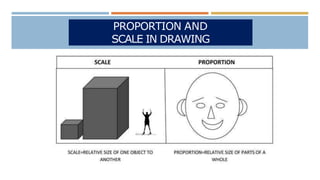
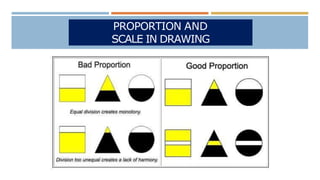
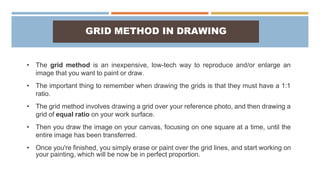
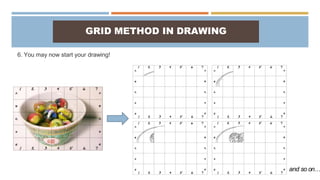
The document discusses proportion and scale in technical drawings. It defines proportion as the relative size of parts within an object or artwork, while scale refers to the size of objects in relation to one another. Examples of scales include 1:10, 1/4 in. = 1 ft., and 1-to-1. A scale drawing shows an object at an accurately reduced or enlarged size indicated by a ratio, such as 1:10. Commonly used scales are full-size, reduced, and enlarged. The grid method is also described as a way to transfer an image by drawing grids over the reference photo and drawing surface to maintain correct proportions.