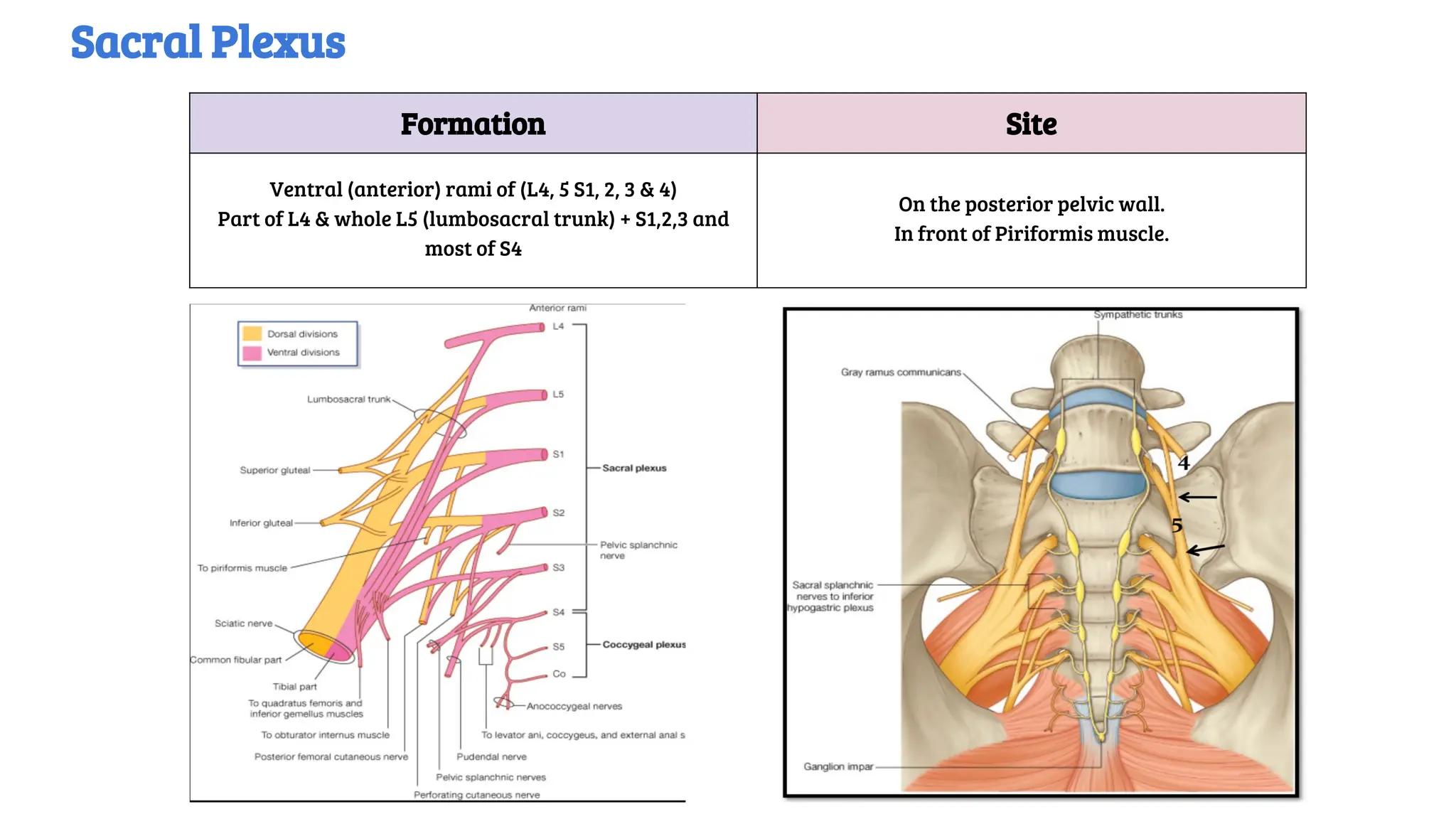
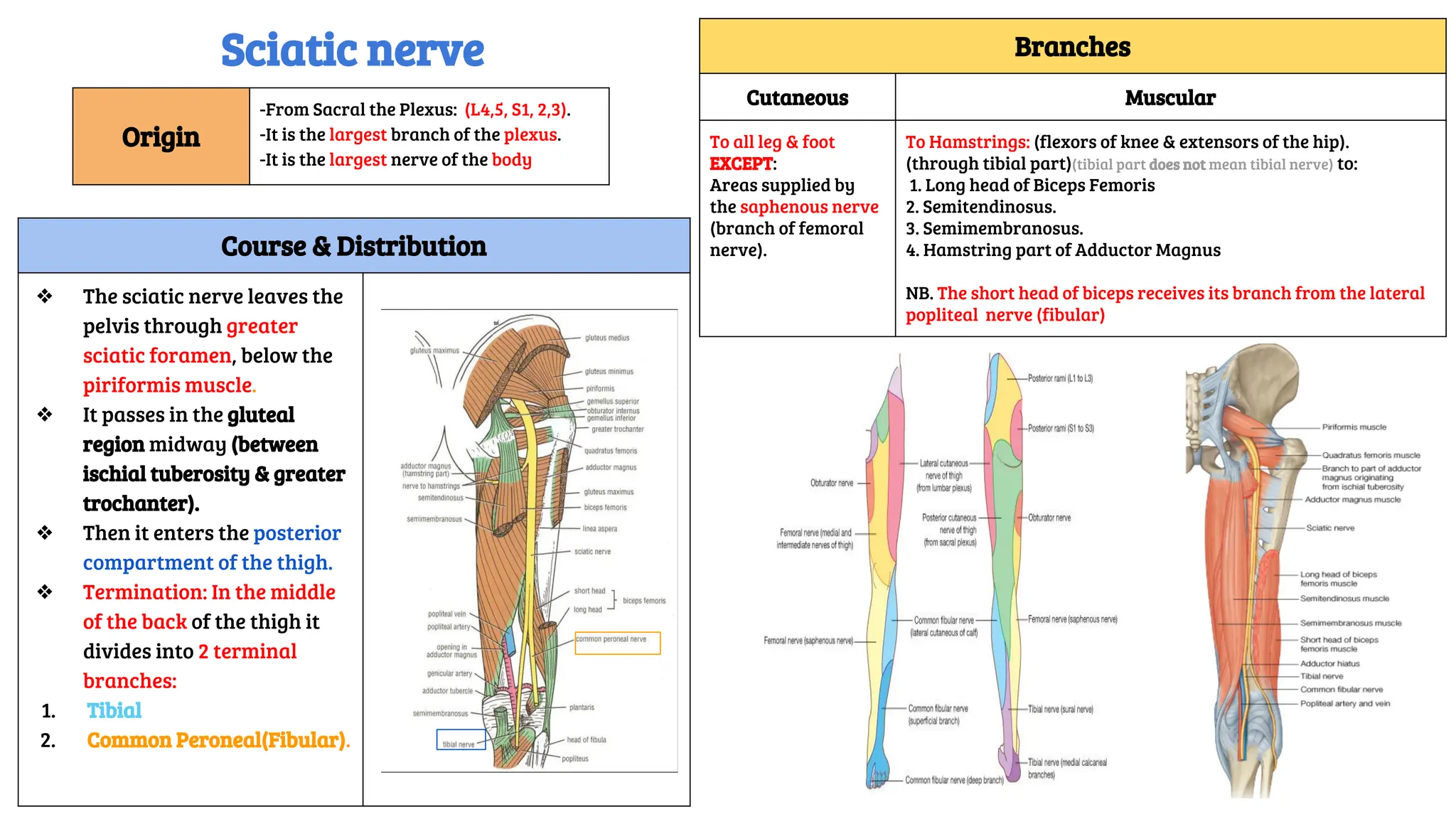
