The document provides an overview of SAP solutions, including:
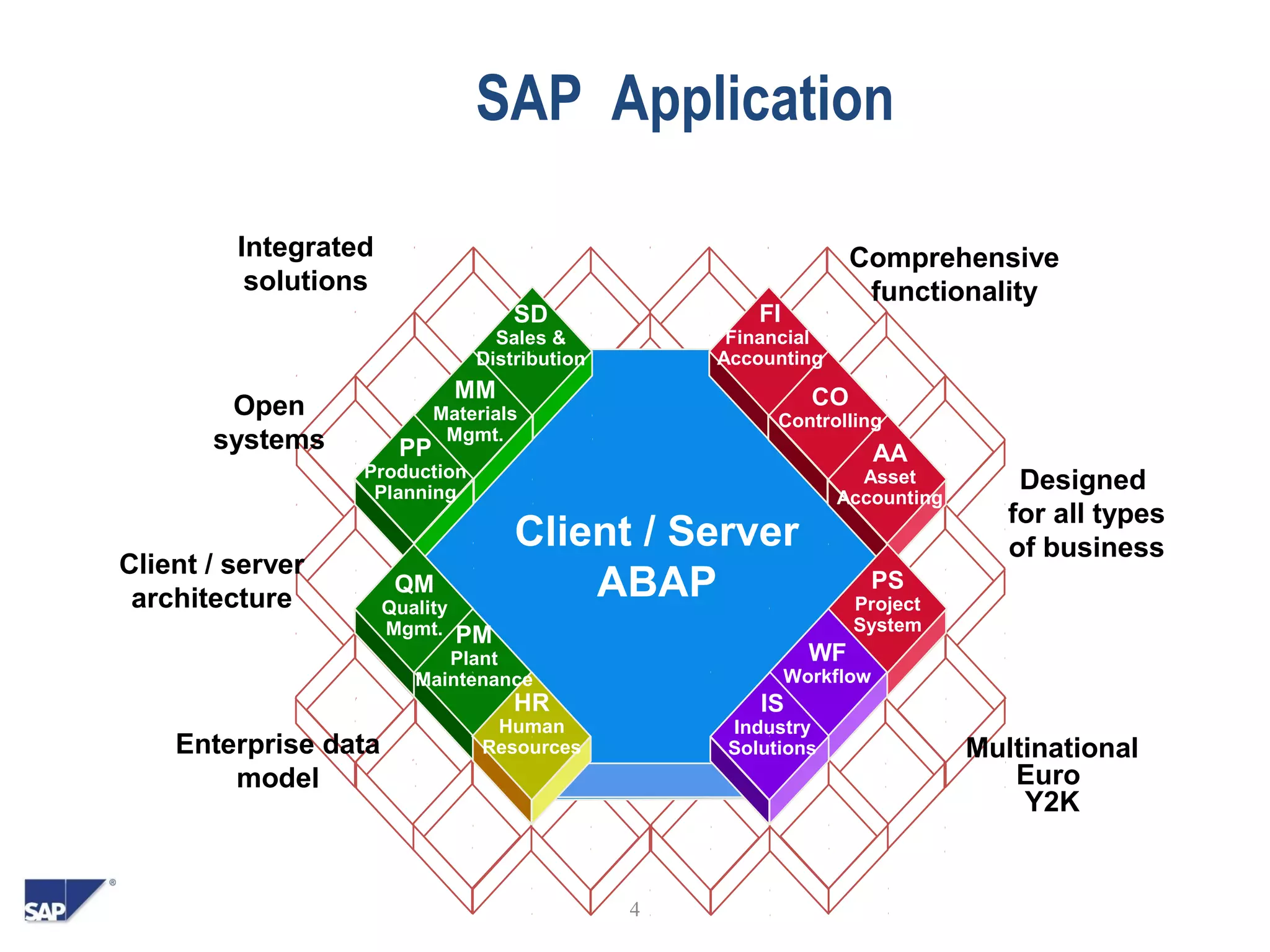
- SAP is an ERP software package used by many large companies worldwide to integrate business processes.
