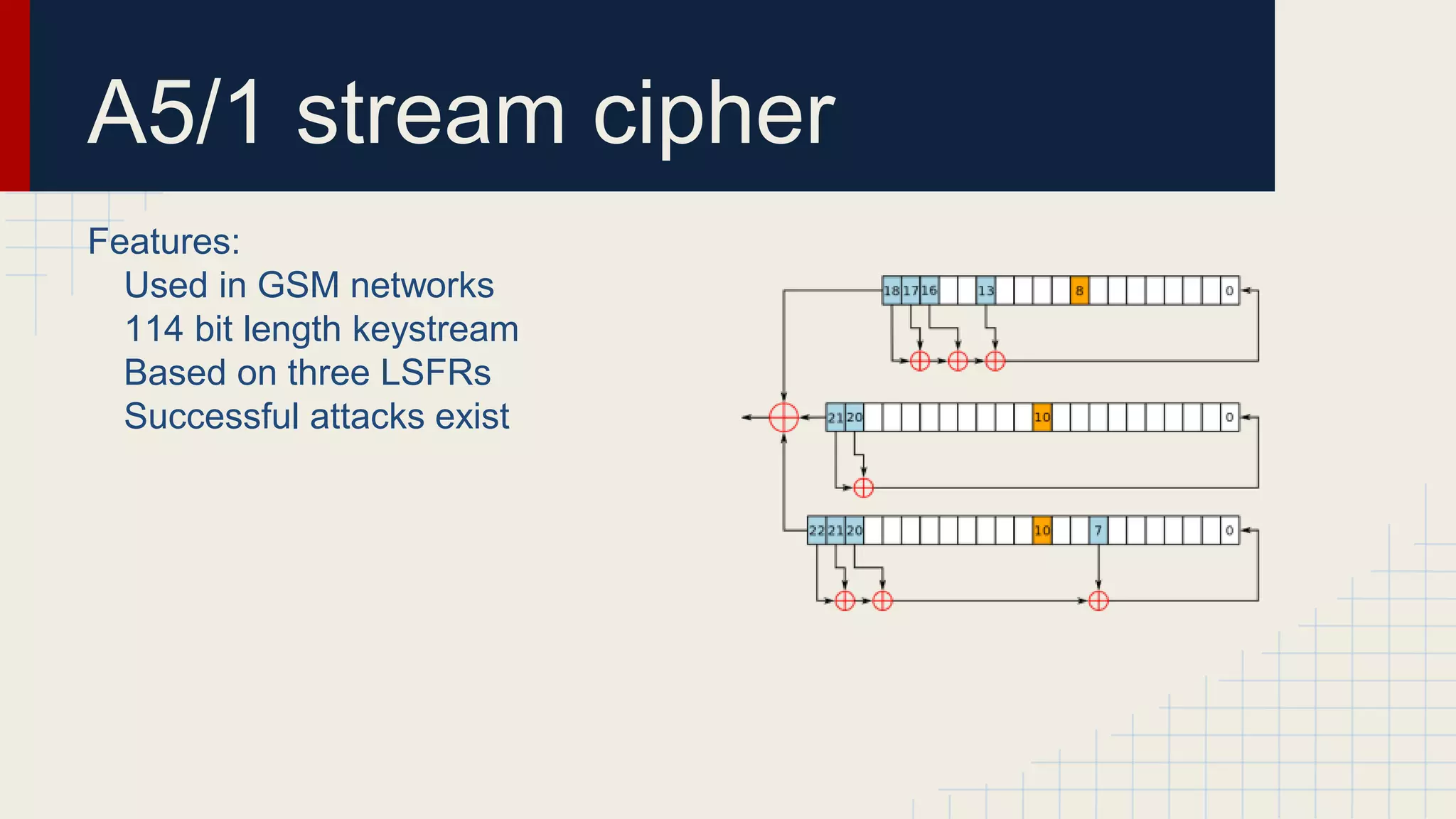
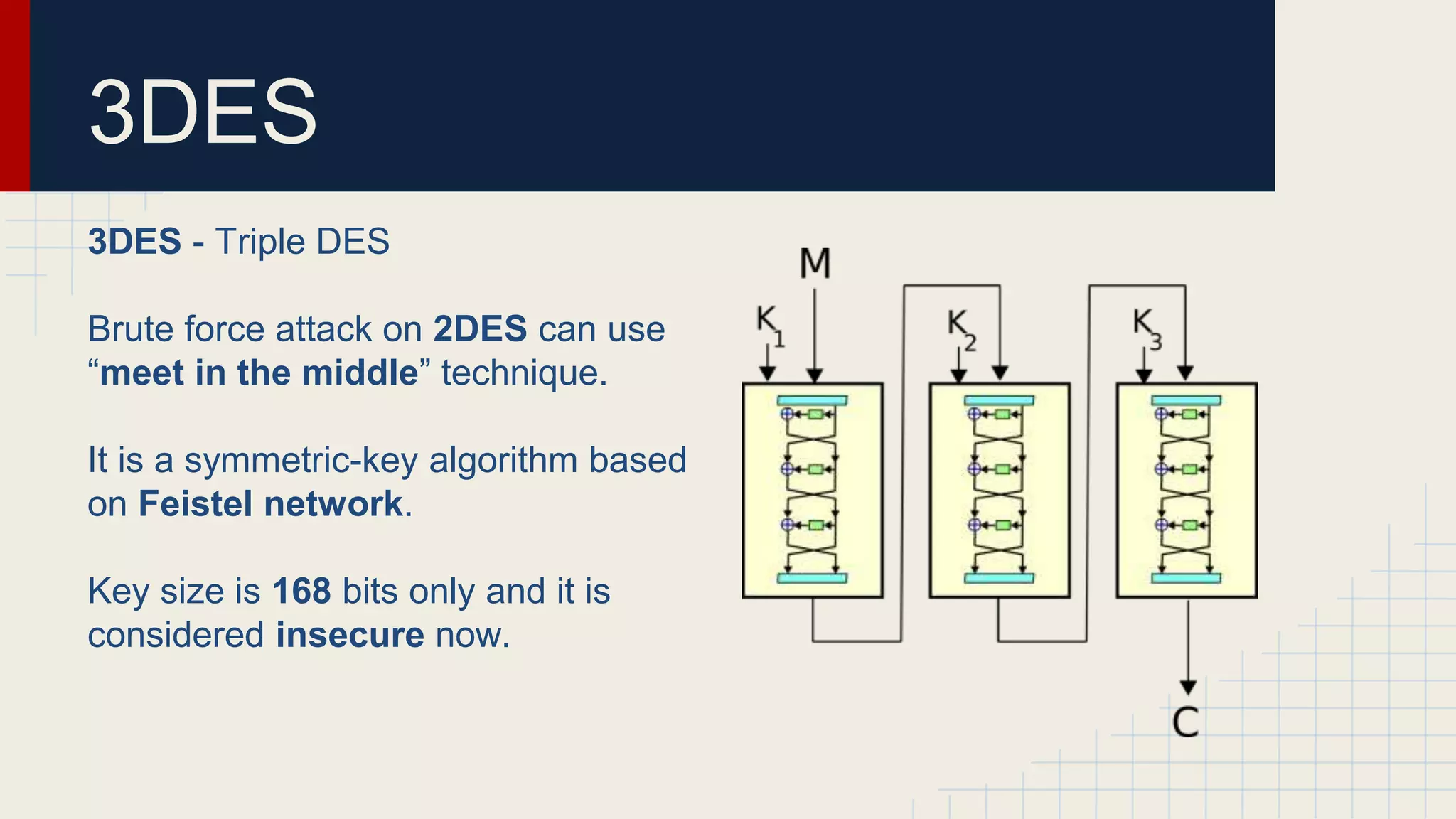
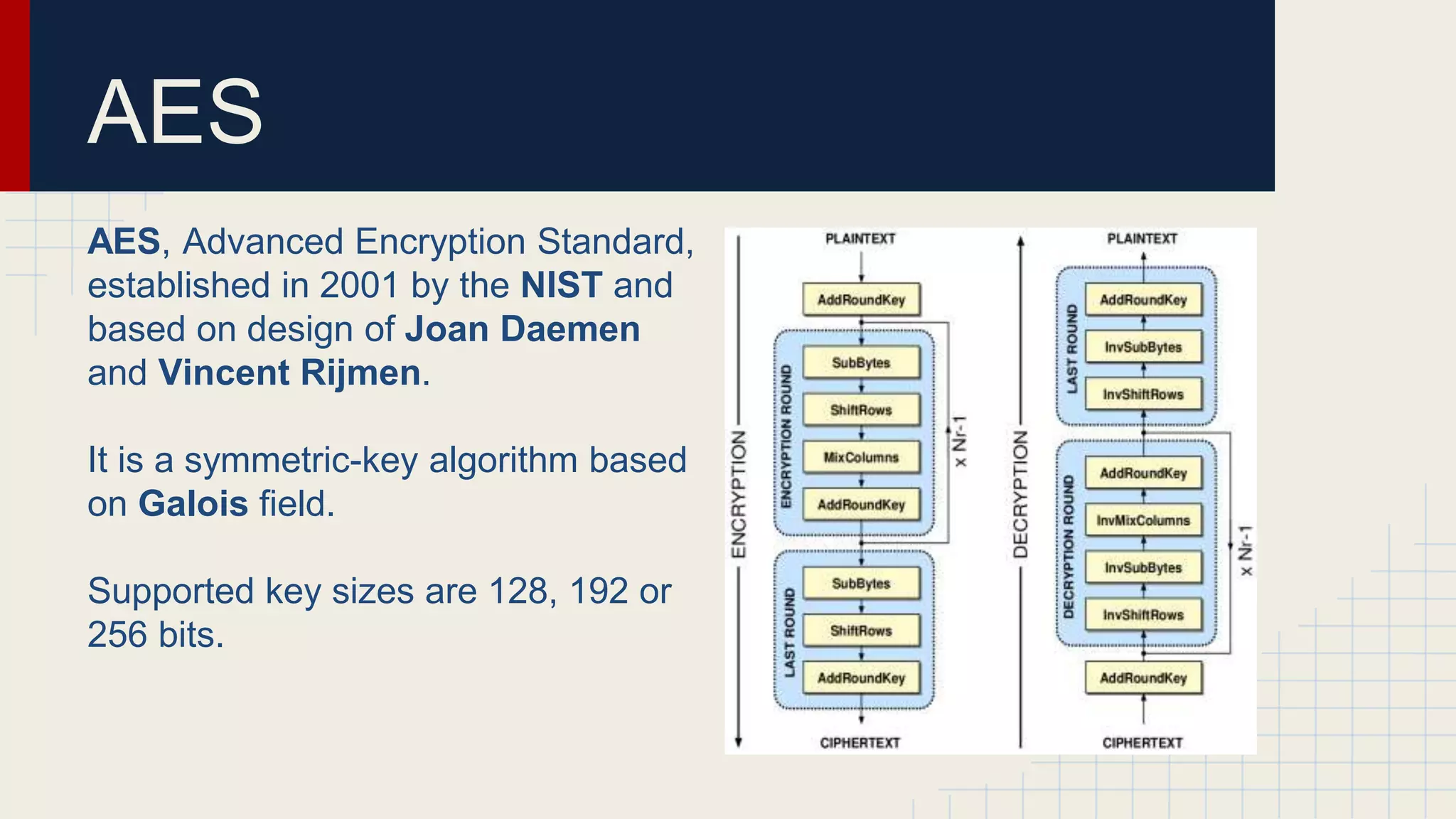
This document provides an overview of popular encryption algorithms. It discusses both symmetric and asymmetric ciphers such as the one-time pad, stream ciphers like A5/1, symmetric block ciphers including DES, 3DES and AES, and asymmetric ciphers RSA and elliptic curve cryptography. It also covers block cipher modes of operation like ECB, CBC, OFB, CFB and CTR. The one-time pad requires truly random keys of the same length as plain text but is impractical. AES with 128-256 bit keys is now secure standard, while DES and 3DES are insecure due to small key sizes. RSA uses 1024-4096 bit keys but is slower than elliptic curve cryptography which provides equivalent security with smaller