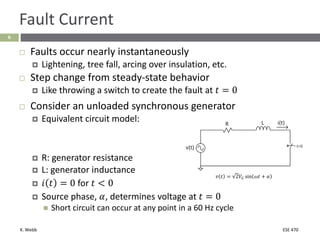
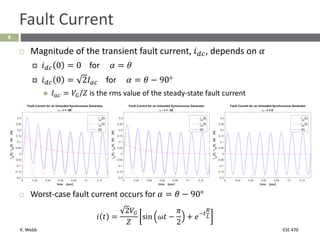
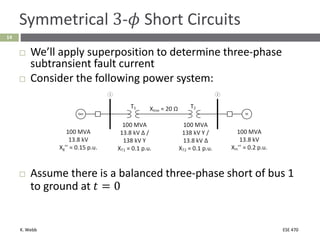
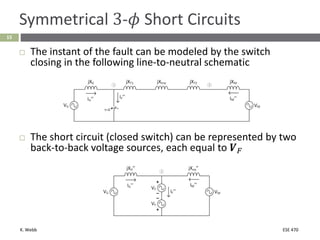
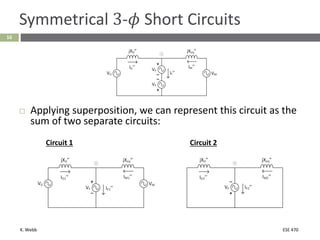
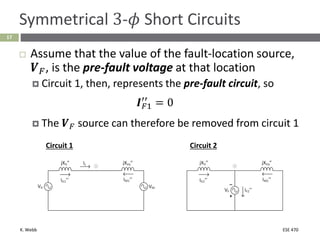
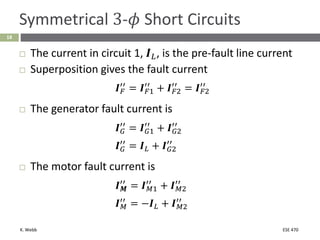
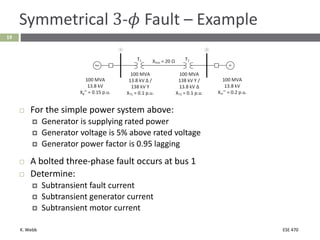
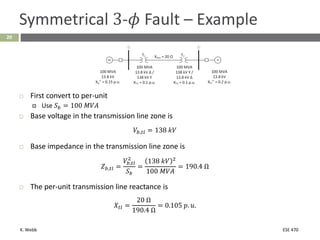
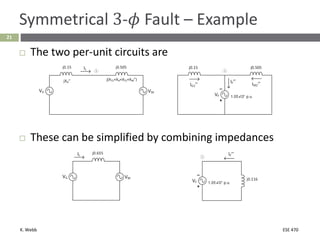
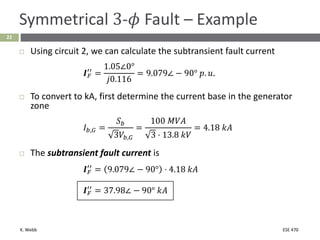
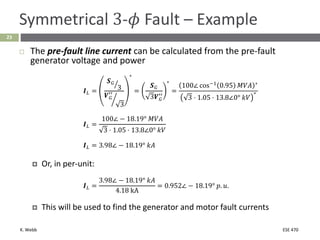
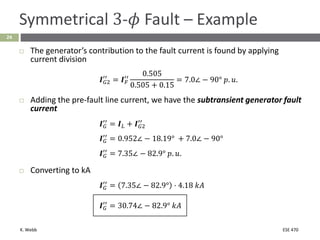
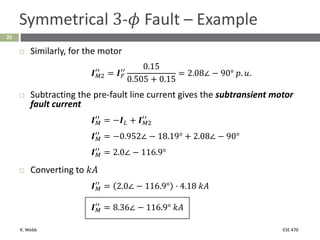
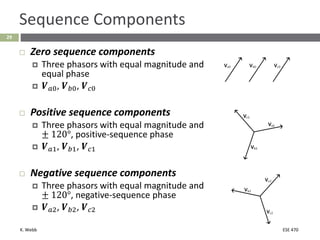
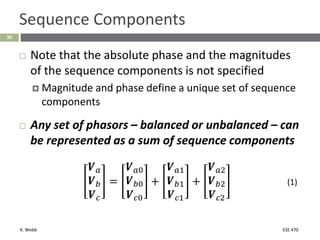
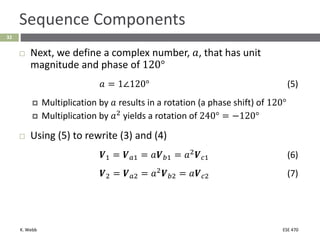
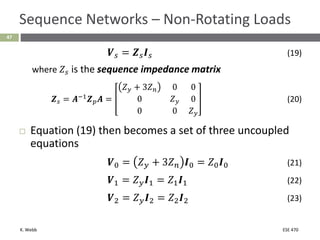