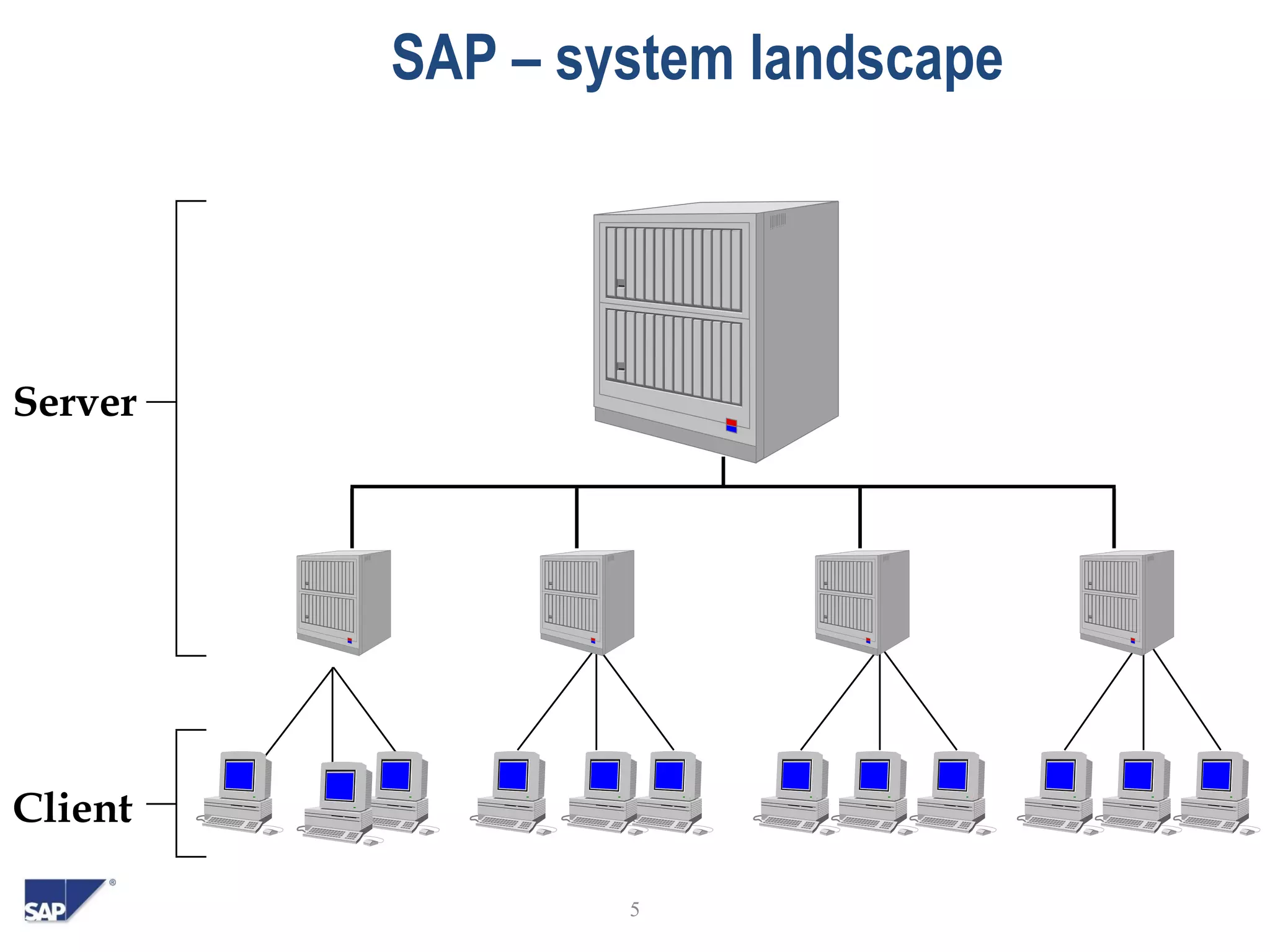
- It uses a client/server model and includes modules for finance, human resources, sales, procurement and other functions.
