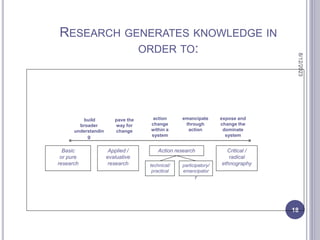
The document outlines advanced research methods in quantitative and qualitative research, exploring the definition, purpose, and types of research. It discusses the scientific methodology, including problem identification and hypothesis testing, while emphasizing the importance of both basic and applied research. Philosophical foundations of research, including various epistemological approaches, and the nature of different research designs are also elaborated upon.