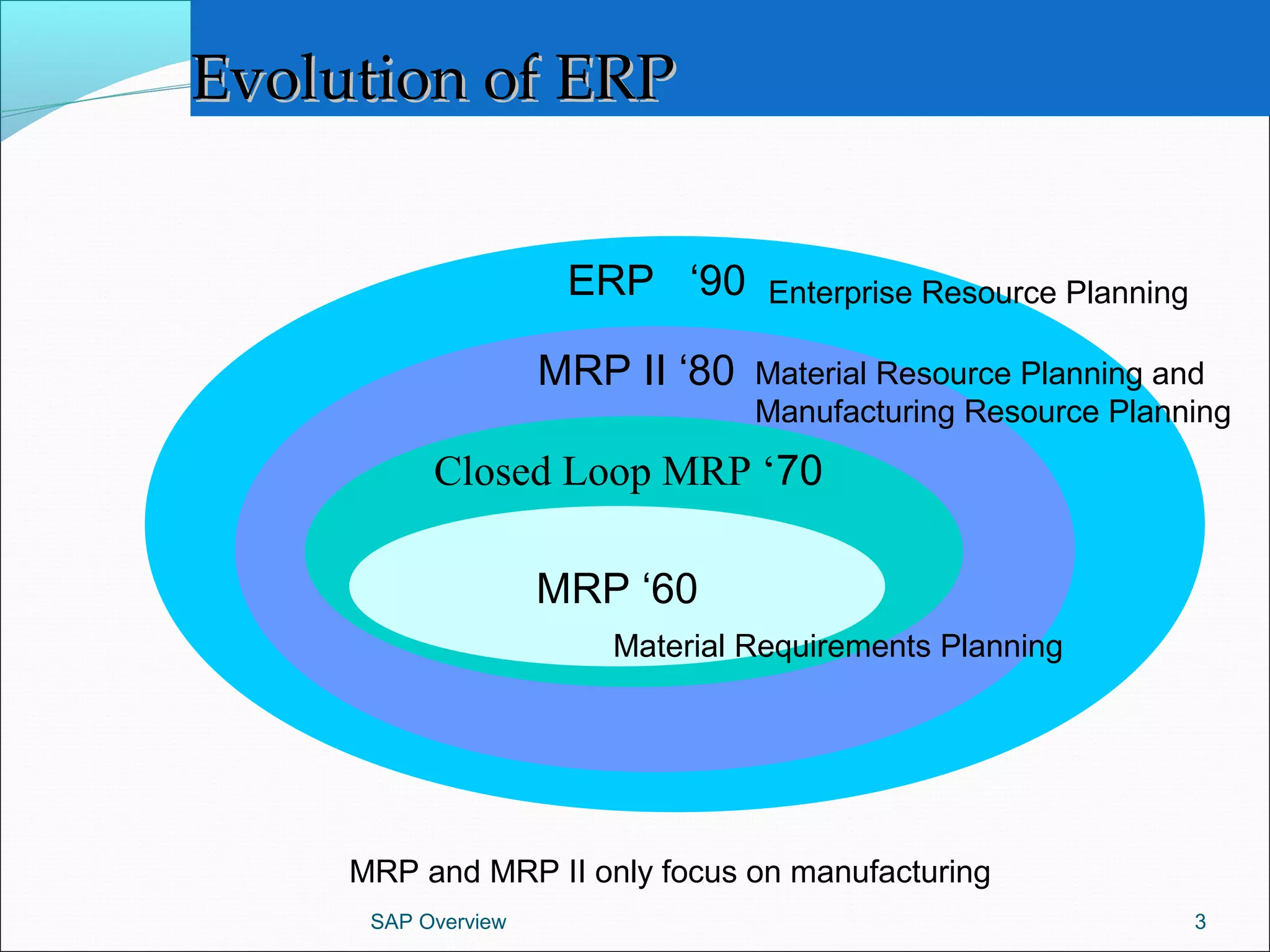