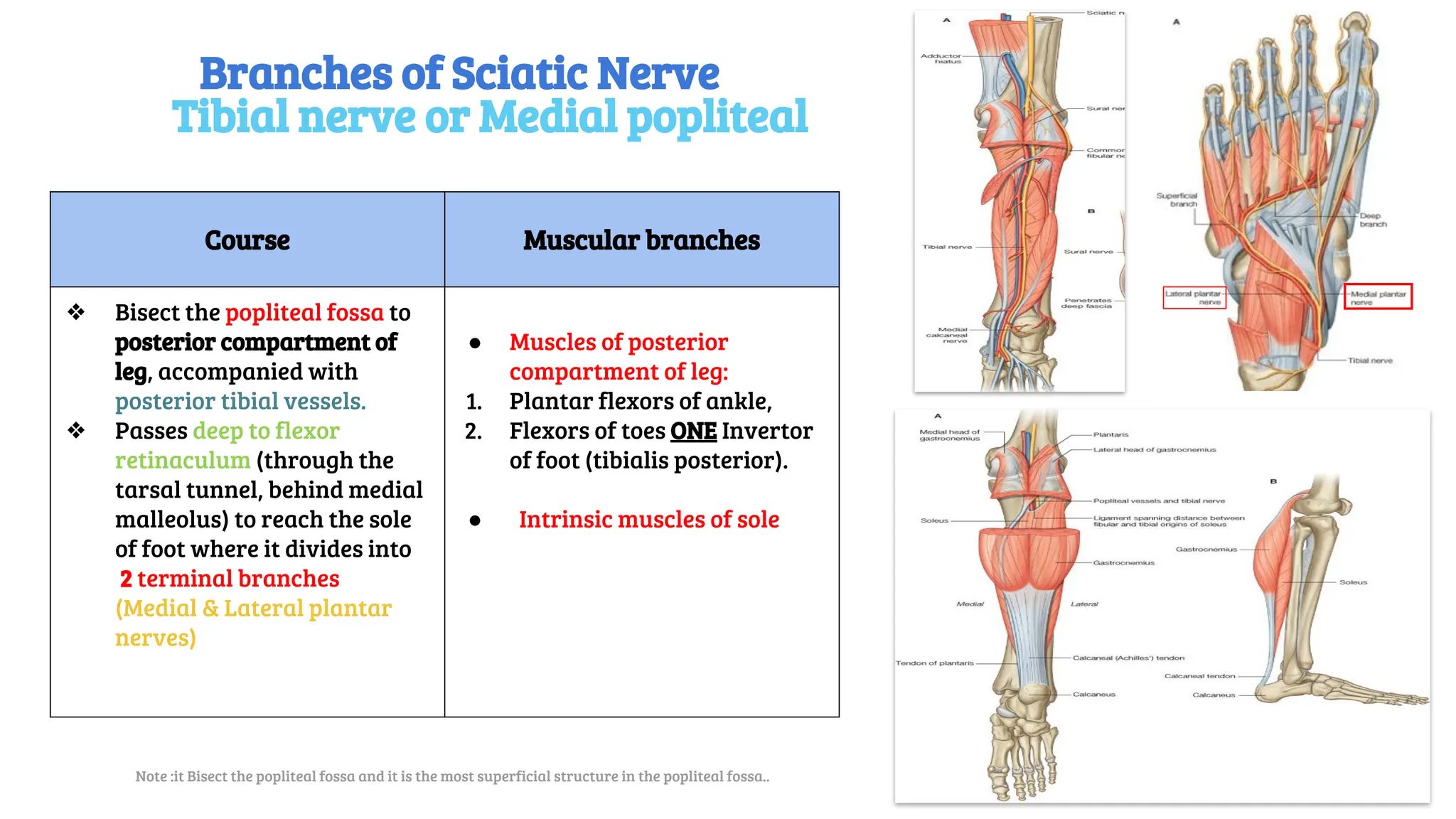
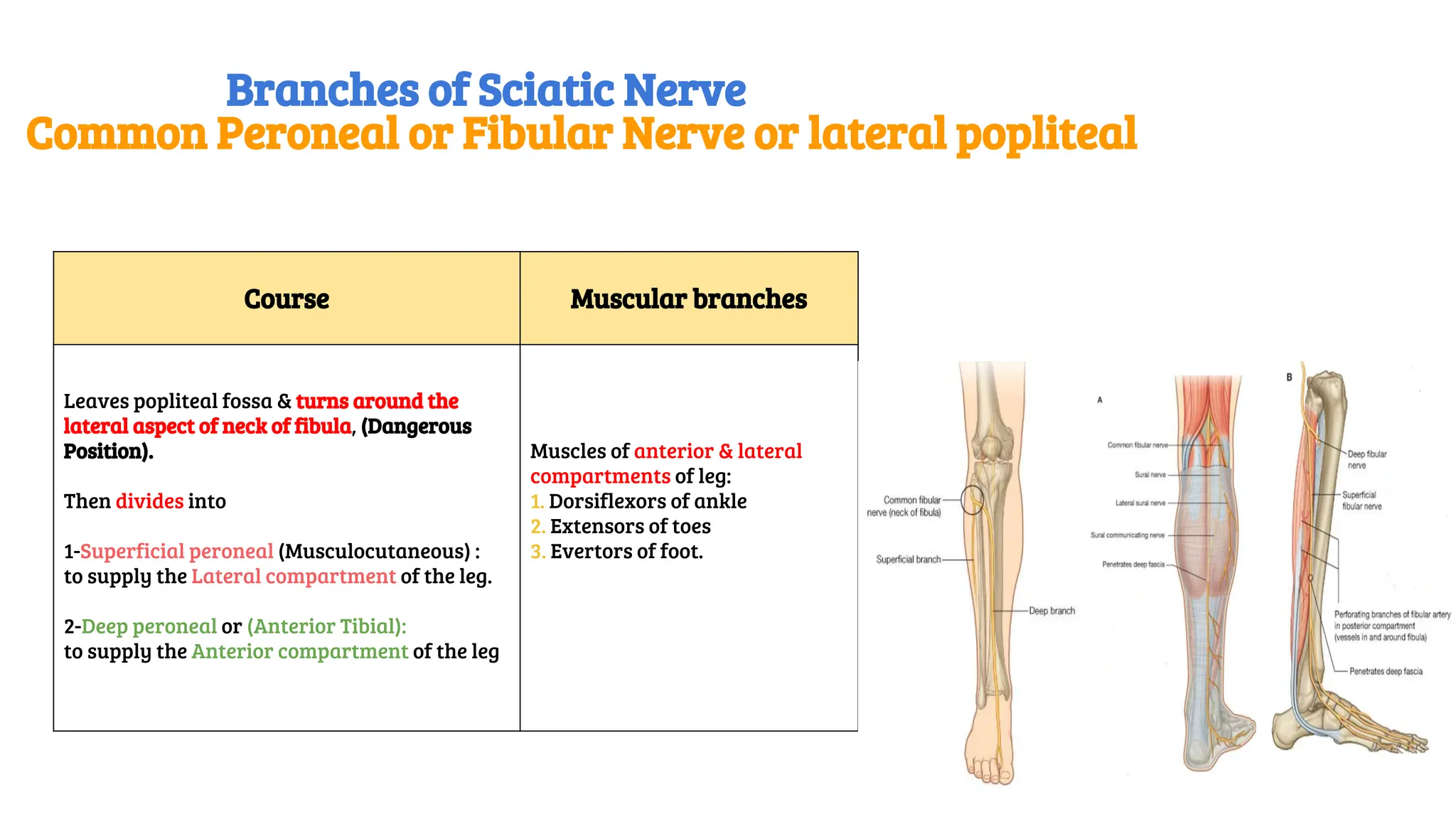
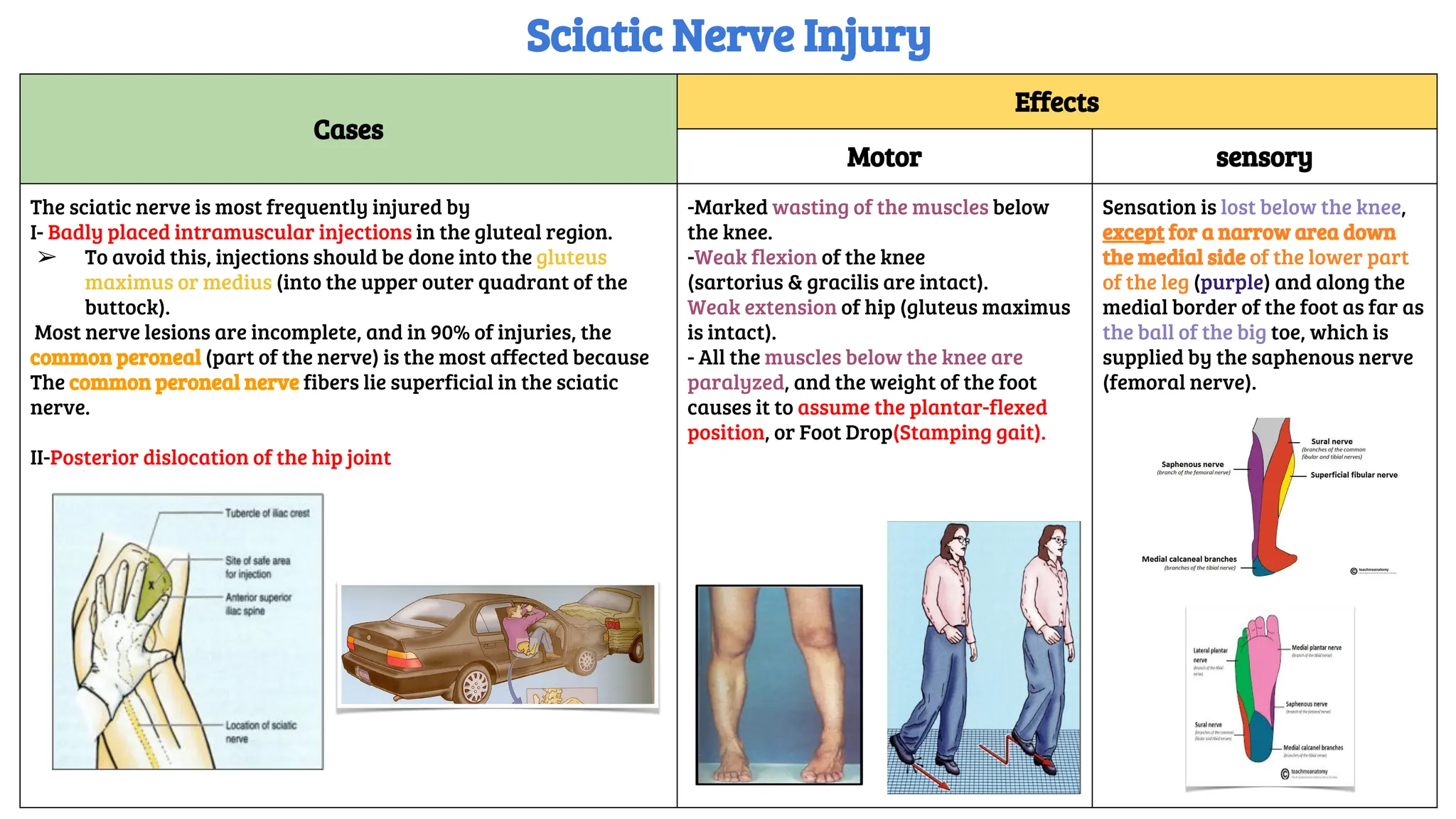
