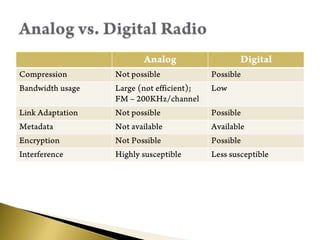
Satellite radio uses satellites and terrestrial repeaters to broadcast over 100 commercial-free music and talk channels across large areas. It provides CD quality audio to subscribers. Key points:
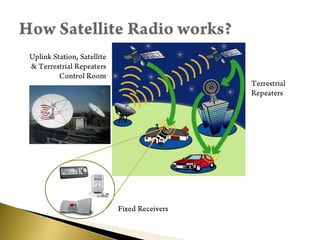
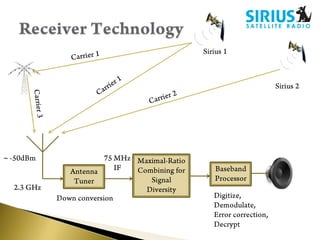
- Signals are transmitted digitally from uplink stations to satellites then to fixed or mobile receivers.
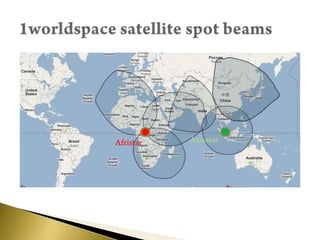
- Coverage is provided by multiple satellites using spot beams. Signals are amplified and retransmitted by the satellites.
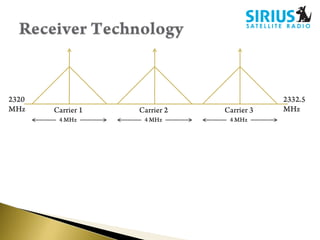
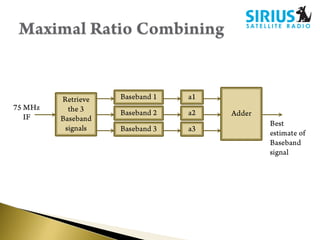
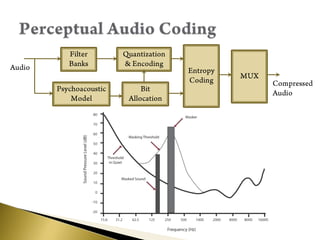
- Receivers use techniques like maximal ratio combining on multiple satellite signals for better reception. Audio is compressed using perceptual coding before transmission.
- Content is protected using encryption and conditional access restricts signals to legitimate subscribers.
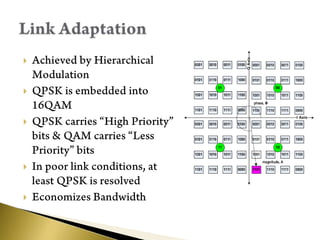
- While offering unique features, satellite radio faces challenges from competition and high subscription/receiver costs