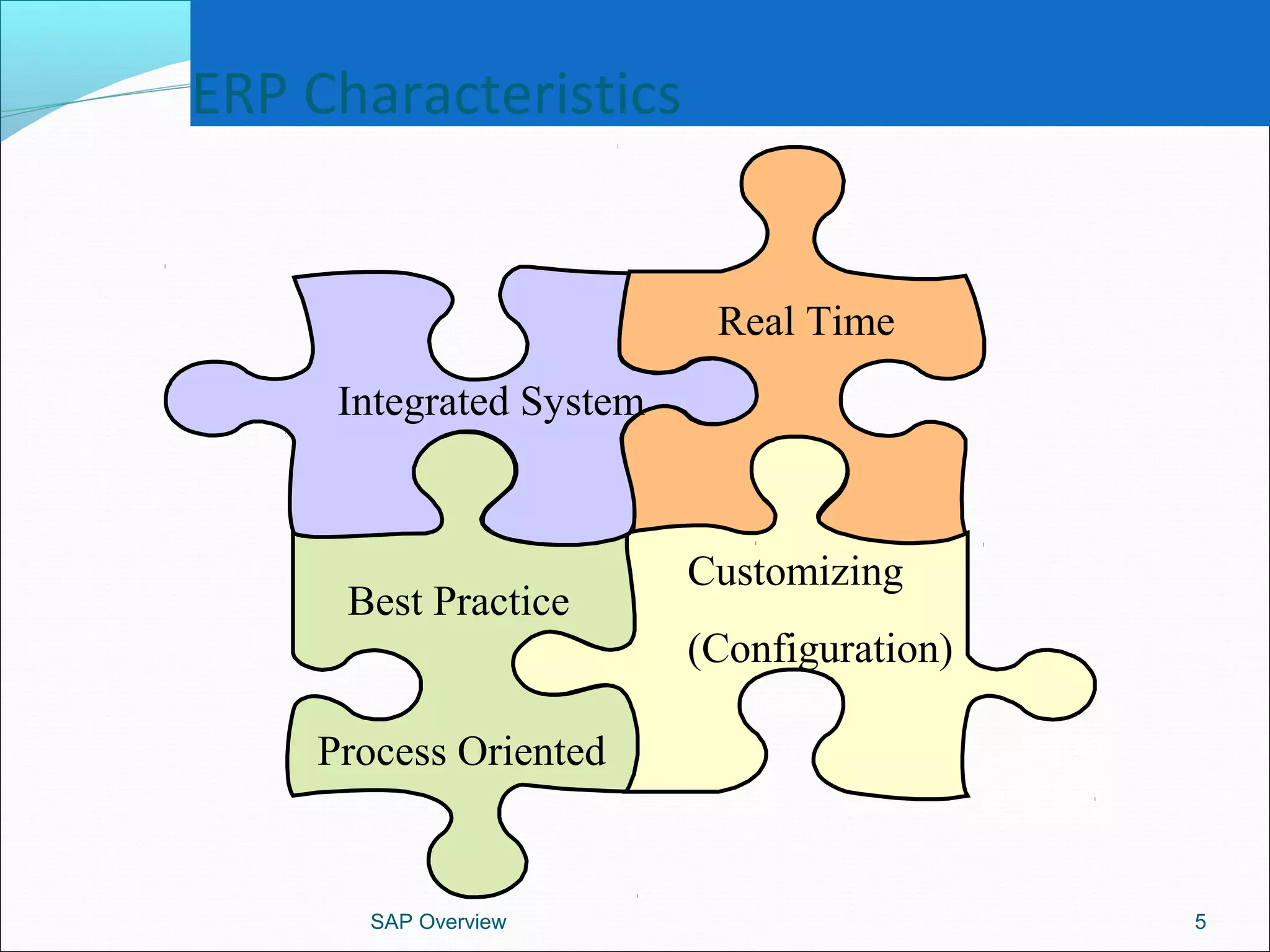
