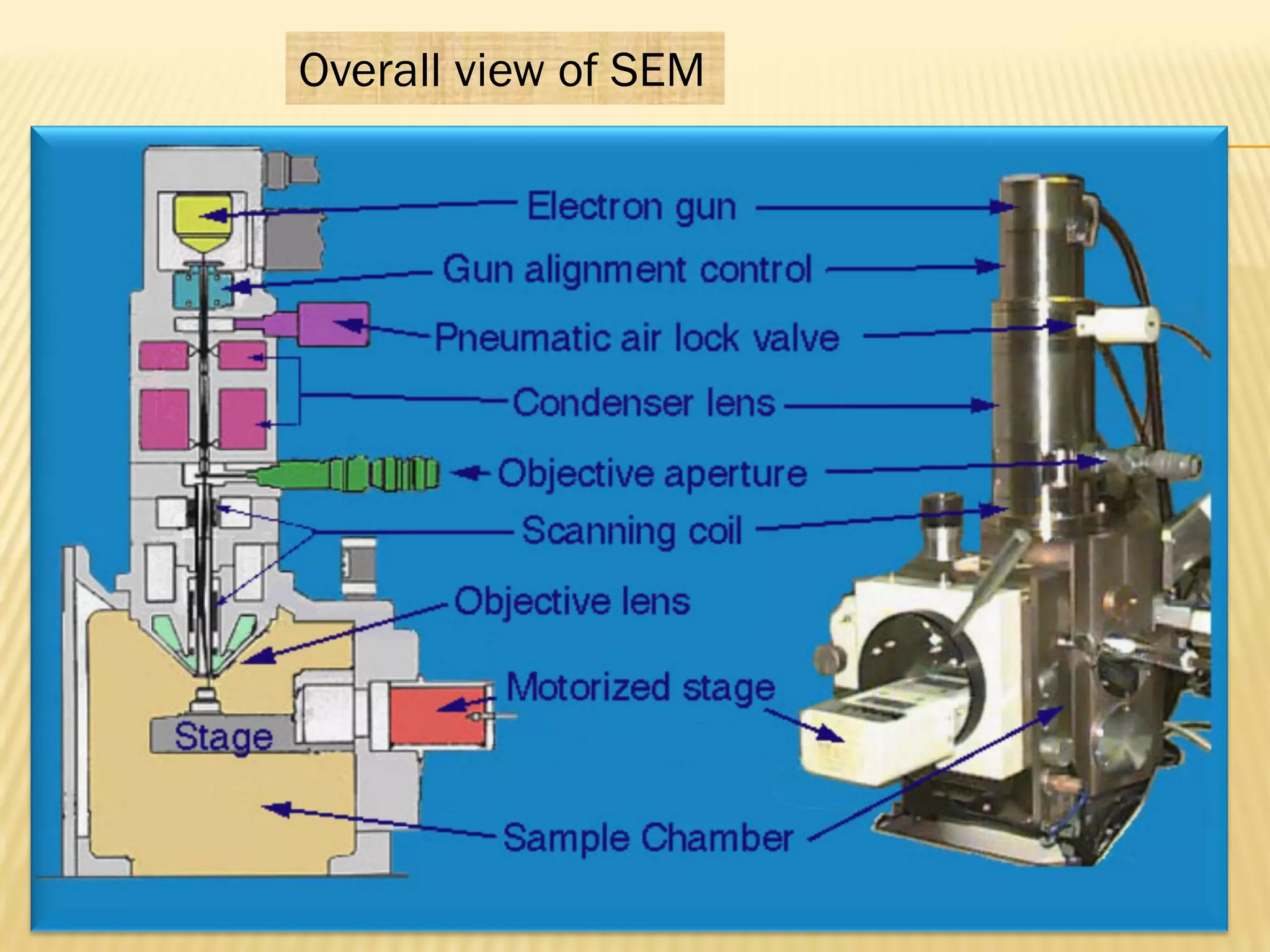
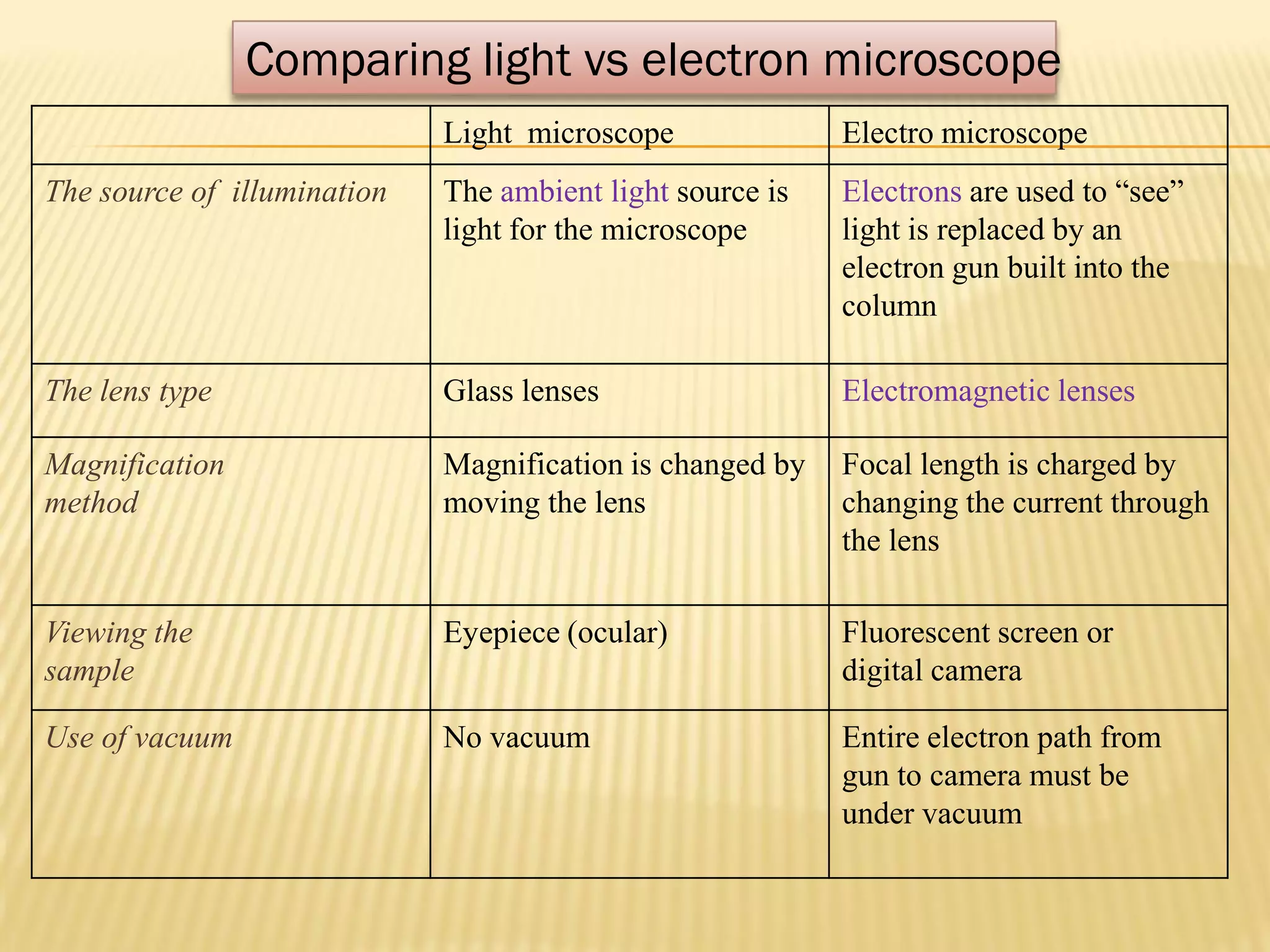
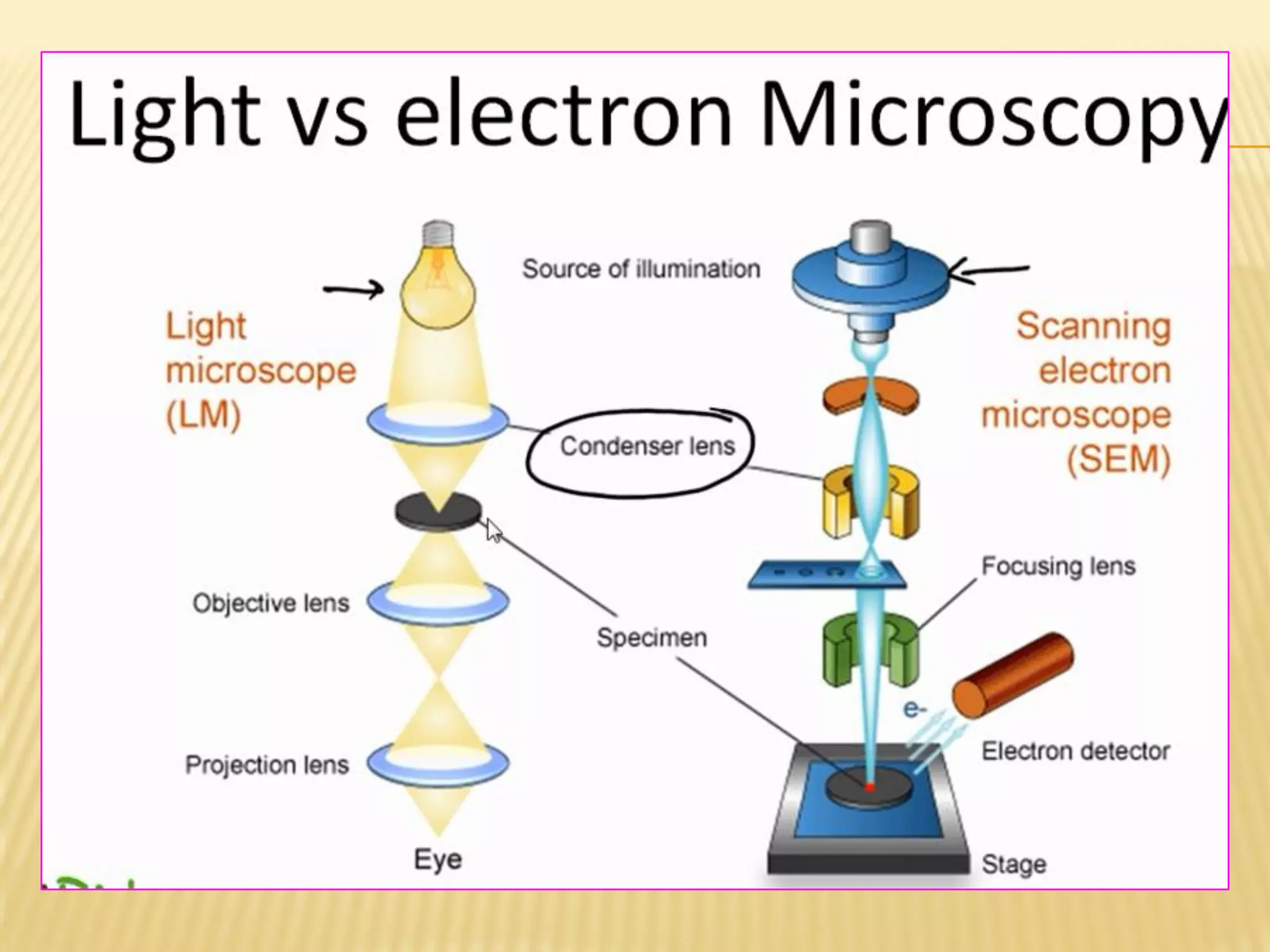
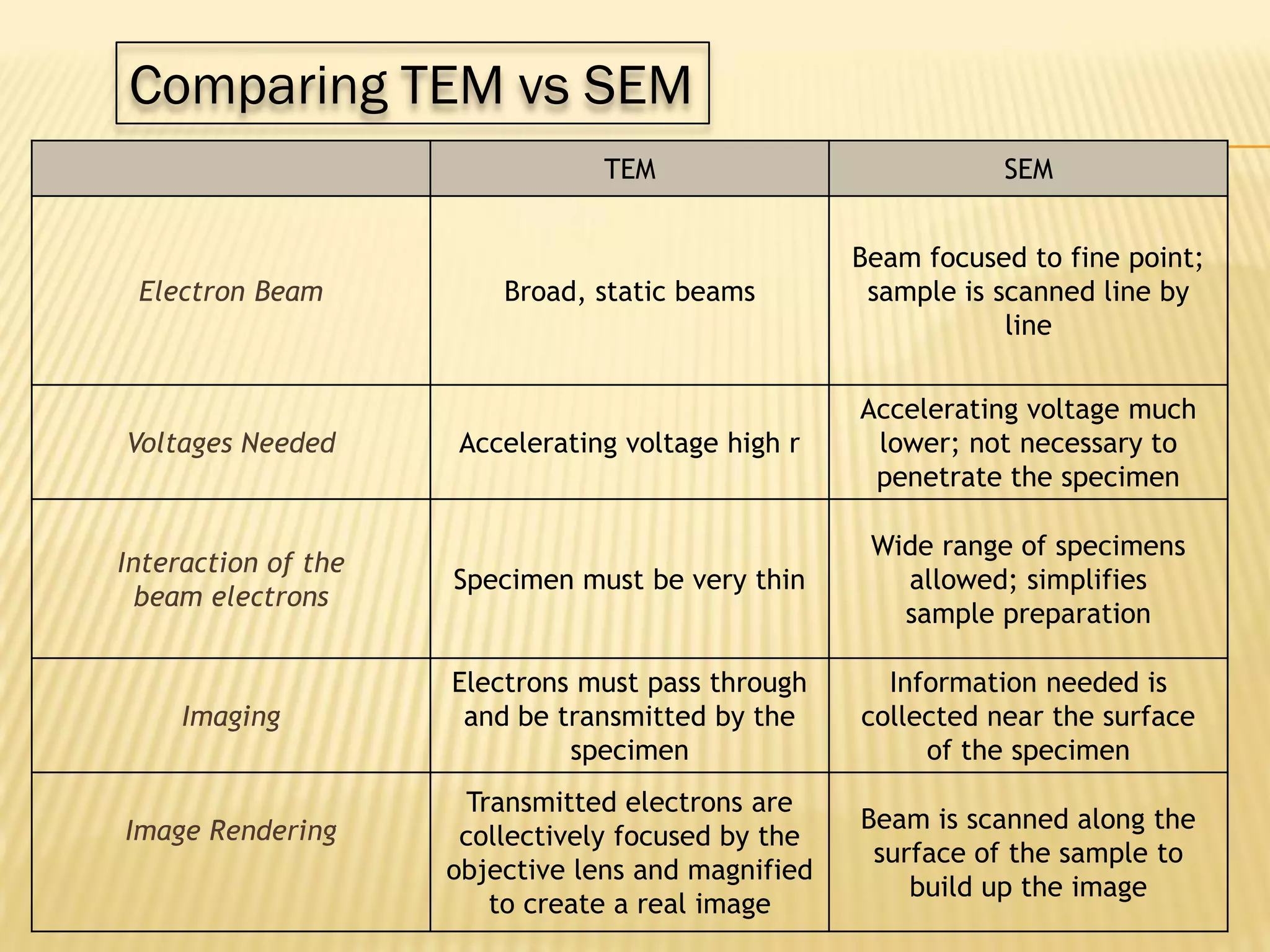
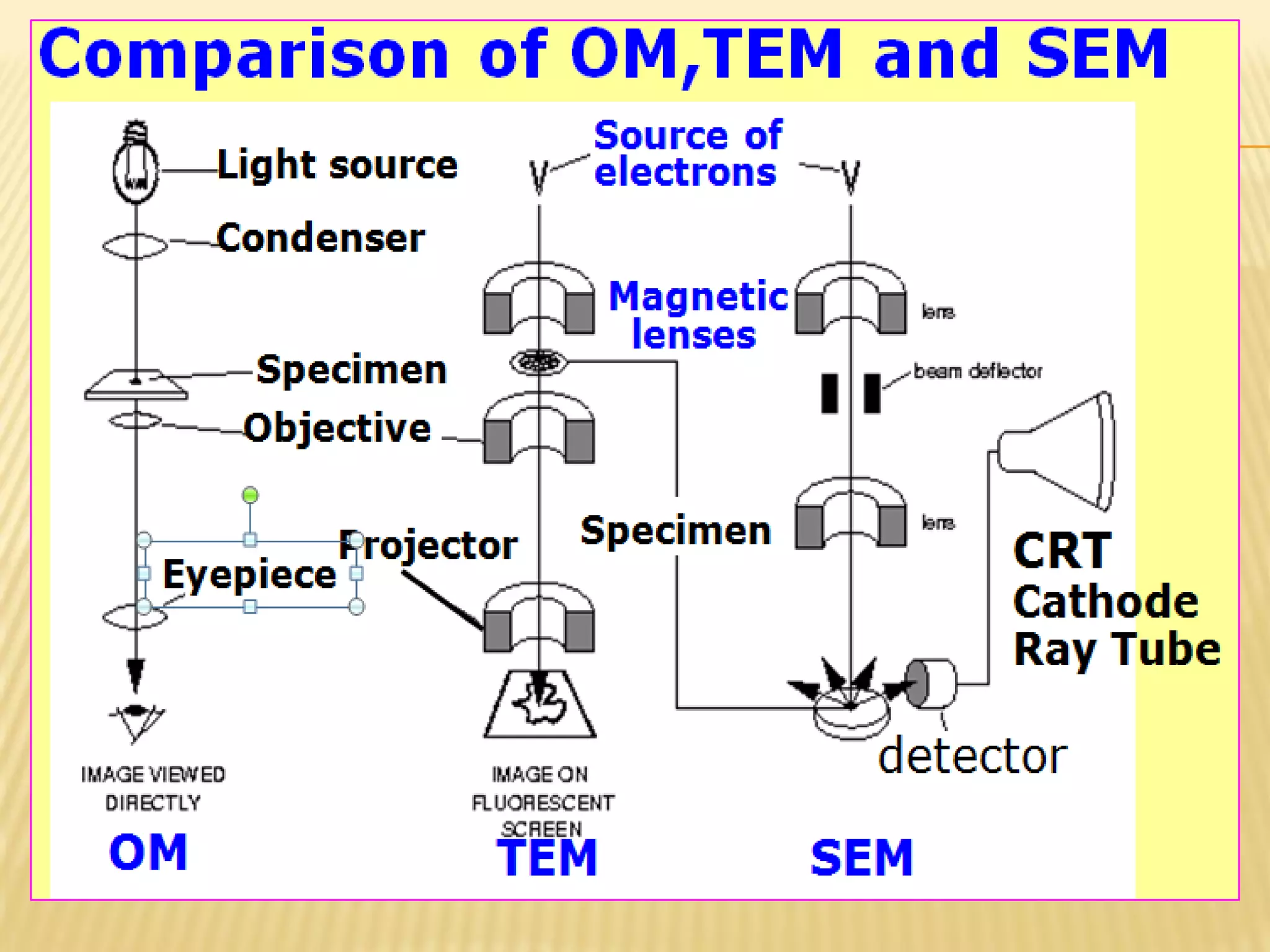