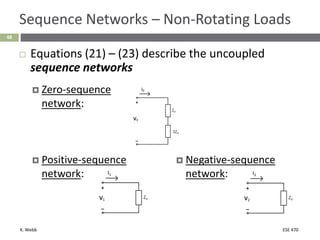
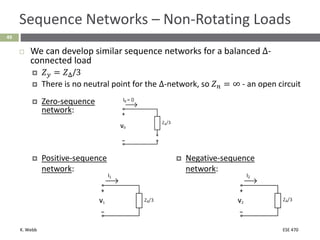
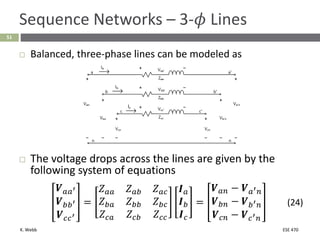
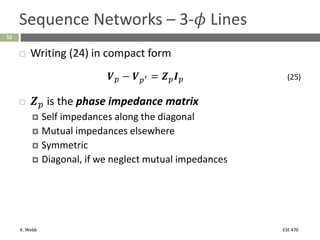
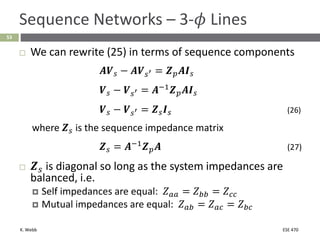
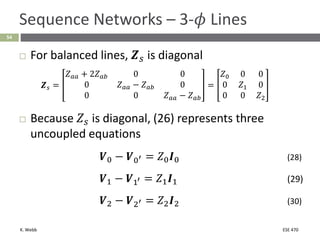
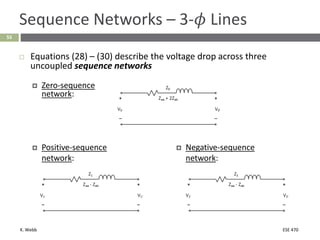
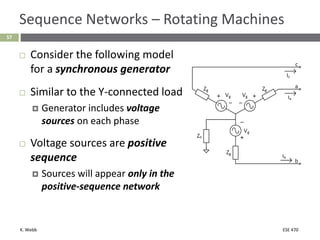
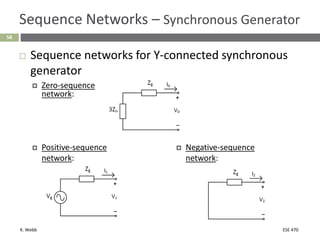
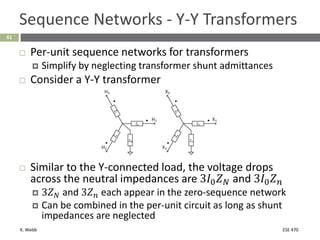
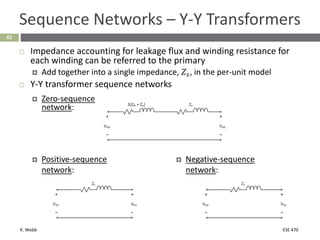
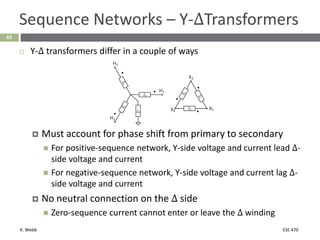
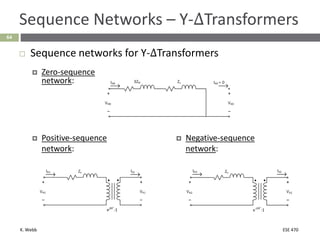
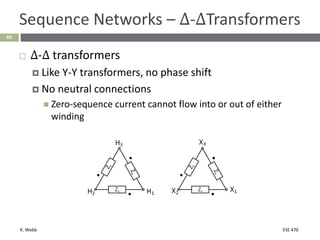
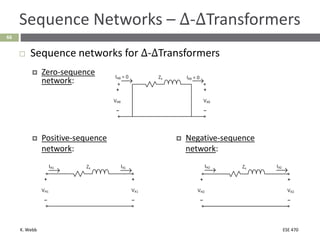
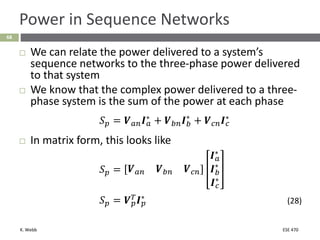
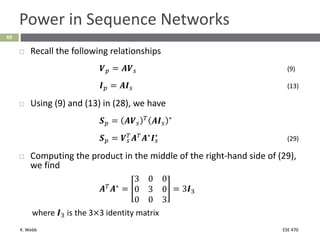
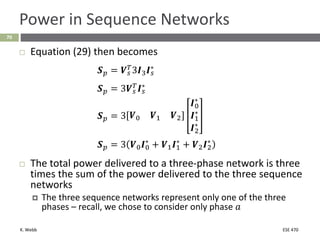
