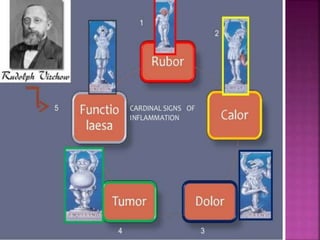
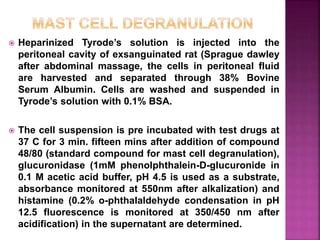
This document summarizes screening methods for evaluating potential anti-inflammatory drugs. It discusses the inflammatory response and various animal models used to test drug candidates, including carrageenan-induced paw edema, cotton pellet-induced granuloma, and UVB-induced erythema in guinea pigs. Several in vitro assays are also described, such as measuring COX inhibition and evaluating the ability of drugs to block mast cell degranulation and platelet-neutrophil adhesion. The goal of these screening methods is to effectively identify drug candidates that can target different phases and components of the inflammatory process.