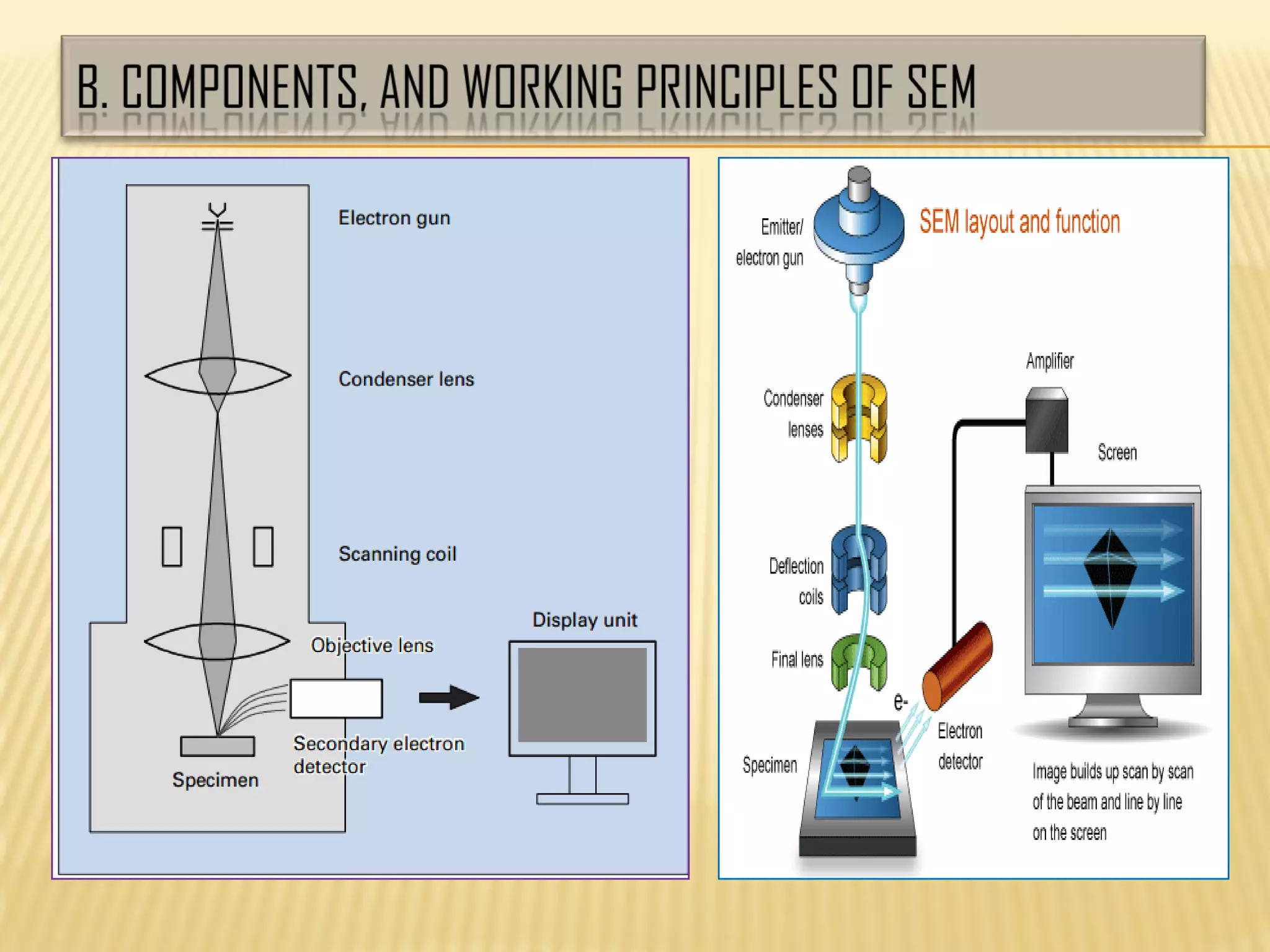
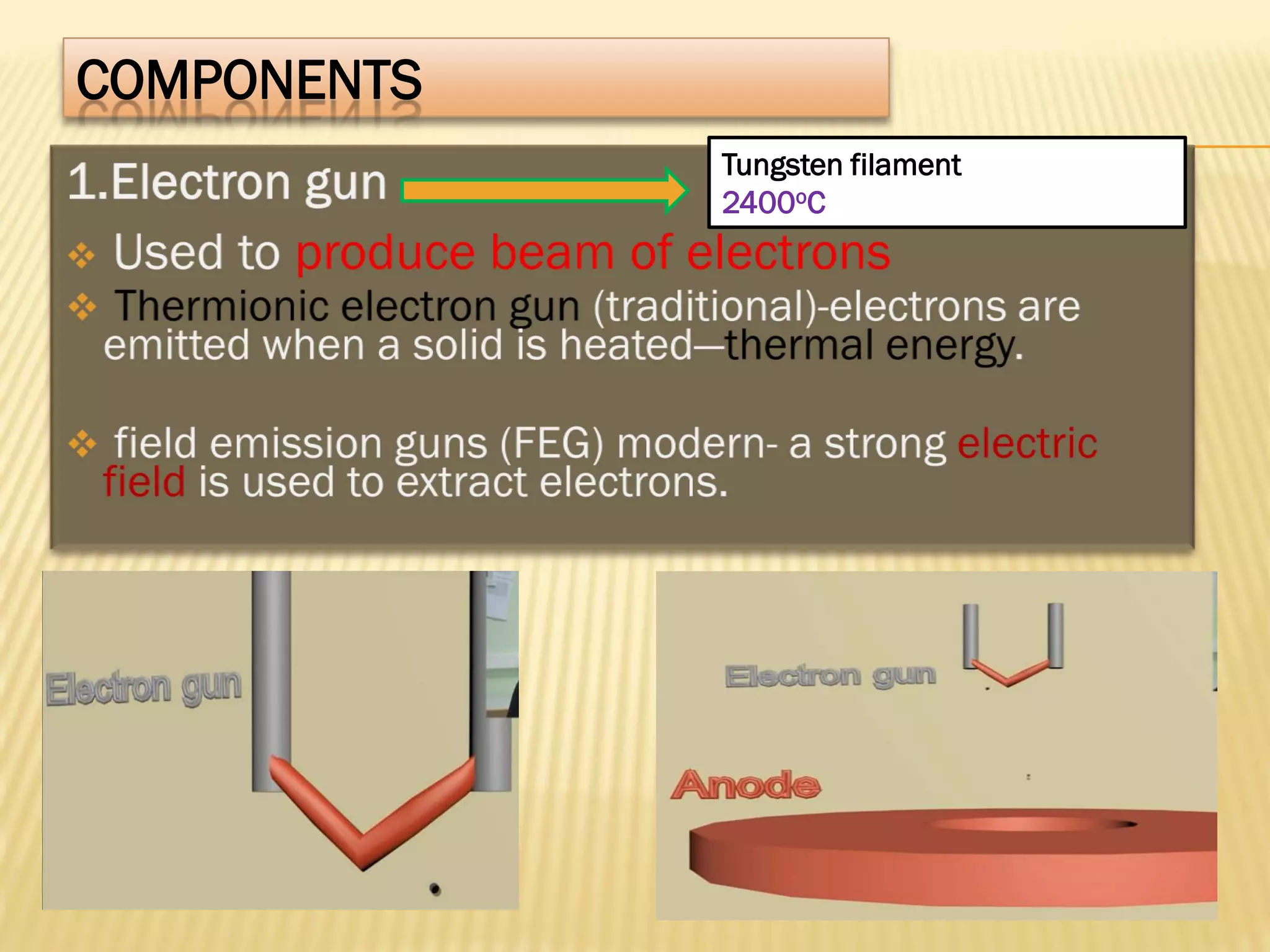
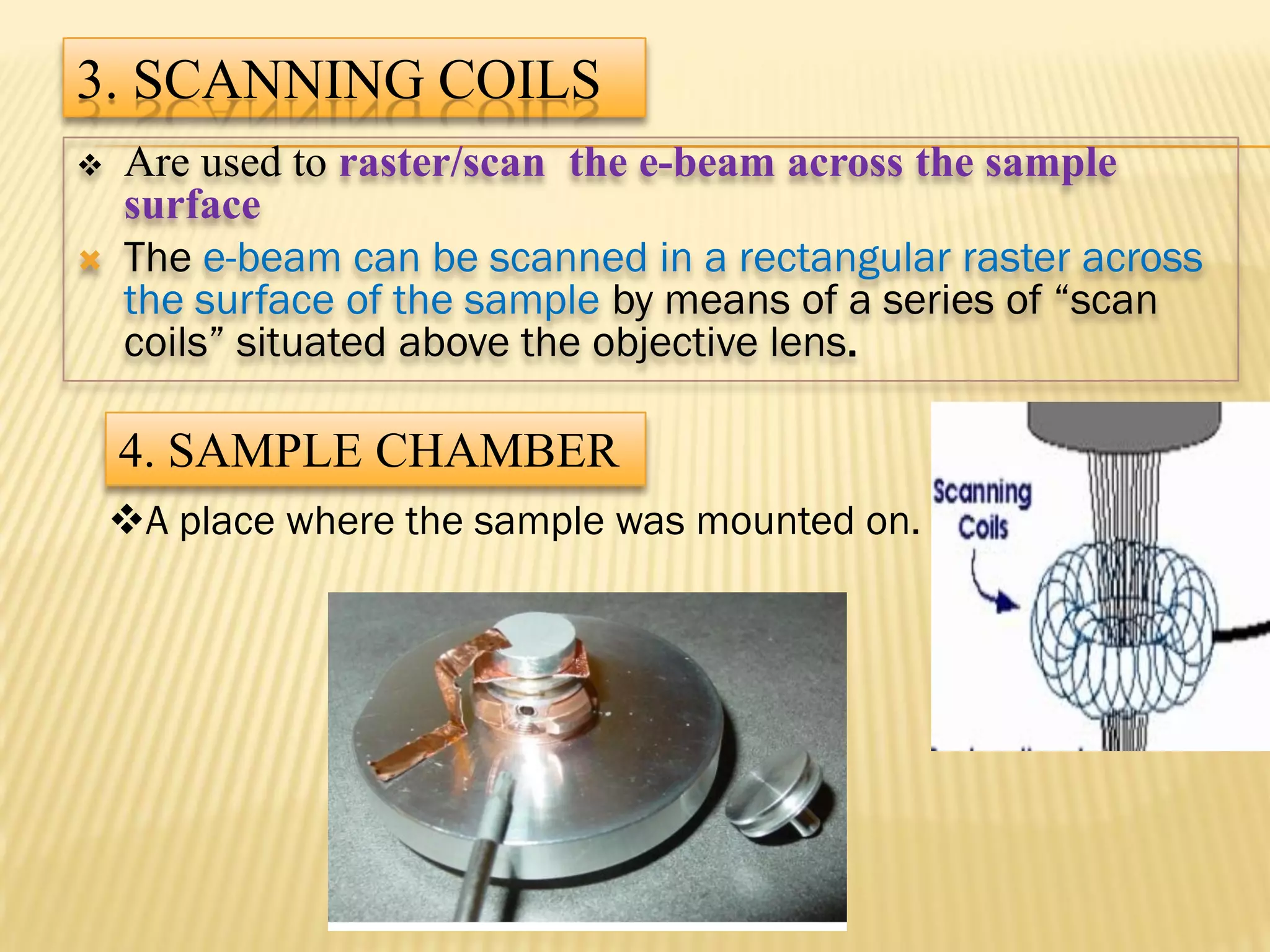
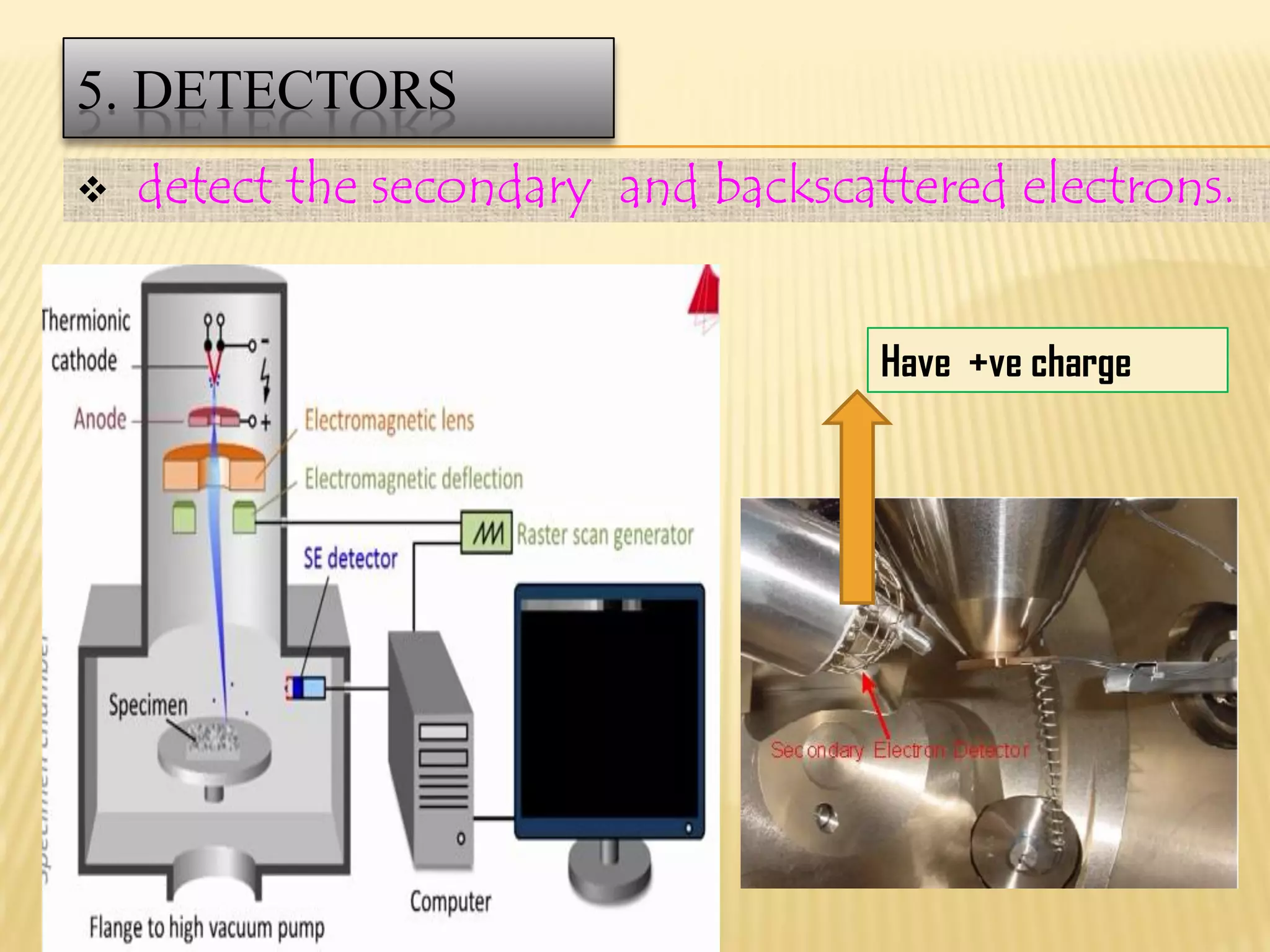
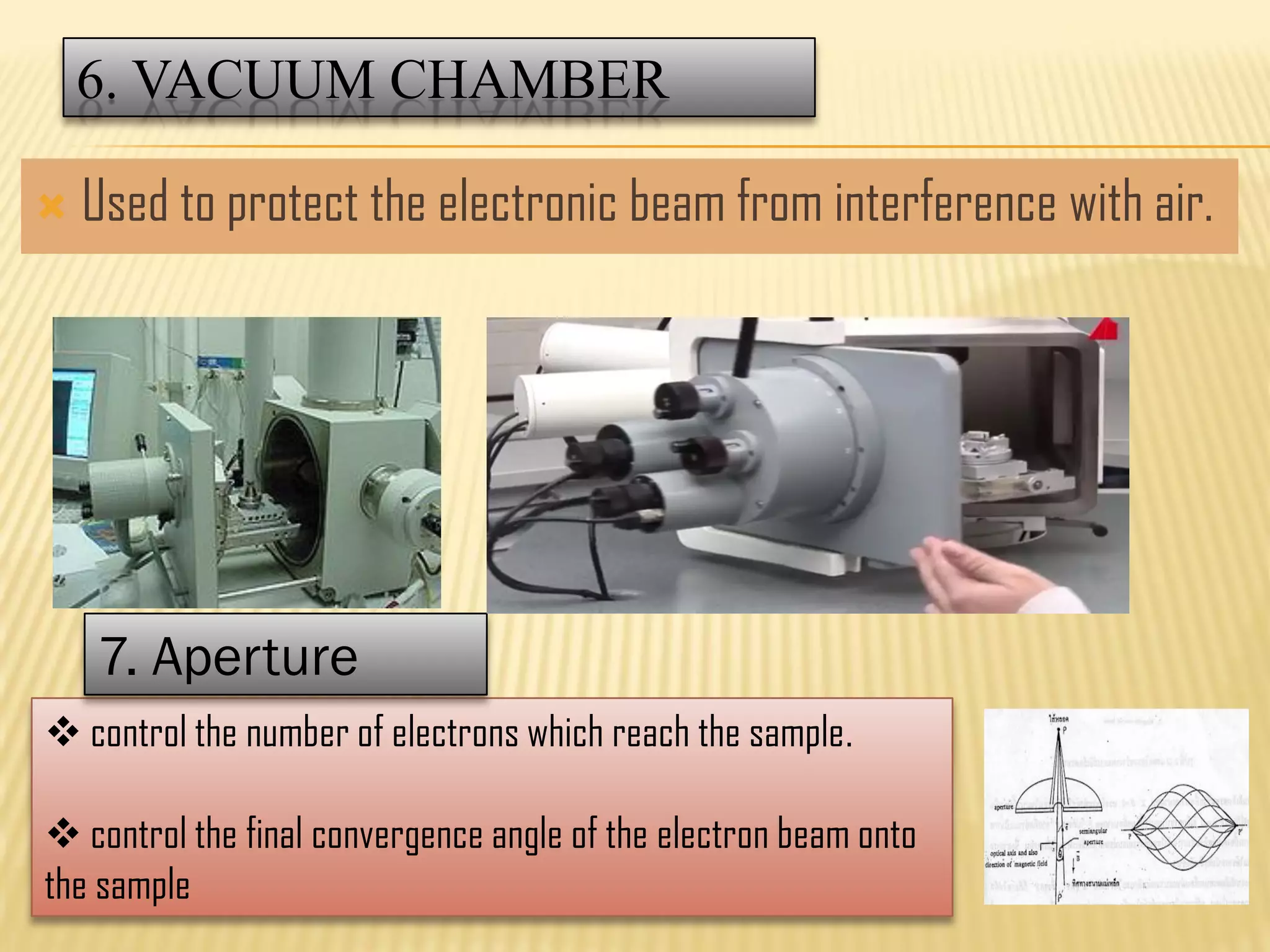
