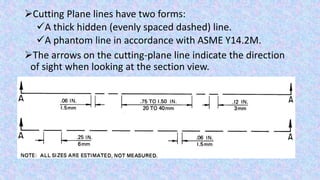
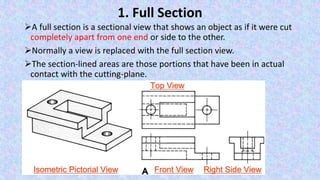
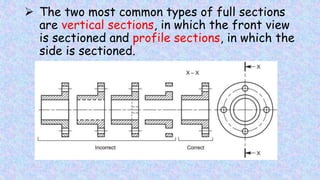
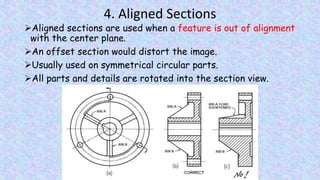
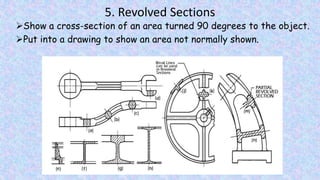
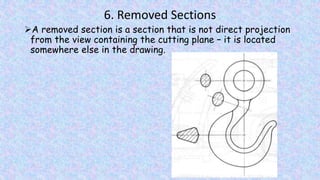
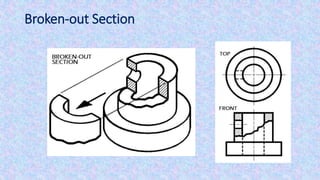
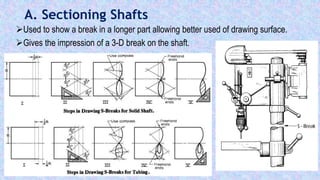
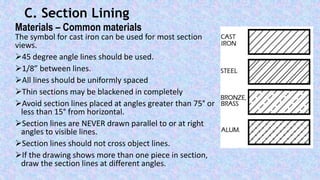
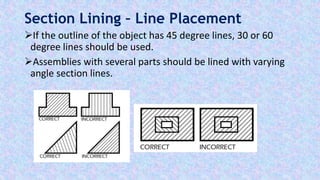
This document provides information on sectional views in engineering drawings. It defines what a sectional view is, how cutting planes work, and the different types of section views including full sections, half sections, offset sections, and broken-out sections. It also discusses guidelines for section lining techniques, including line placement, materials, and special cases for things like ribs, webs, and rotated features. The document aims to explain the principles and applications of section views in detailed technical drawings.