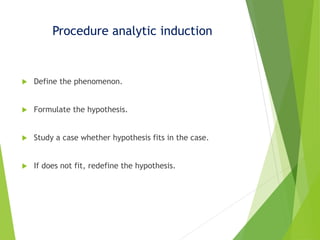
This document discusses scientific social science research and the scientific method. It explains that social science research refers to the scientific study of human behavior and interaction. The scientific method relies on evidence, concepts, objectivity, and logical reasoning processes like induction and deduction. Induction involves studying individual cases to draw generalizations, while deduction applies general principles to specific cases. For research to be considered scientific, it must follow a systematic process including defining the problem, formulating hypotheses, collecting quantitative data, stating clear generalizations, and fully reporting the research process and methods of analysis.