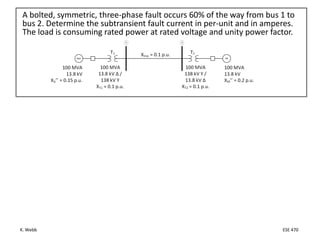
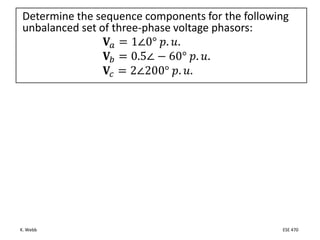
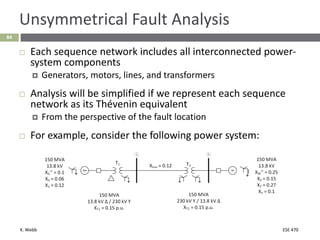
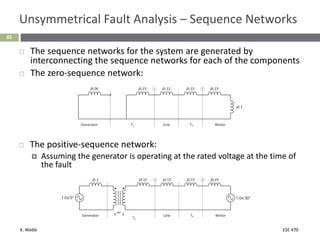
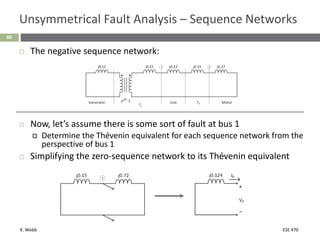
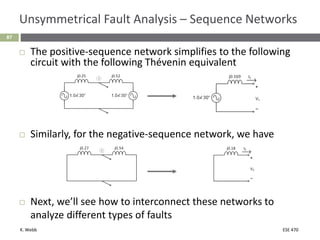
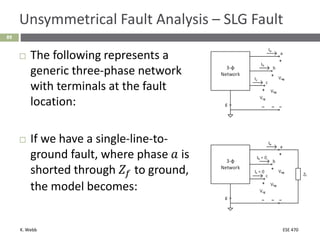
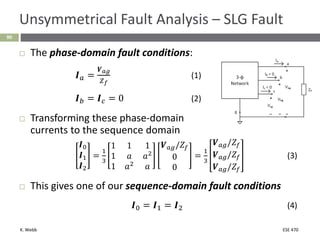
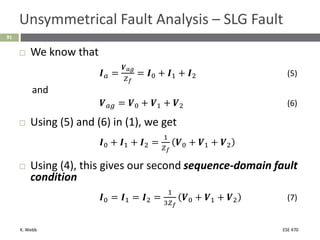
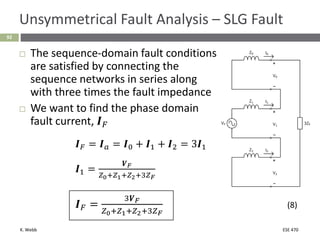
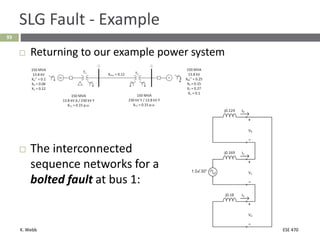
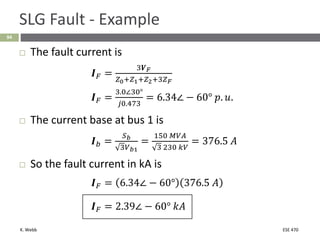
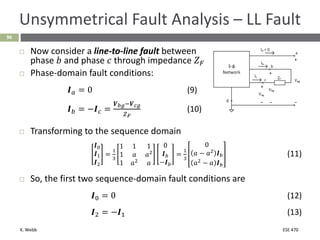
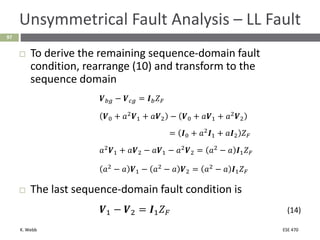
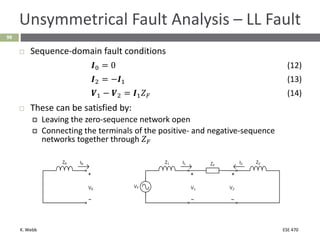
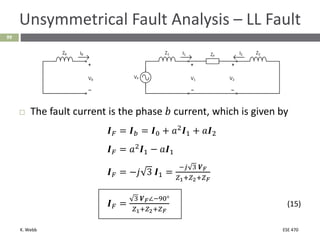
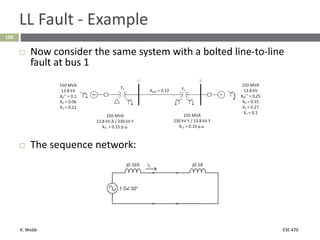
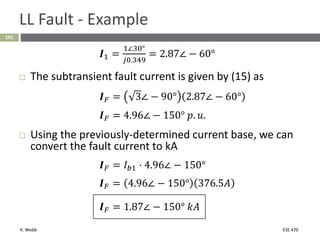
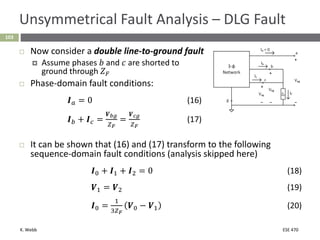