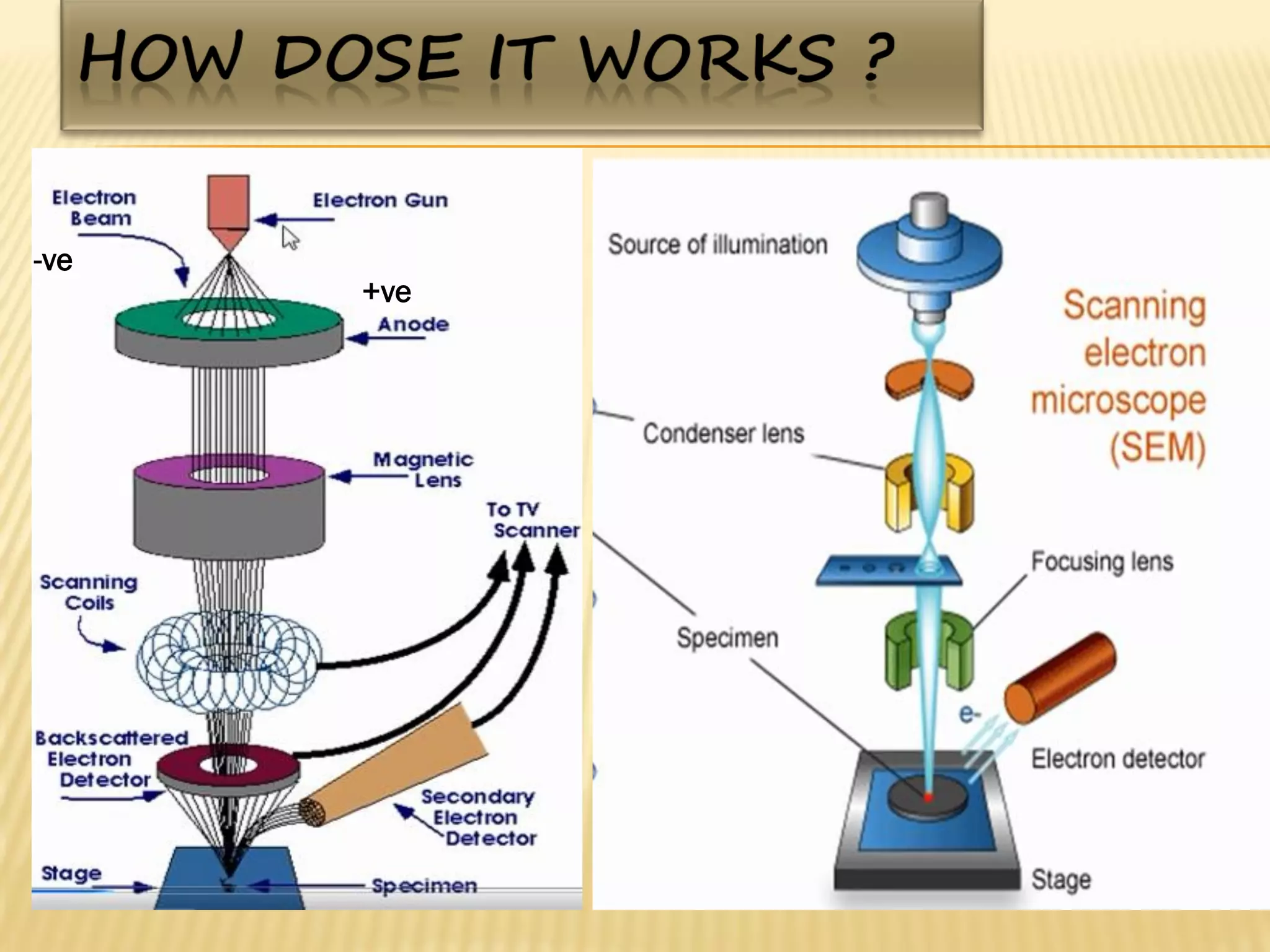
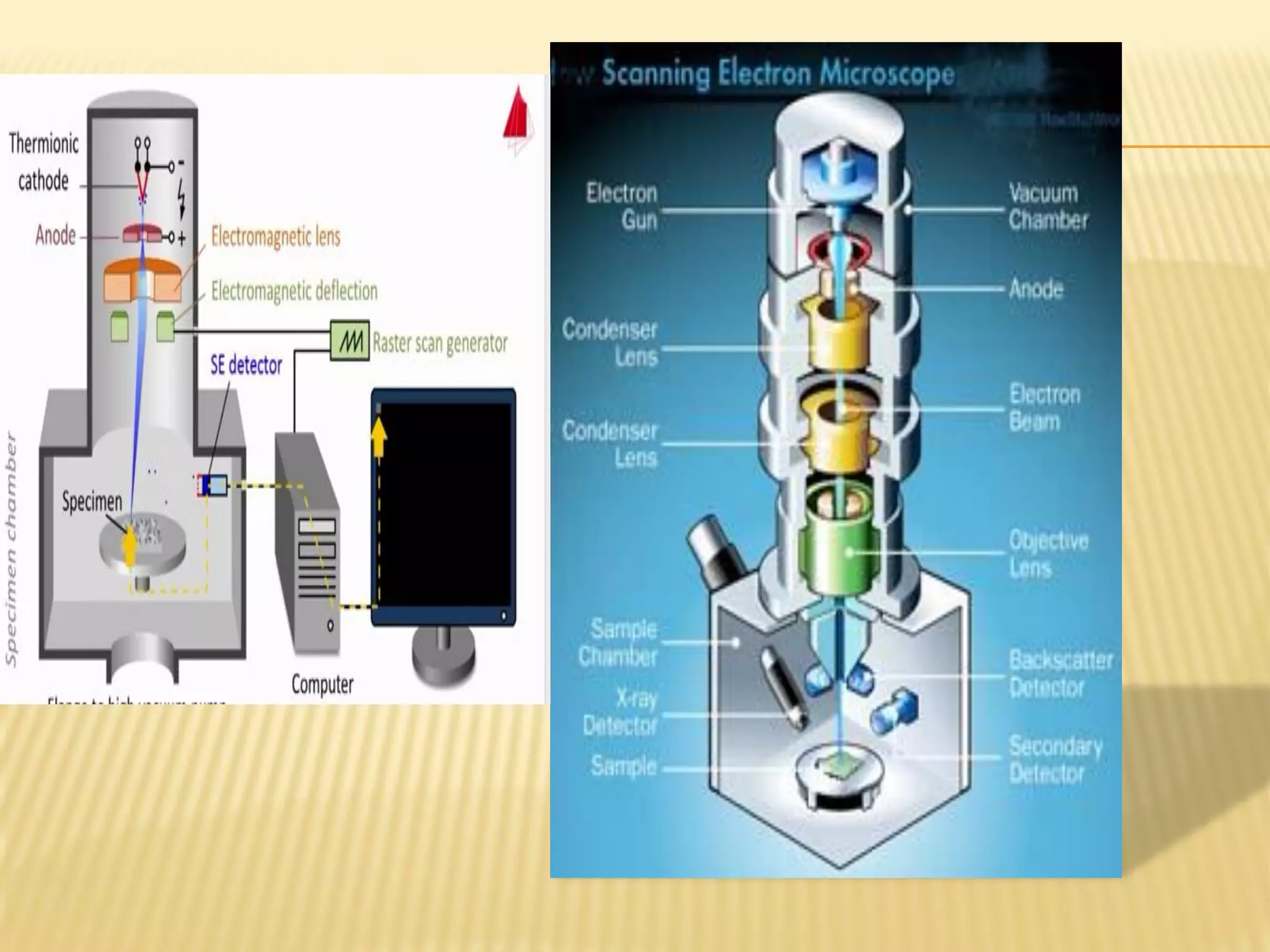
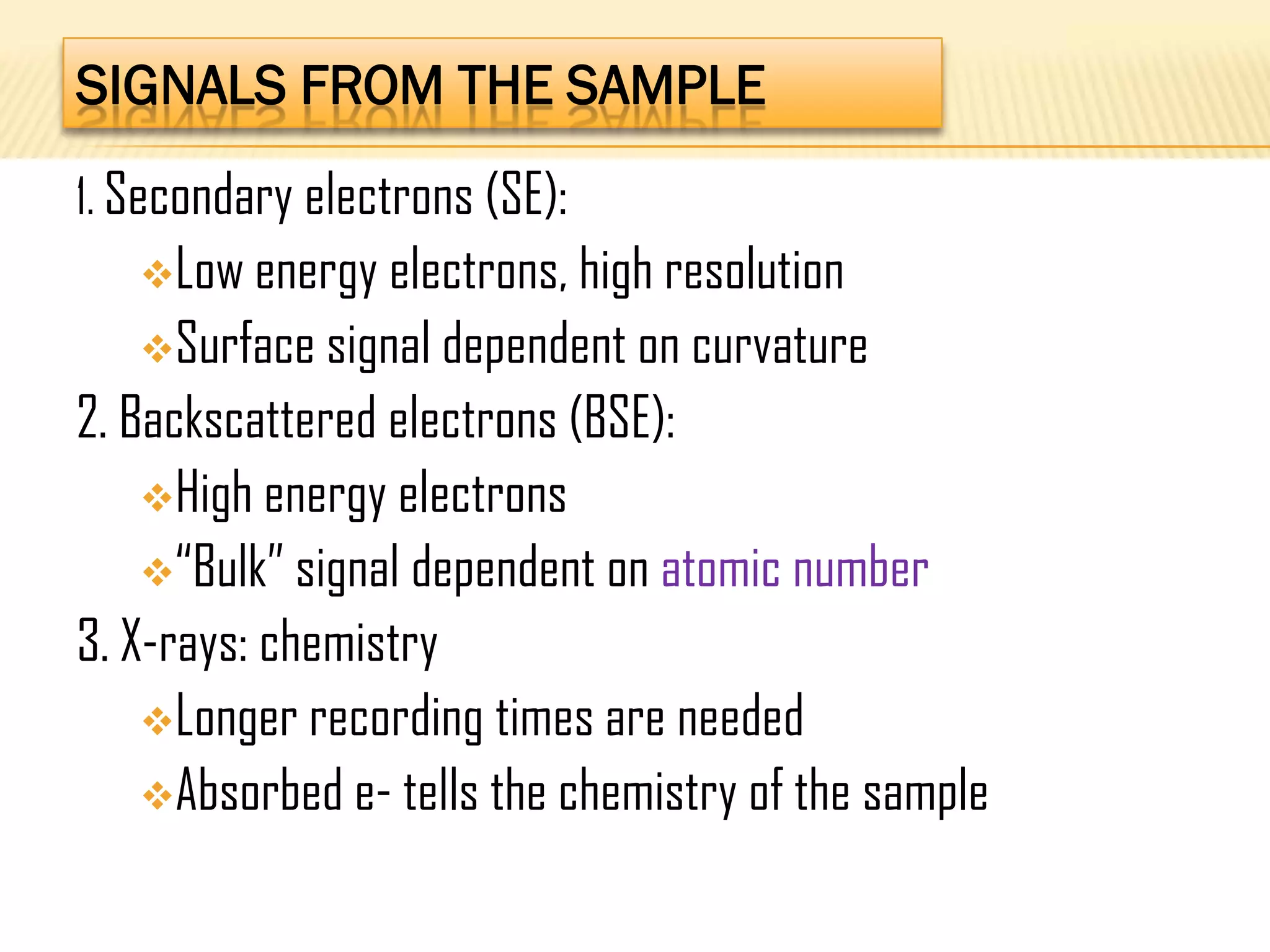
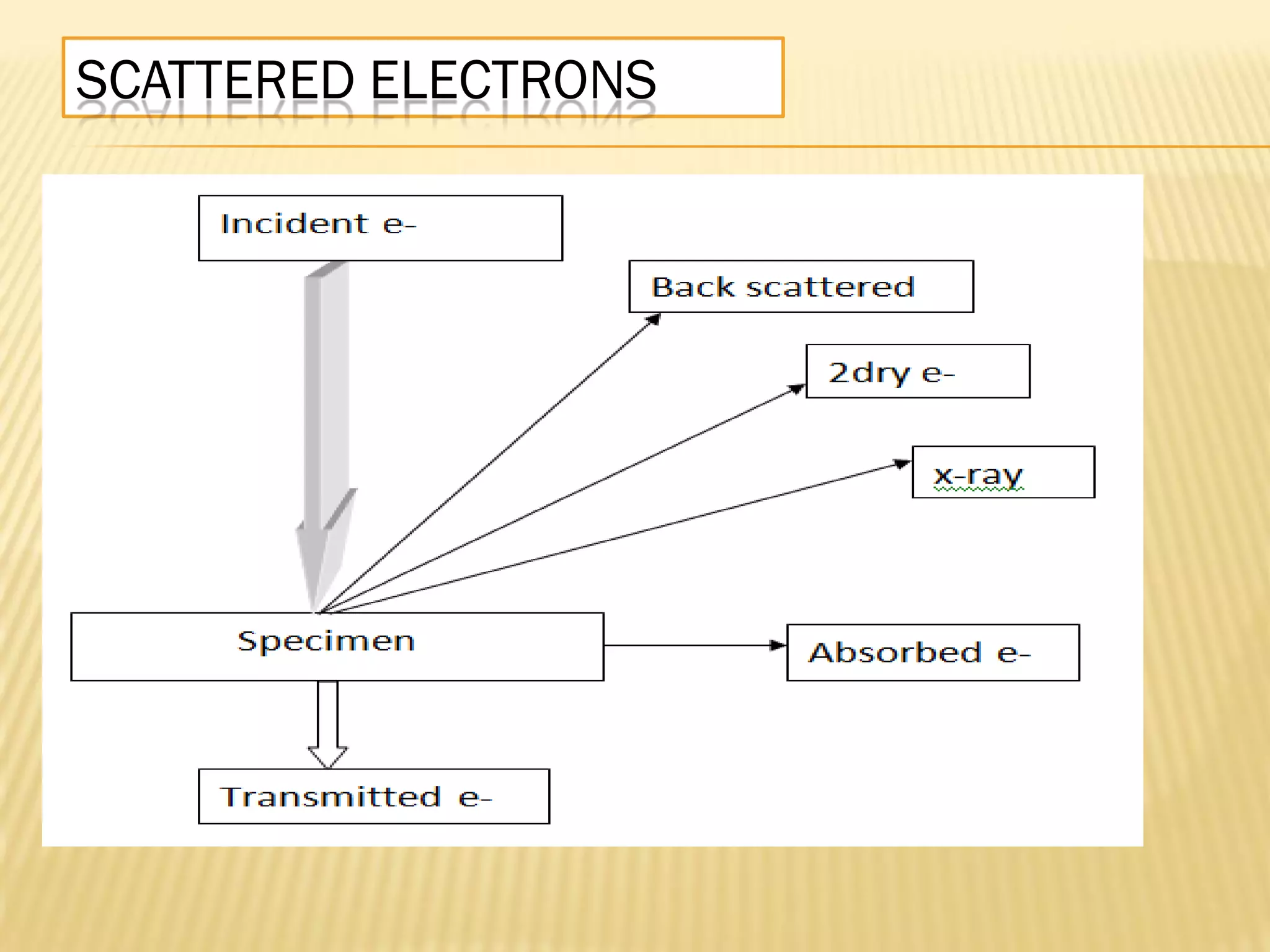
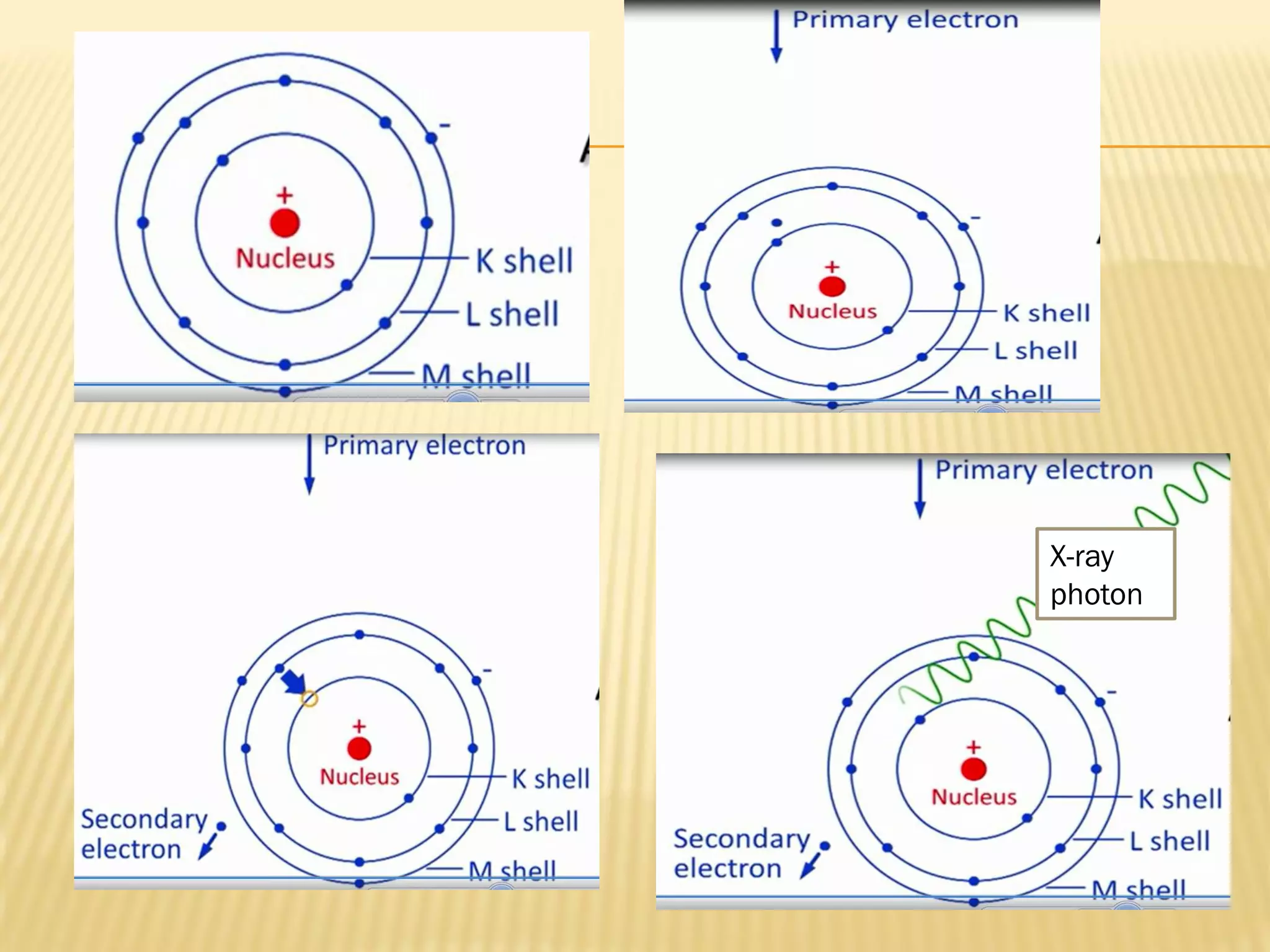
