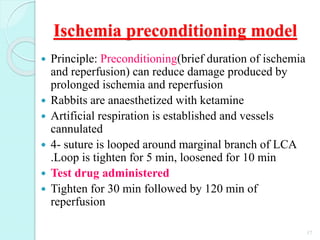
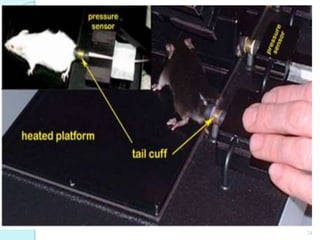
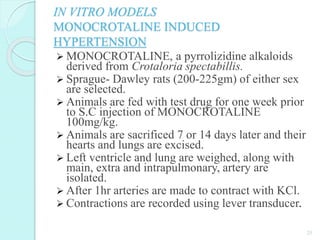
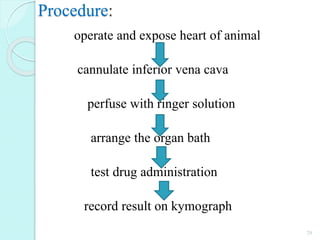
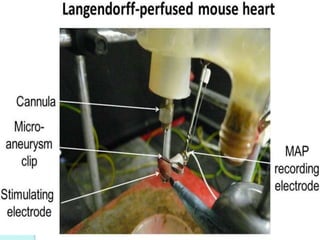
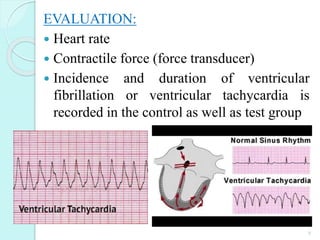
The document discusses various screening methods for cardiovascular drugs, particularly focusing on antiarrhythmic, anti-anginal, and antihypertensive drugs, utilizing both in-vitro and in-vivo models. It details specific techniques such as the Langendorff technique for isolating hearts and methods for inducing arrhythmias, as well as methods for assessing drug efficacy through animal studies. The document provides experimental procedures, observations, and comparison methods used to evaluate the pharmacological effects of these drugs.







![procedure
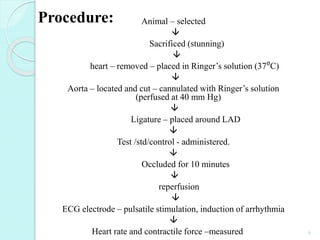
Animals [Male rats (300-400g)]
Anesthetized
Test / std/control – administered
↓
Aconitine (5μg/kg +0.1N HNO₃) (administered
through saphenous vein)
↓
ECG – Recorded (lead II)
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cardiacactivity-200419153942/85/screening-method-of-cardiovascular-activity-11-320.jpg)