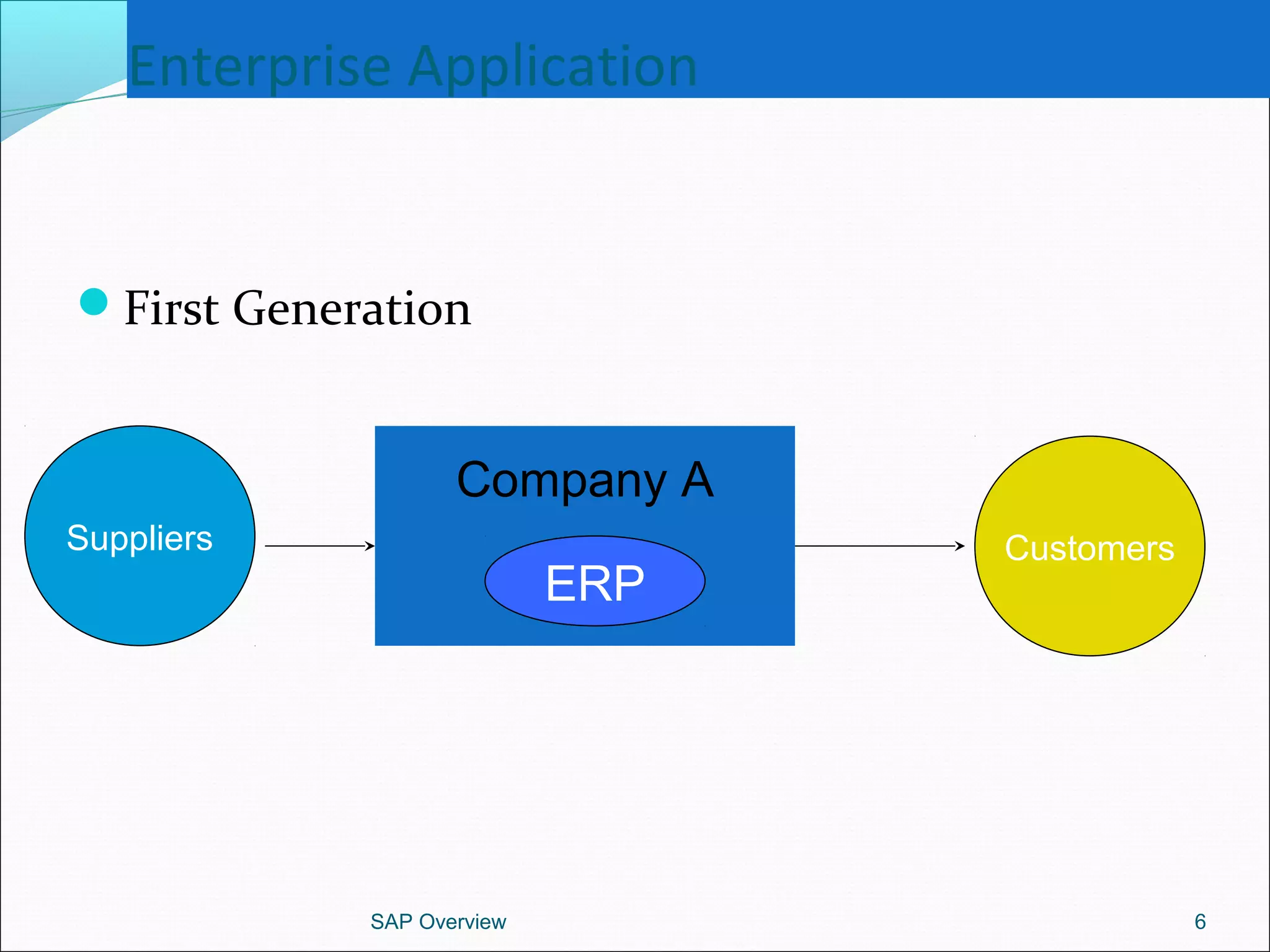
