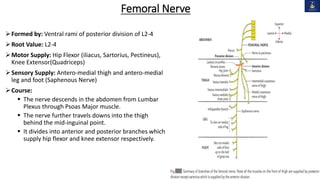
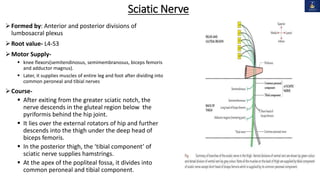
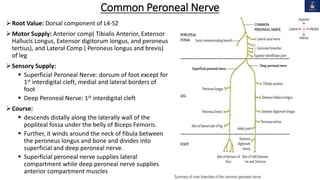
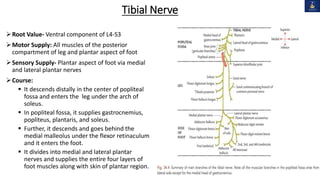
This document discusses peripheral nerve injuries of the lower limb, summarizing the anatomy and clinical presentation of injuries to the femoral nerve, sciatic nerve, common peroneal nerve, and tibial nerve. It describes the formation, motor and sensory innervation, and typical course of each nerve. Common sites of injury and resulting functional deficits are outlined. Physical exam maneuvers to test motor and sensory function are also provided.