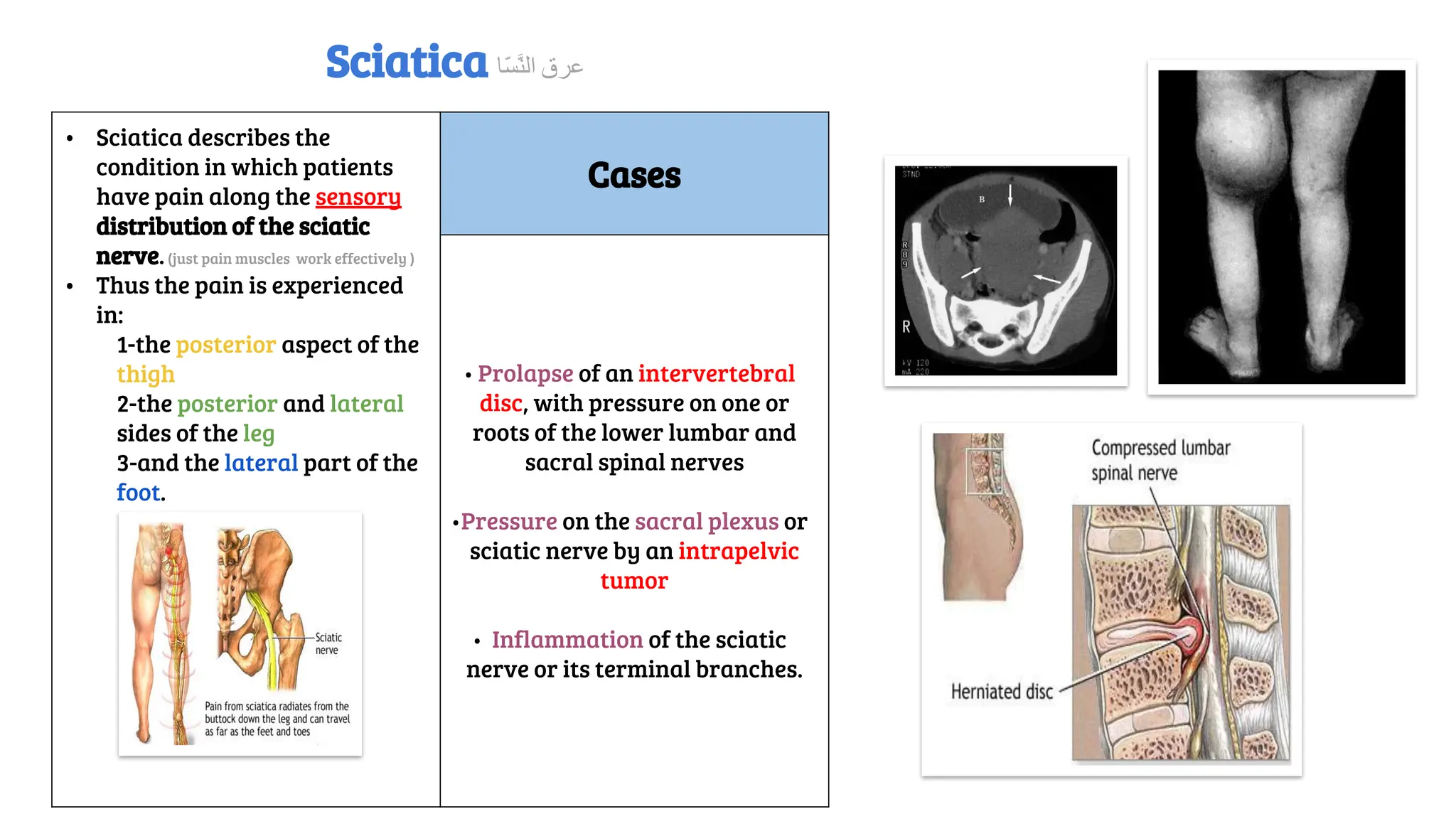
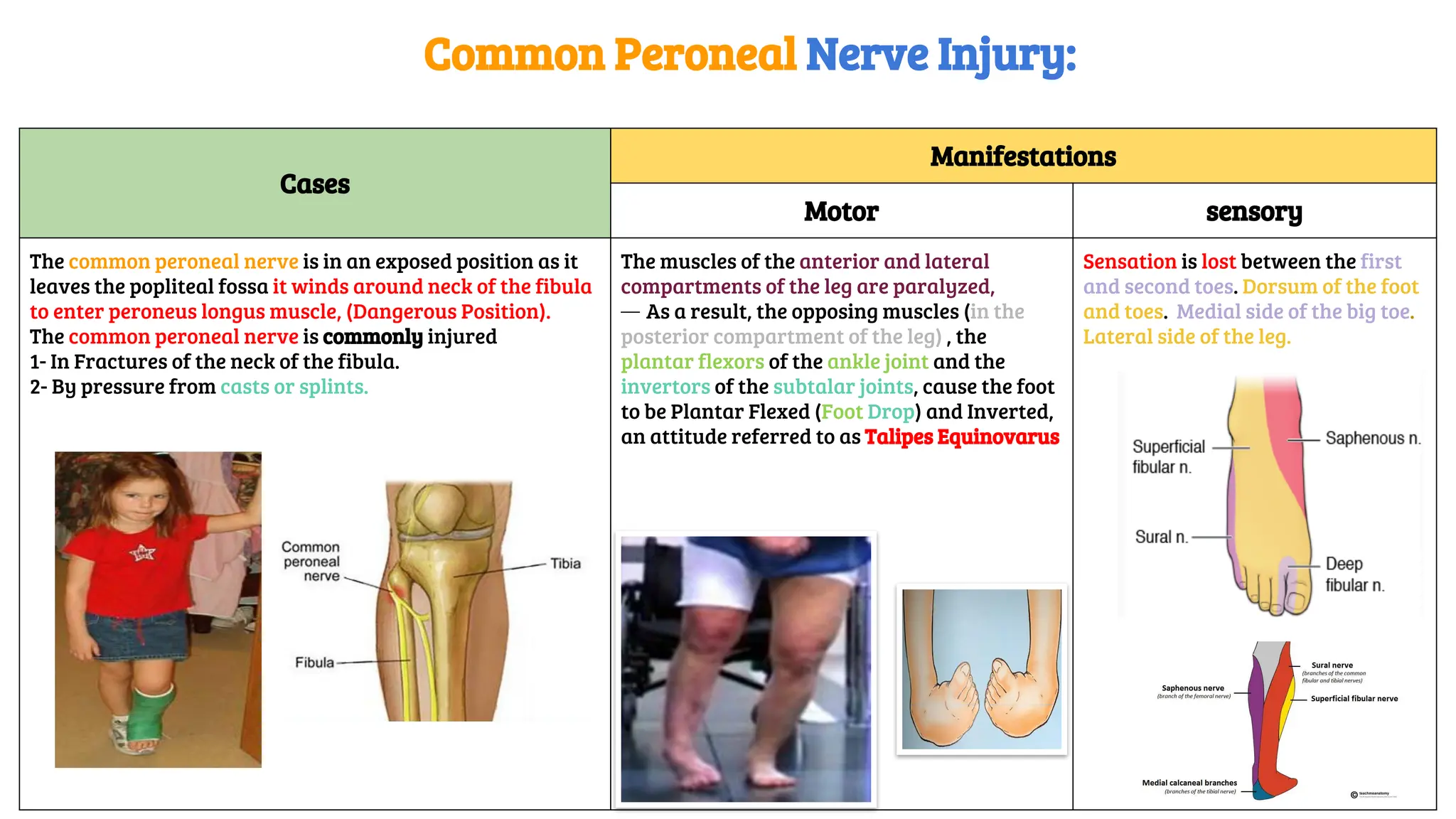