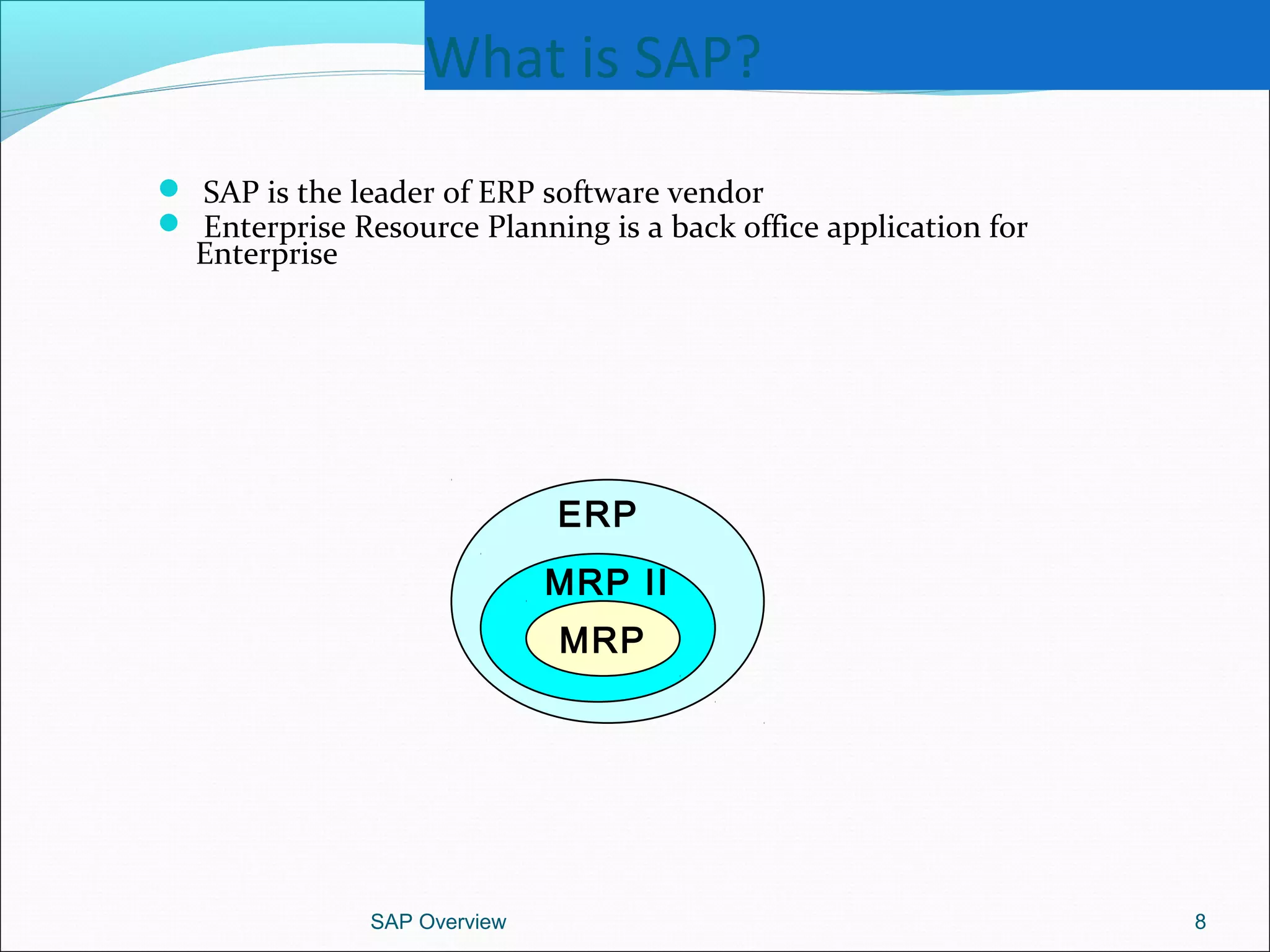
