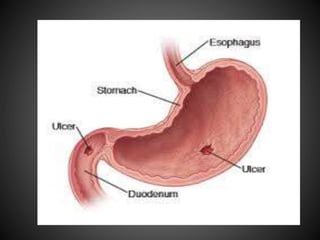
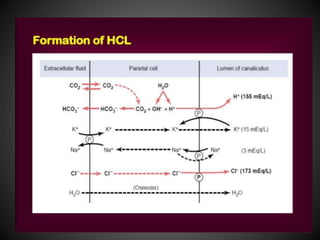
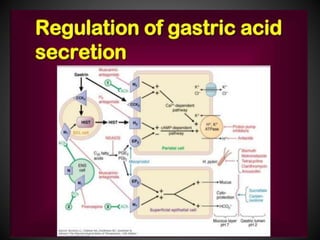
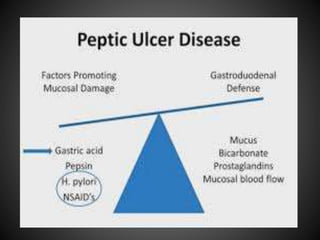
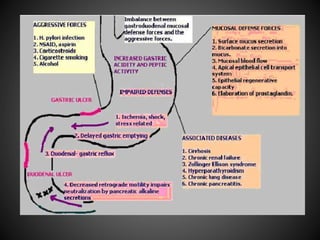
This document summarizes peptic ulcers, including their causes, symptoms, complications, and treatment. Peptic ulcers are chronic inflammatory conditions involving the stomach and duodenum caused by excess acid and pepsin. Common symptoms include abdominal pain and bleeding. Untreated ulcers can lead to complications like bleeding, infection, or obstruction. Various factors like heredity, diet, medications, and infections contribute to ulcer development. Treatment involves reducing acid secretion using proton pump inhibitors, H2 blockers, or antacids. Animal models are used in research to study ulcer development and potential new treatments.













![• In- vitro models:-
1. [I125 ] Gastrin Binding Assay
2. Tiotidine Binding Assay
3. H+/K+- ATPase Inhibiting Assay](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antiulcerscreeningmodels-181112145757/85/Antiulcer-screening-models-19-320.jpg)
















![IN- VITRO
• [ 125I ]GASTRIN BINDING ASSAY:
• Gastrin( G cell of gastric antrum)
• Bind to CCK2 receptor of parential cell =
release HCl
• Bing CCK2 receptor of ECL cell = release
histamine– act on H2 receptor – release HCl
• Compound withgastrin receptor antagonist
can be potent antiulcer agent](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antiulcerscreeningmodels-181112145757/85/Antiulcer-screening-models-36-320.jpg)


![EVALUATION:-
• The total binding , non specific binding and
specific binding is been determined
• Percentage of specially bounded [125 I] Gastrin
displaced by given concentration of the test
compound calculated
• The higher the displace of [125 I] gastrin , the
more the antagonistic effect of the test drug.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antiulcerscreeningmodels-181112145757/85/Antiulcer-screening-models-39-320.jpg)






