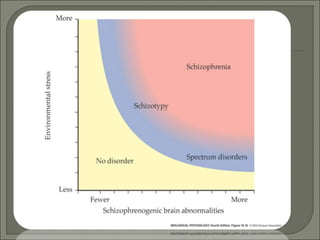
- Schizophrenia was originally described as having distinct subtypes with different symptoms, but all involve dissociative thinking. Genes on multiple chromosomes have been implicated in schizophrenia risk. Environmental factors like lower birth weight, stress in pregnancy, and advanced paternal age may also play a role.
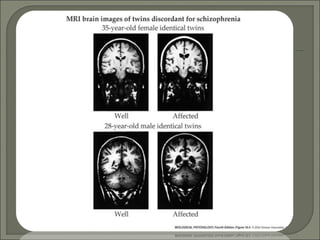
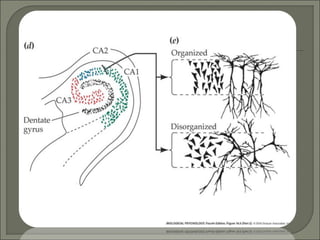
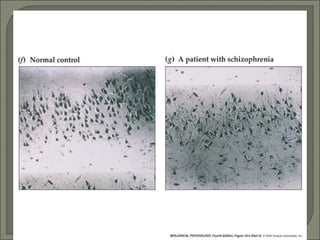
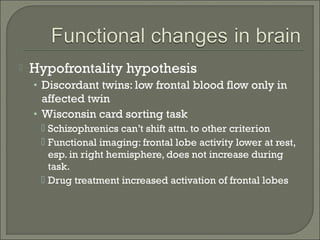
- Brain abnormalities in schizophrenia include enlarged ventricles, reduced hippocampal and prefrontal cortex volume, and abnormal prefrontal function. The hypofrontality hypothesis suggests dysfunction in prefrontal regions, supported by brain imaging studies. Psychedelic drugs can induce schizophrenia-like symptoms, and NMDA receptor antagonists like PCP and ketamine also produce similar effects in animals. Current drug treatments target dopamine and serotonin receptors.