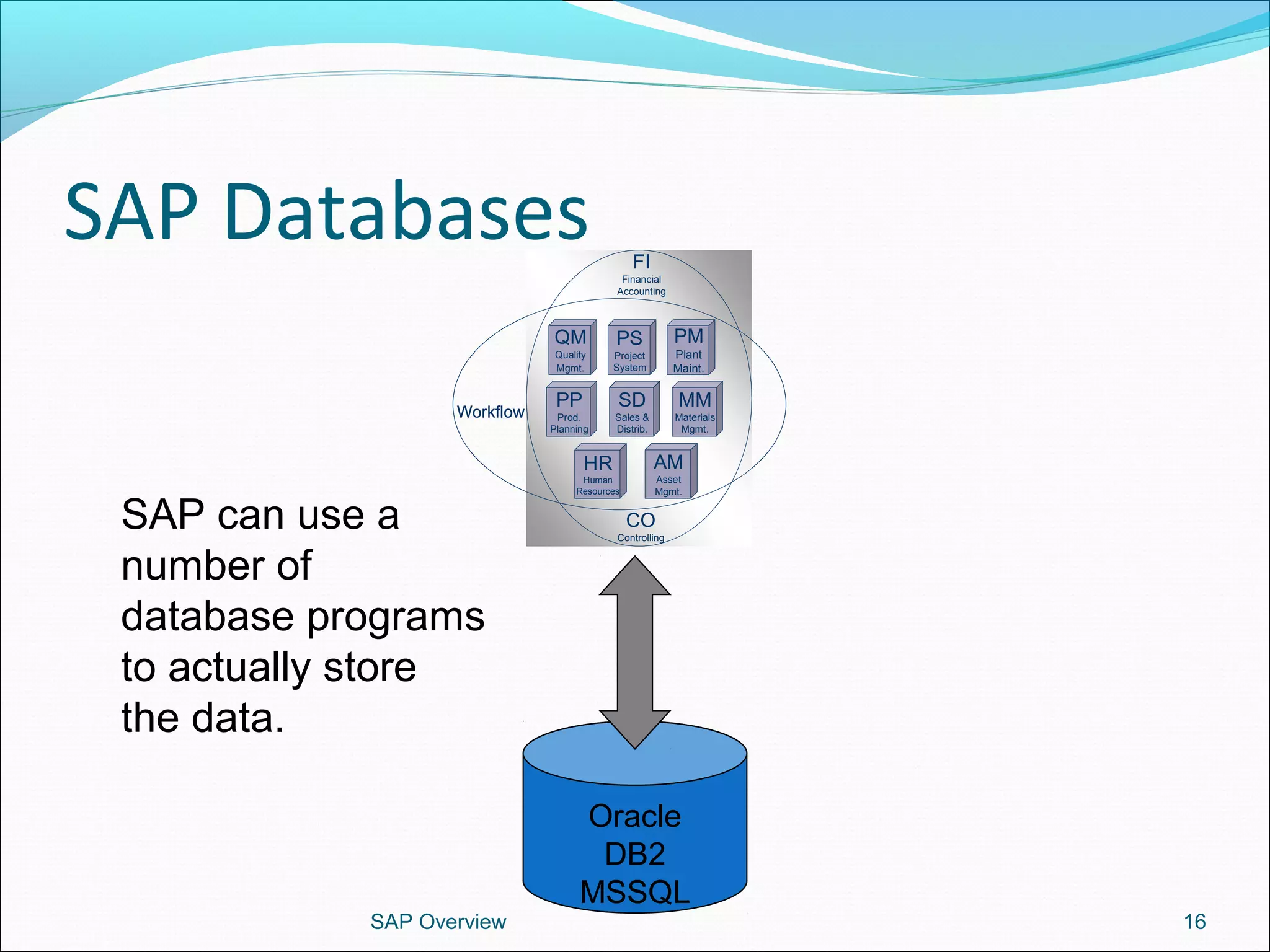