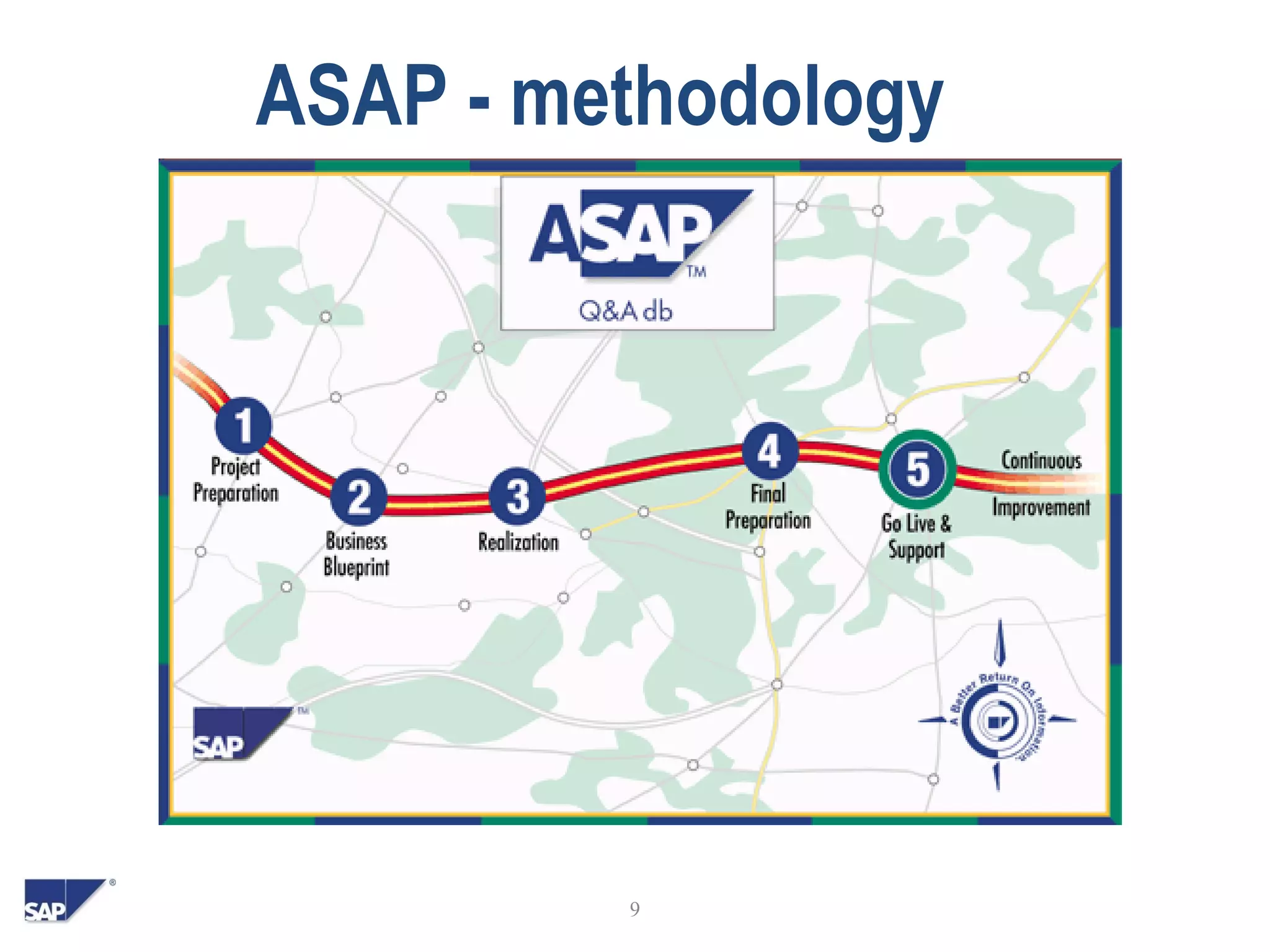
- The overview discusses SAP's system landscape, business benefits, and ASAP methodology for implementation projects.
