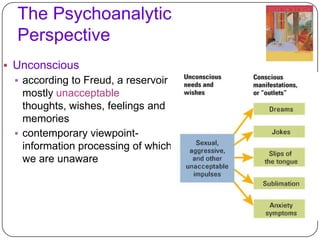
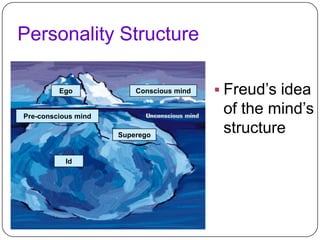
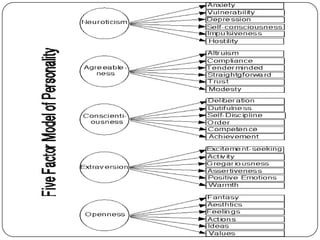
The document discusses how personality is shaped by both nature and nurture. It describes personality as a consistent pattern of thoughts, feelings and behaviors. While genes play a role, most scientists believe environmental factors like family, culture and physical conditions have the greatest influence on personality development. Birth order, parental characteristics, and cultural norms around individualism or collectivism can impact worldviews and traits. Freud's psychoanalytic perspective also influenced theories on unconscious motivations and personality structure. Homeopathic remedies are proposed to relate to distinct personality types.