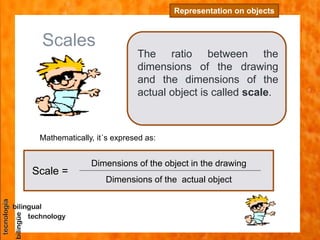
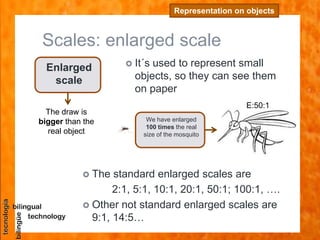
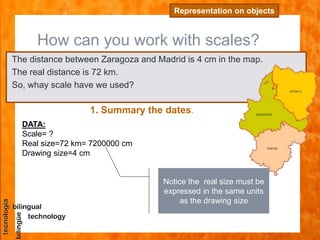
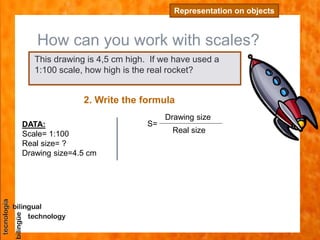
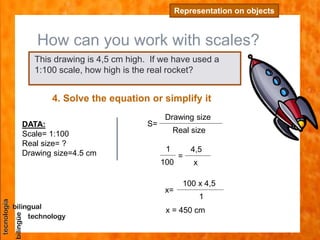
The document discusses scales used in technical drawings to represent objects that are too large or too small to draw at their actual dimensions. It defines scale as the ratio between the dimensions of an object in a drawing compared to the actual object. Different types of scales are used - reduced scales make drawings smaller, actual scales are the same size, and enlarged scales make drawings bigger. Examples are provided of calculating scales based on given dimensions. The key steps to working with scales are also outlined.