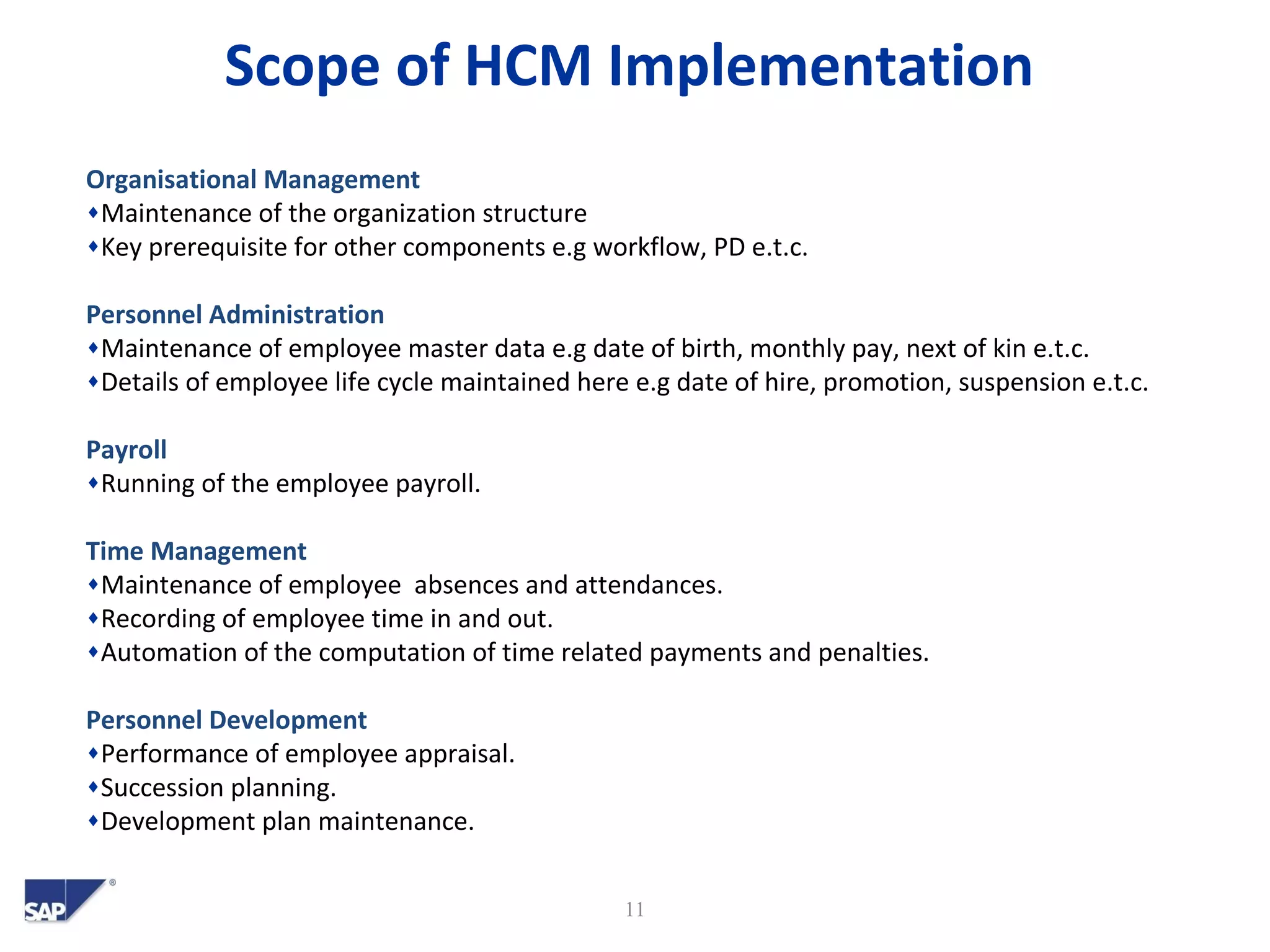
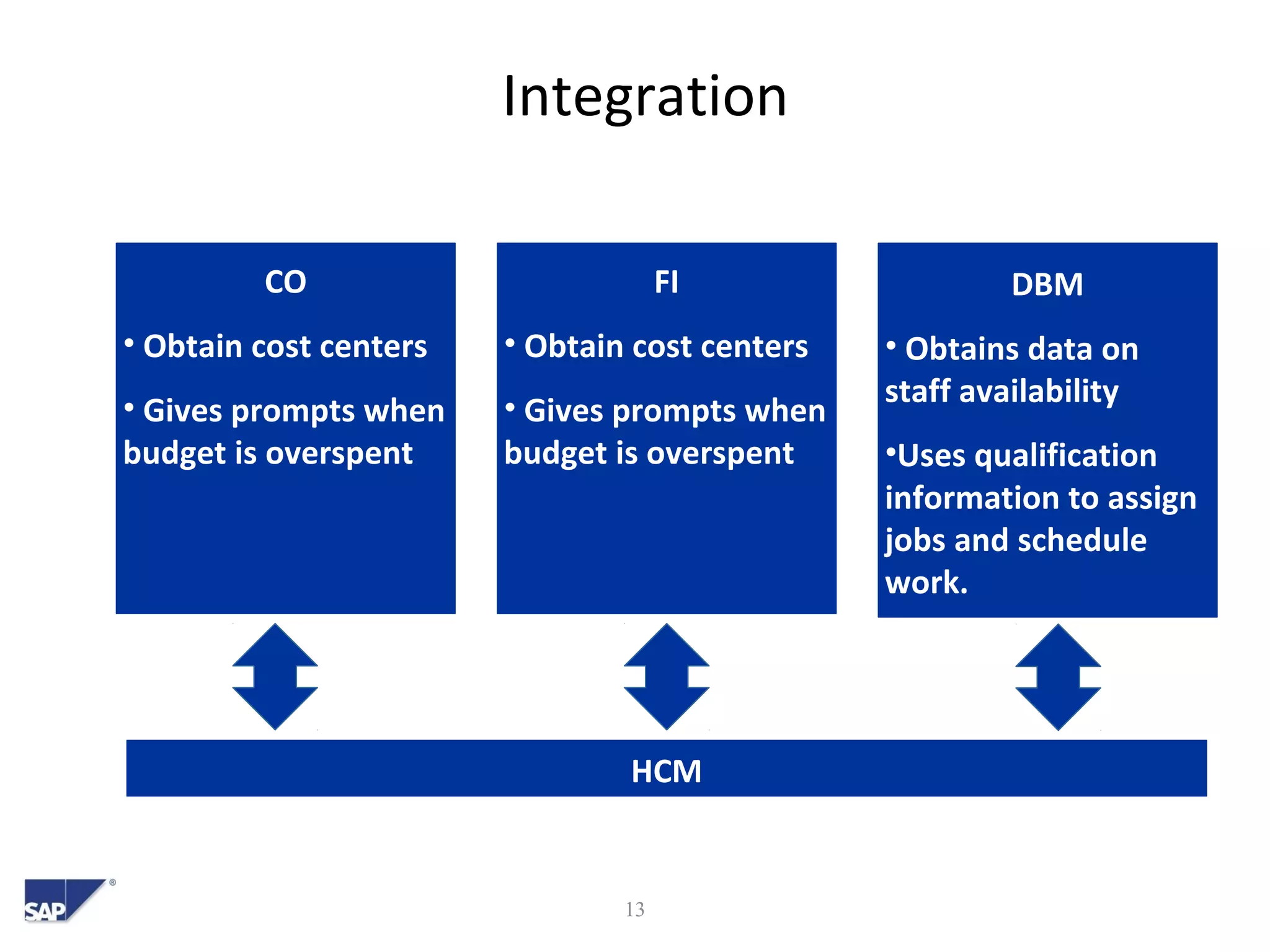
- It also summarizes the scope of an example SAP HCM implementation and how HCM will integrate with other SAP modules like CO, FI and DBM.