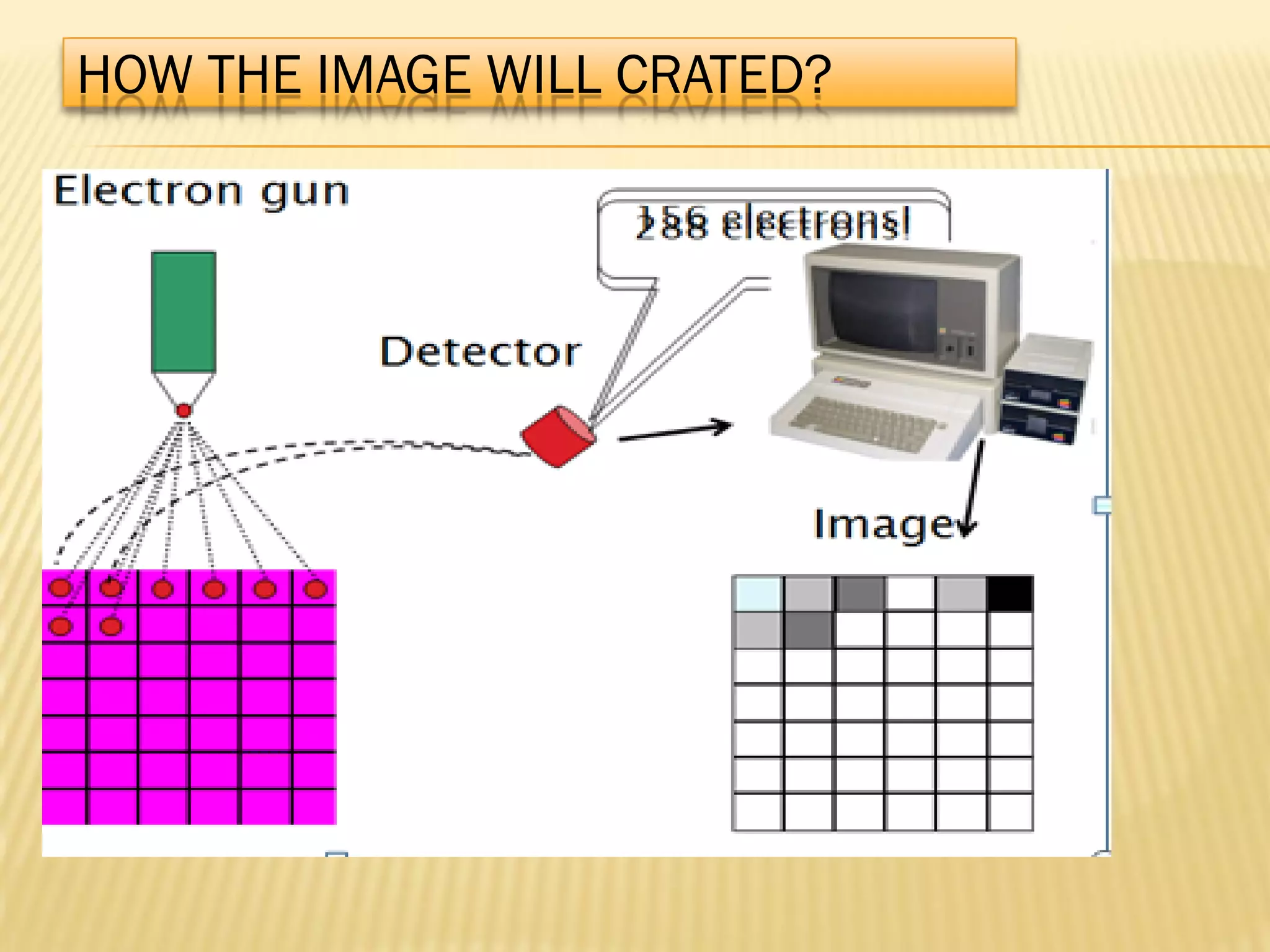
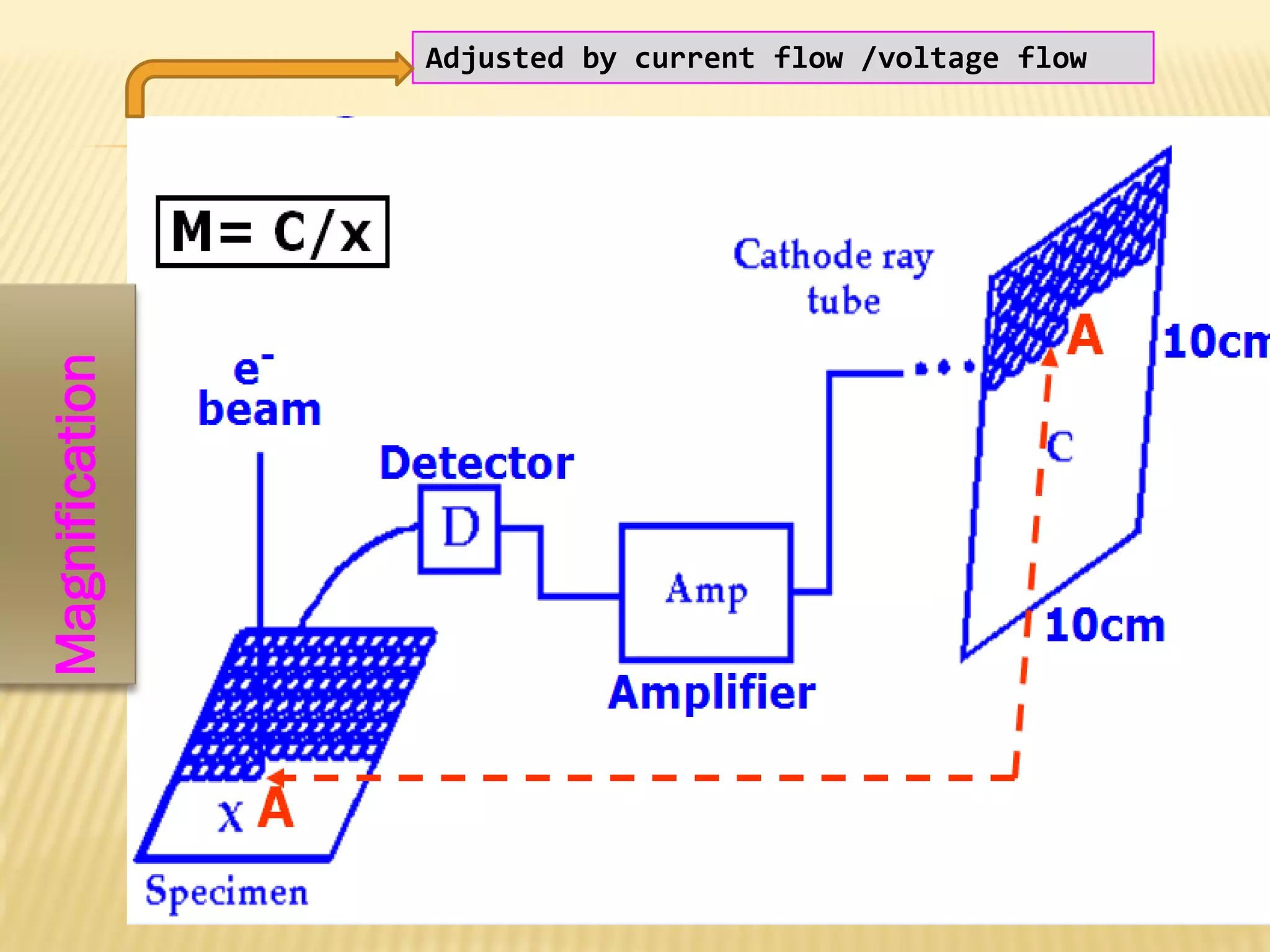
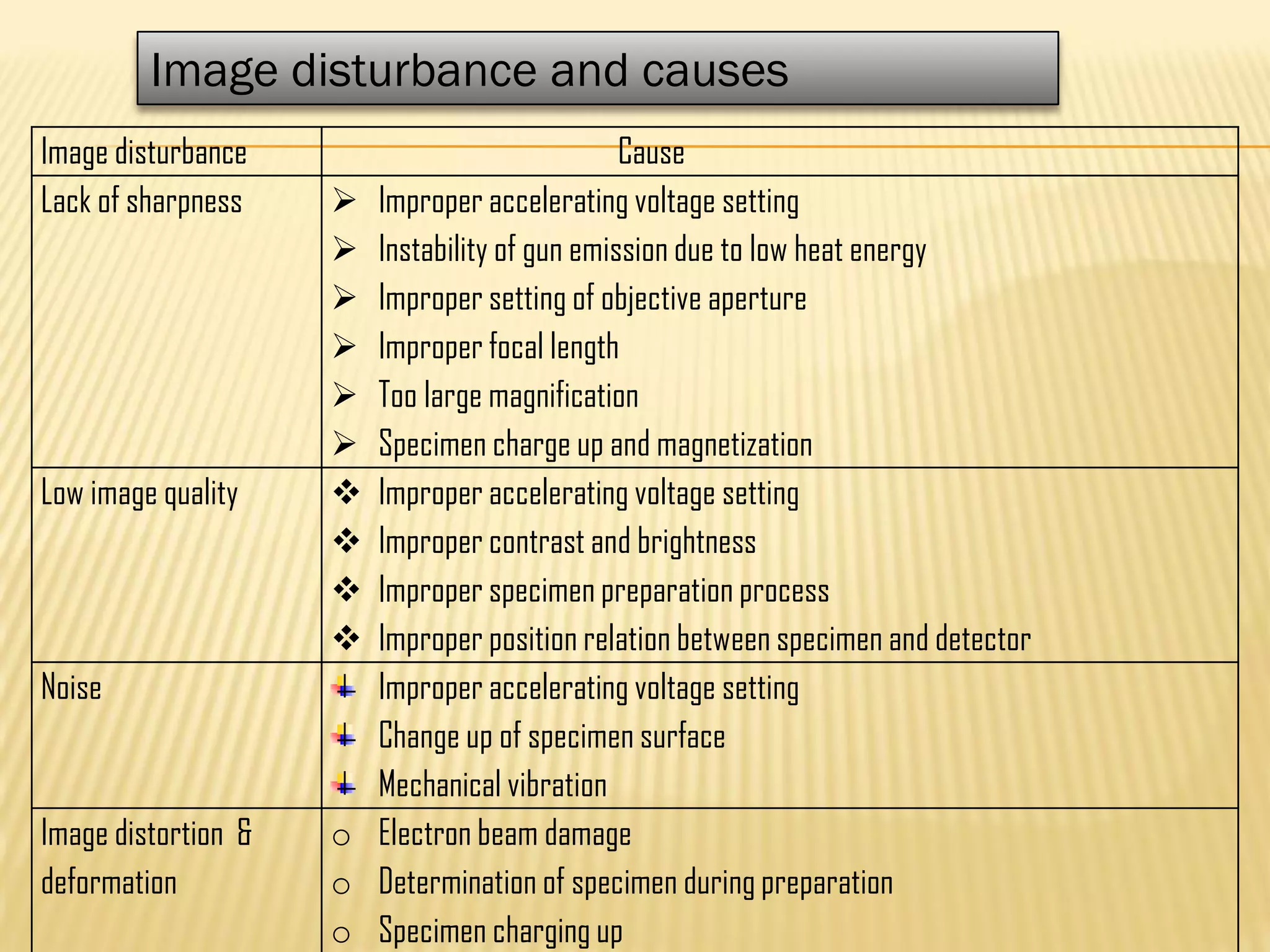
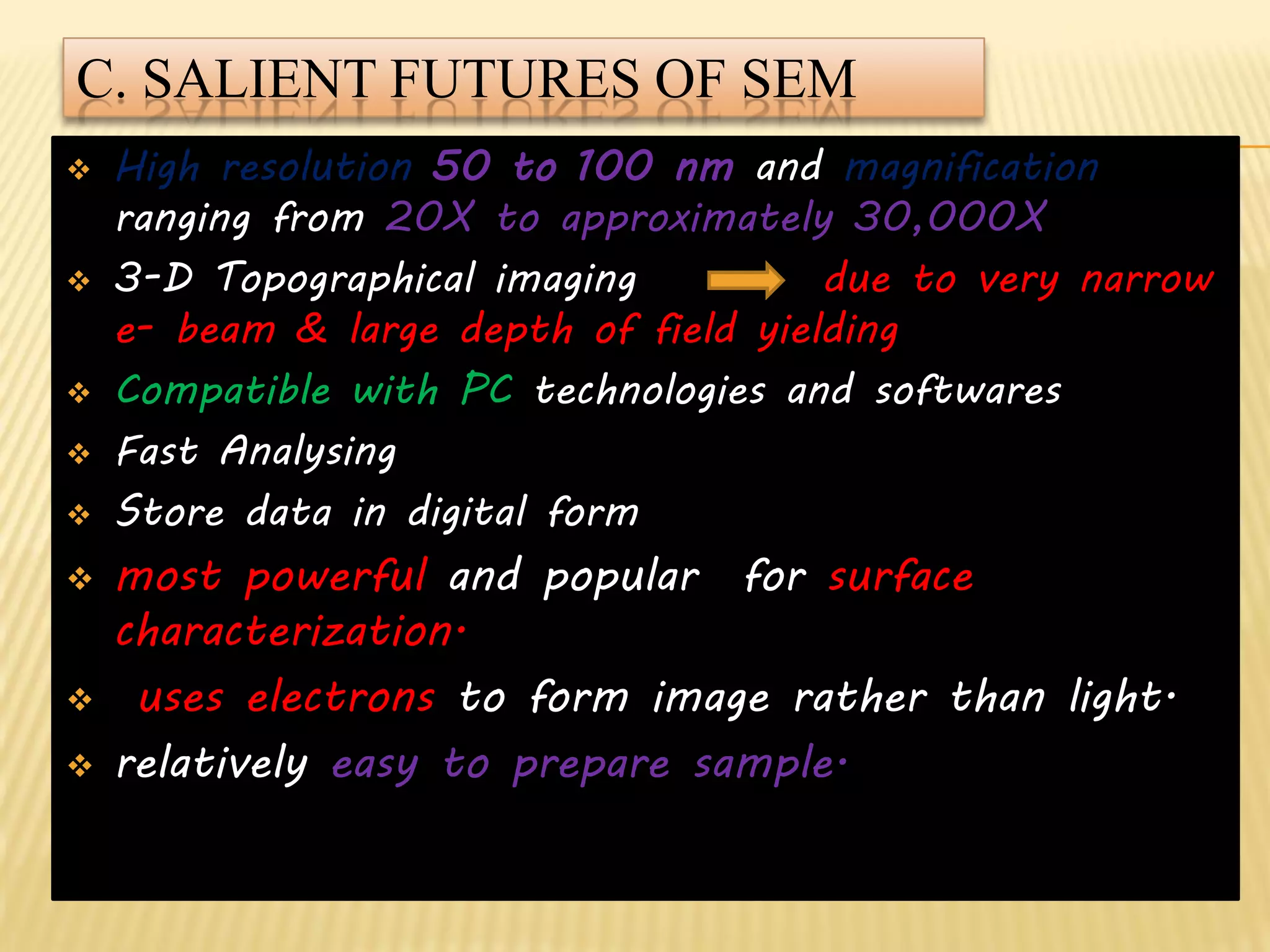
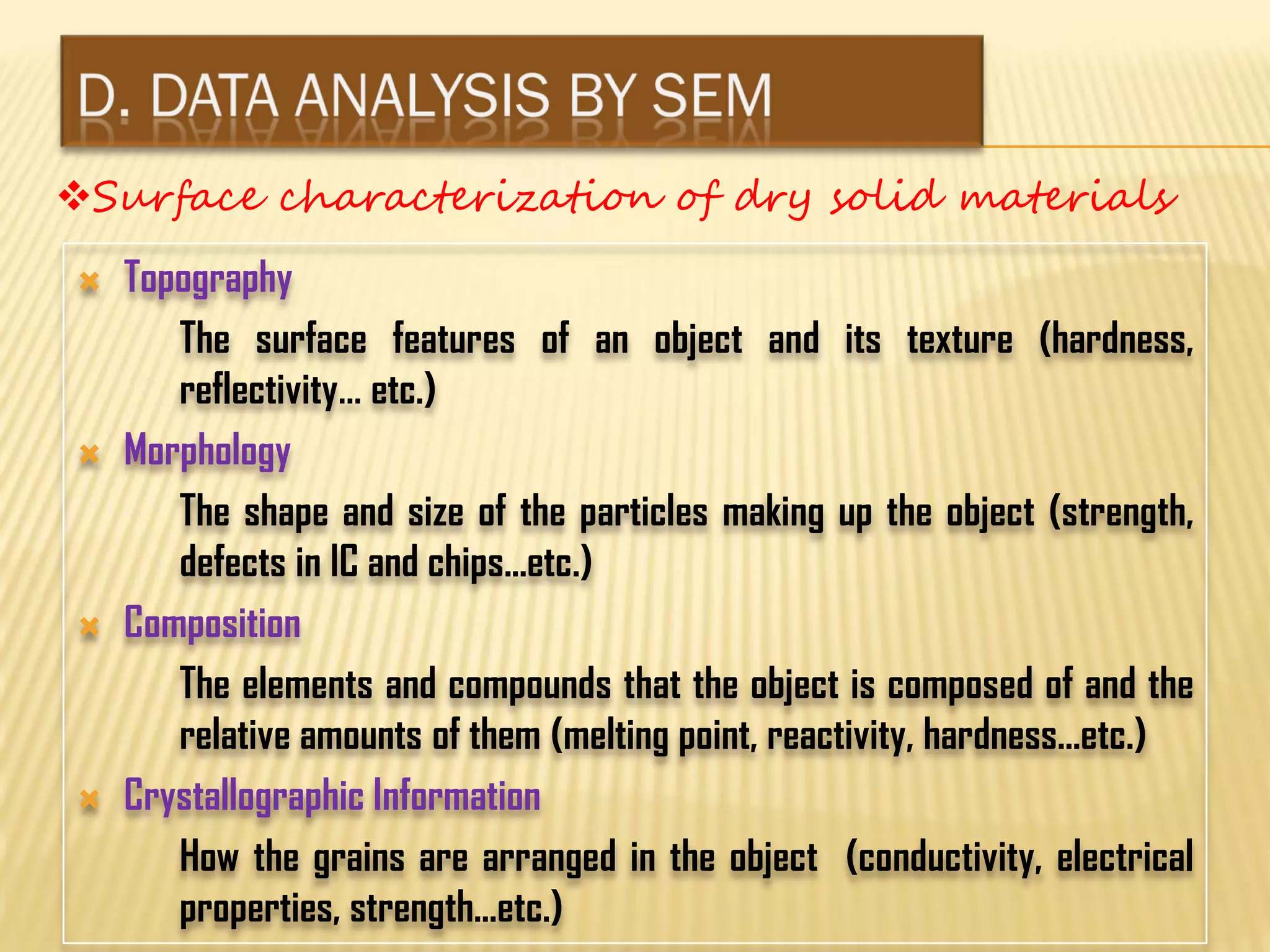