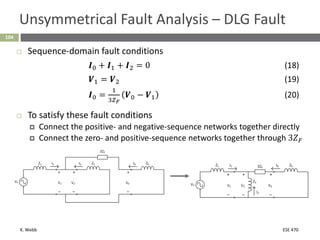
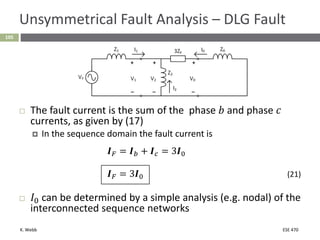
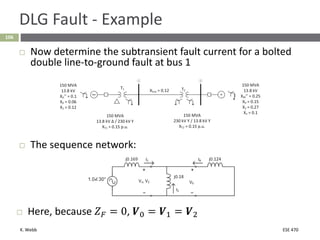
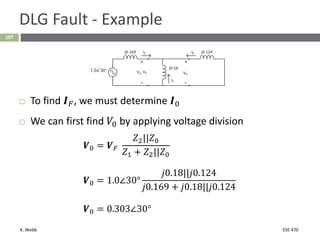
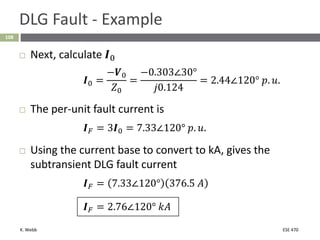
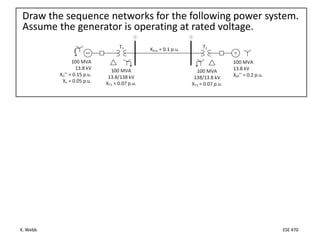
This document section discusses fault analysis in power systems. It begins by defining different types of faults like line-to-ground and line-to-line faults that can result in excessive current. It then discusses fault current calculations for a symmetrical three-phase fault on a simple system using superposition and per-unit calculations. As an example, it calculates the subtransient fault current, generator current, and motor current for a bolted three-phase fault at a bus.