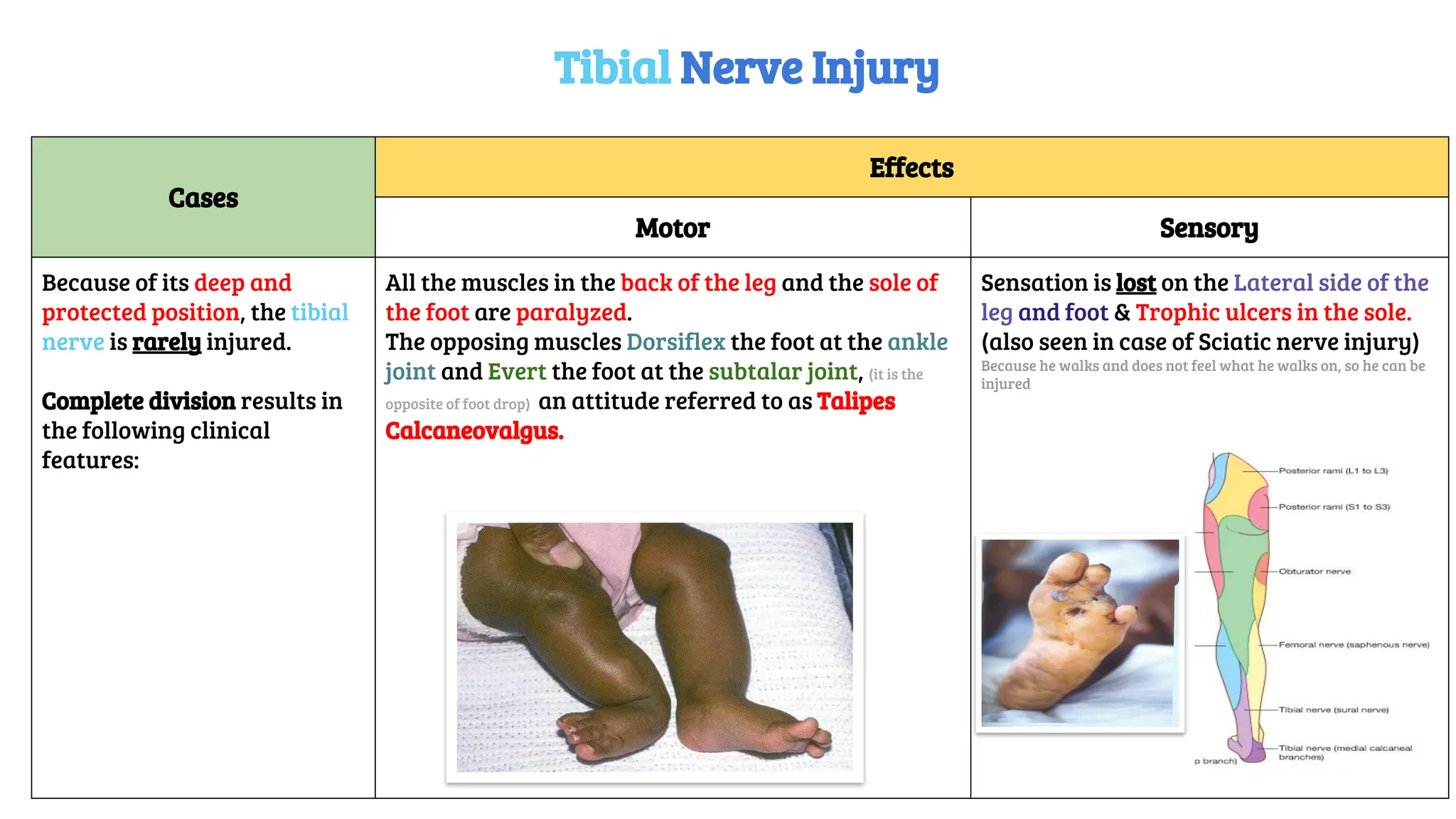
This document provides a detailed overview of the anatomy, course, and branches of the sciatic nerve, including its motor and sensory functions and the potential effects of injury. It highlights the origins of the nerve from the sacral plexus, its trajectory through the pelvis and thigh, and the major branches that supply the leg and foot. Additionally, it discusses common causes and symptoms of sciatic nerve injuries, as well as related anatomy and implications for clinical practice.