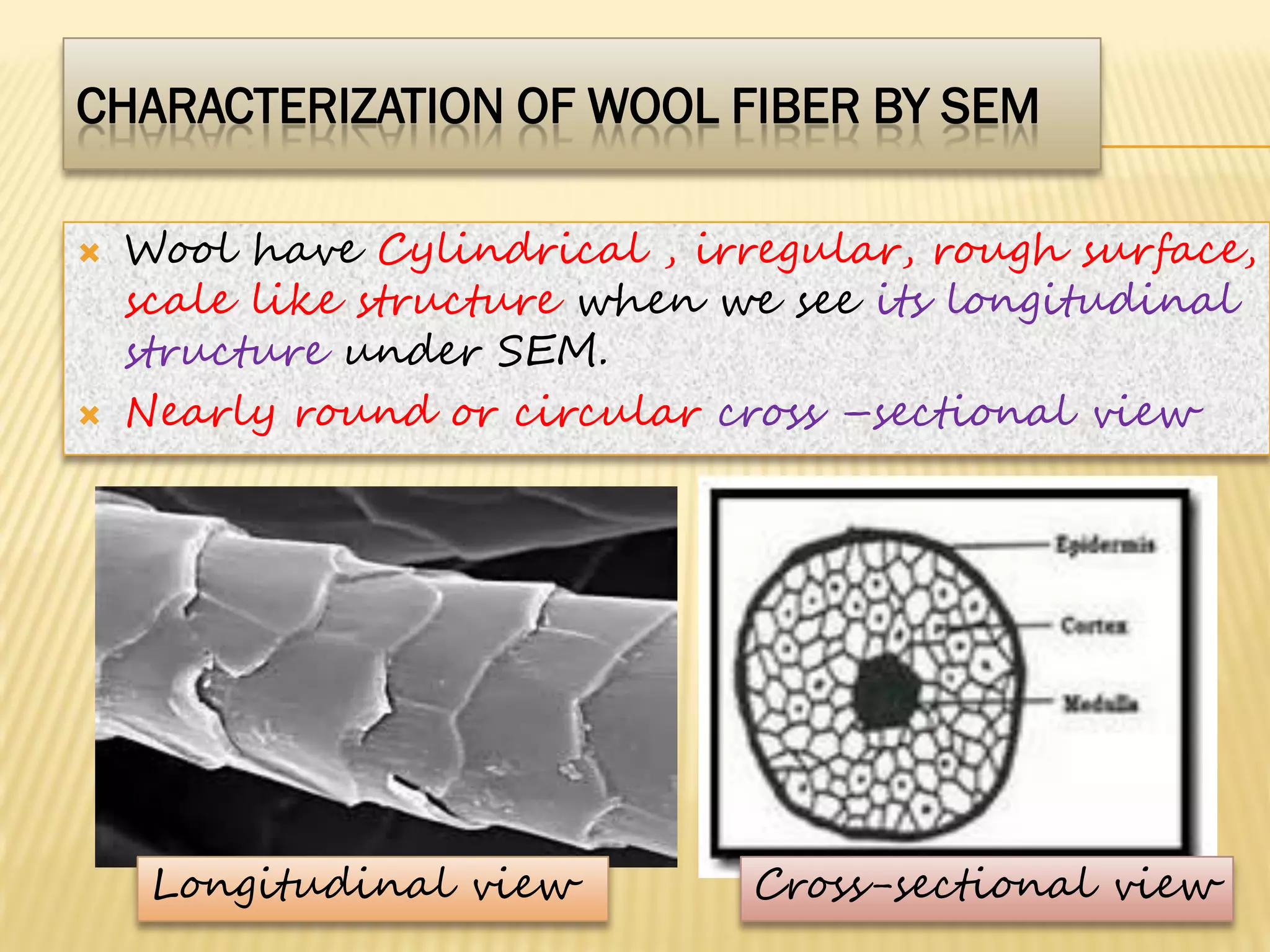
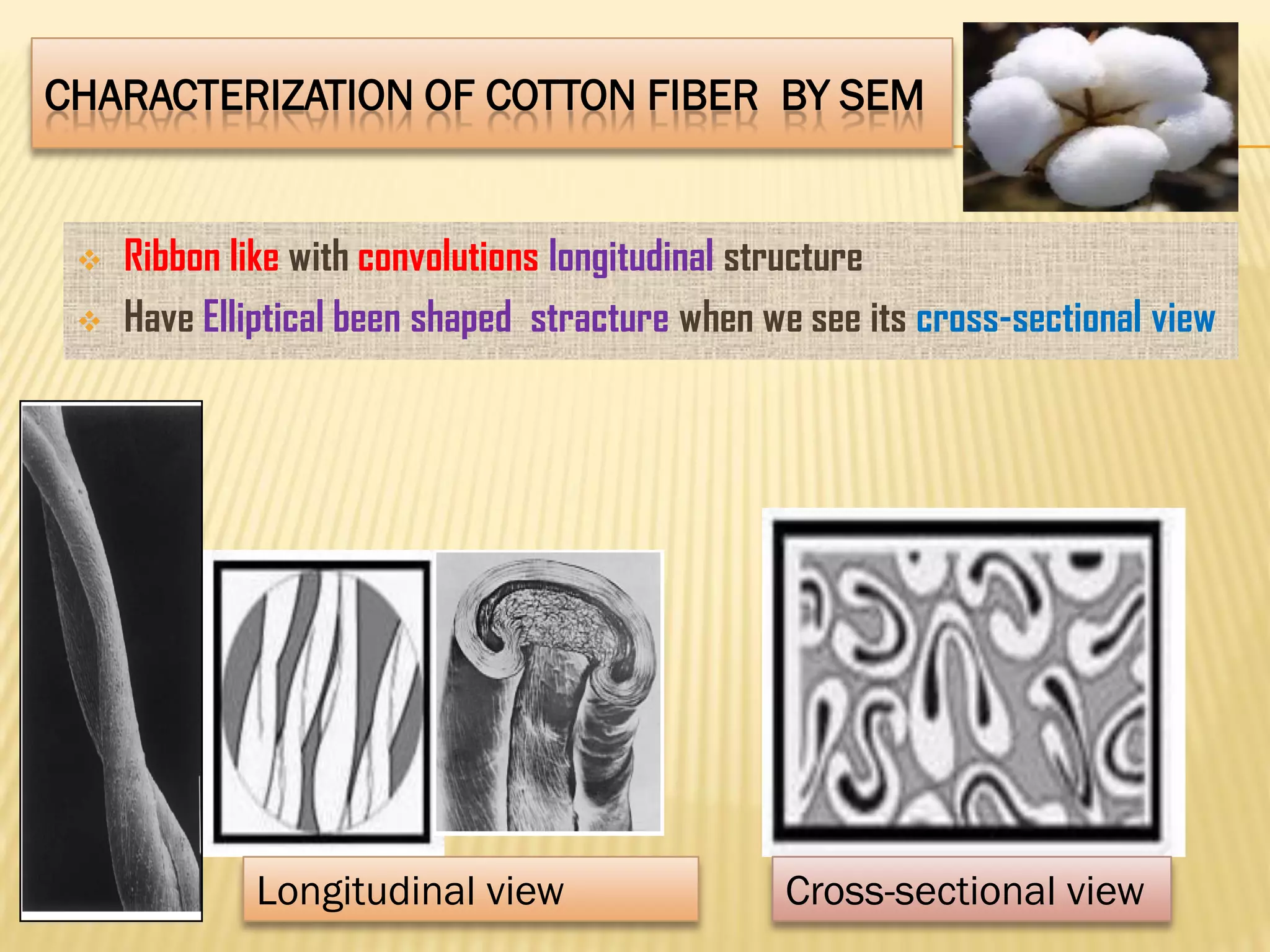
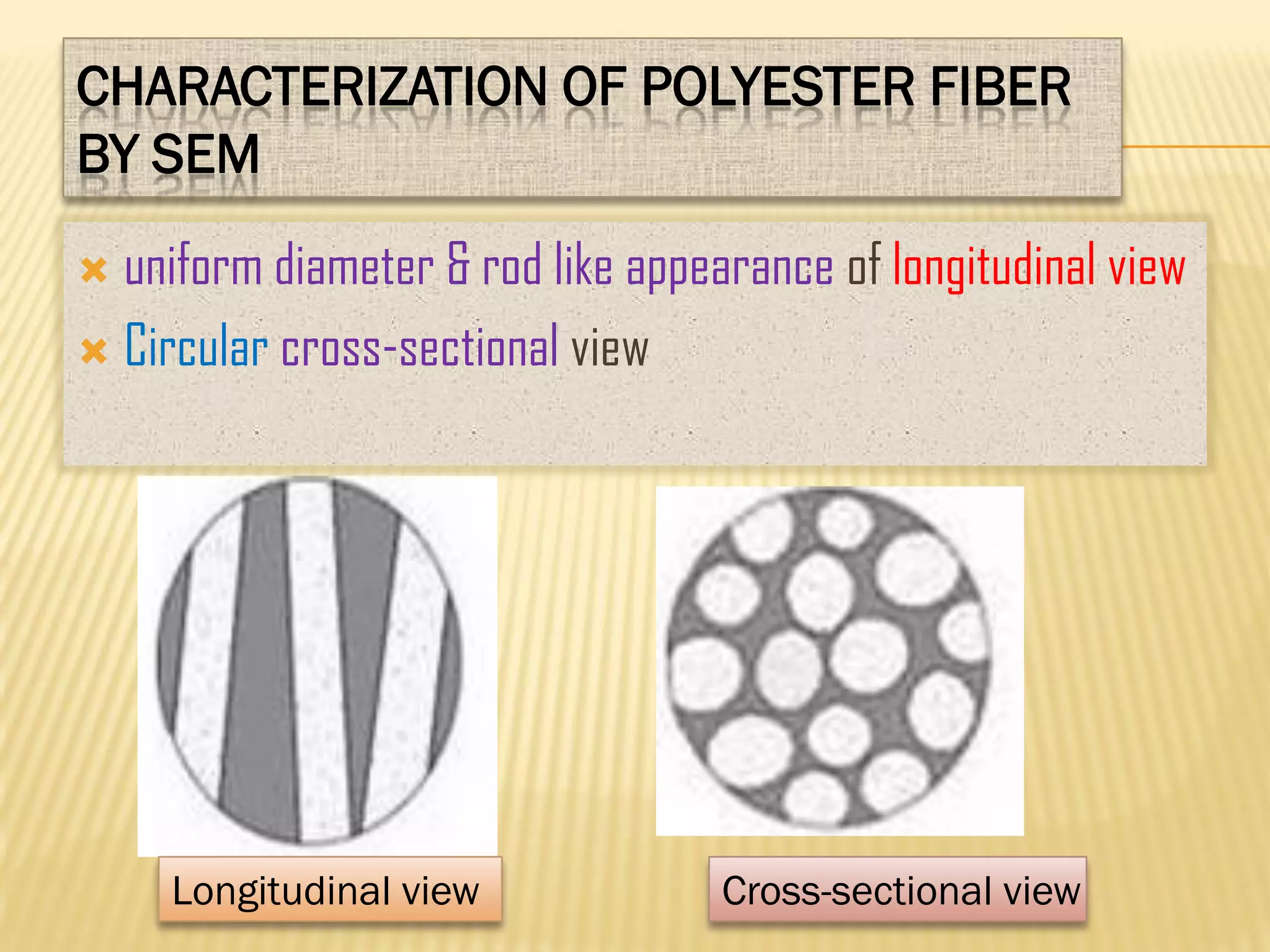
This document discusses the working principles of a scanning electron microscope (SEM) and its use for fiber characterization. It begins with an introduction to SEMs and their components. Key points made include that SEMs use electron beams rather than light to image samples and can achieve higher resolution than light microscopes. The document then covers SEM signals, image formation, resolution factors, sample preparation, and applications for characterizing fibers like wool, cotton and polyester. Limitations discussed include the sample size and need for vacuum and conductive coating. Overall, the document provides a high-level overview of SEM operation and its advantages for examining textile fiber structure and morphology.