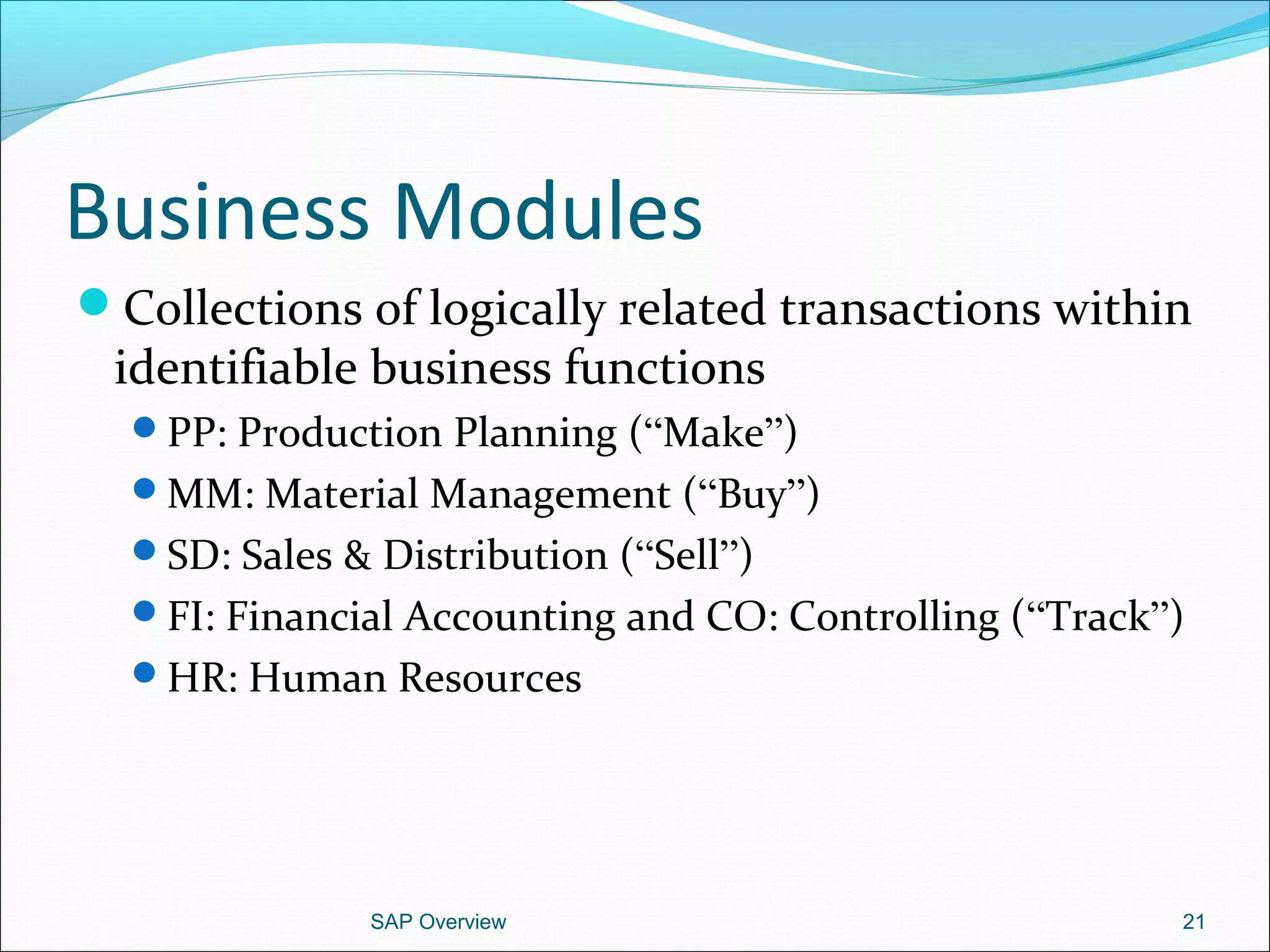
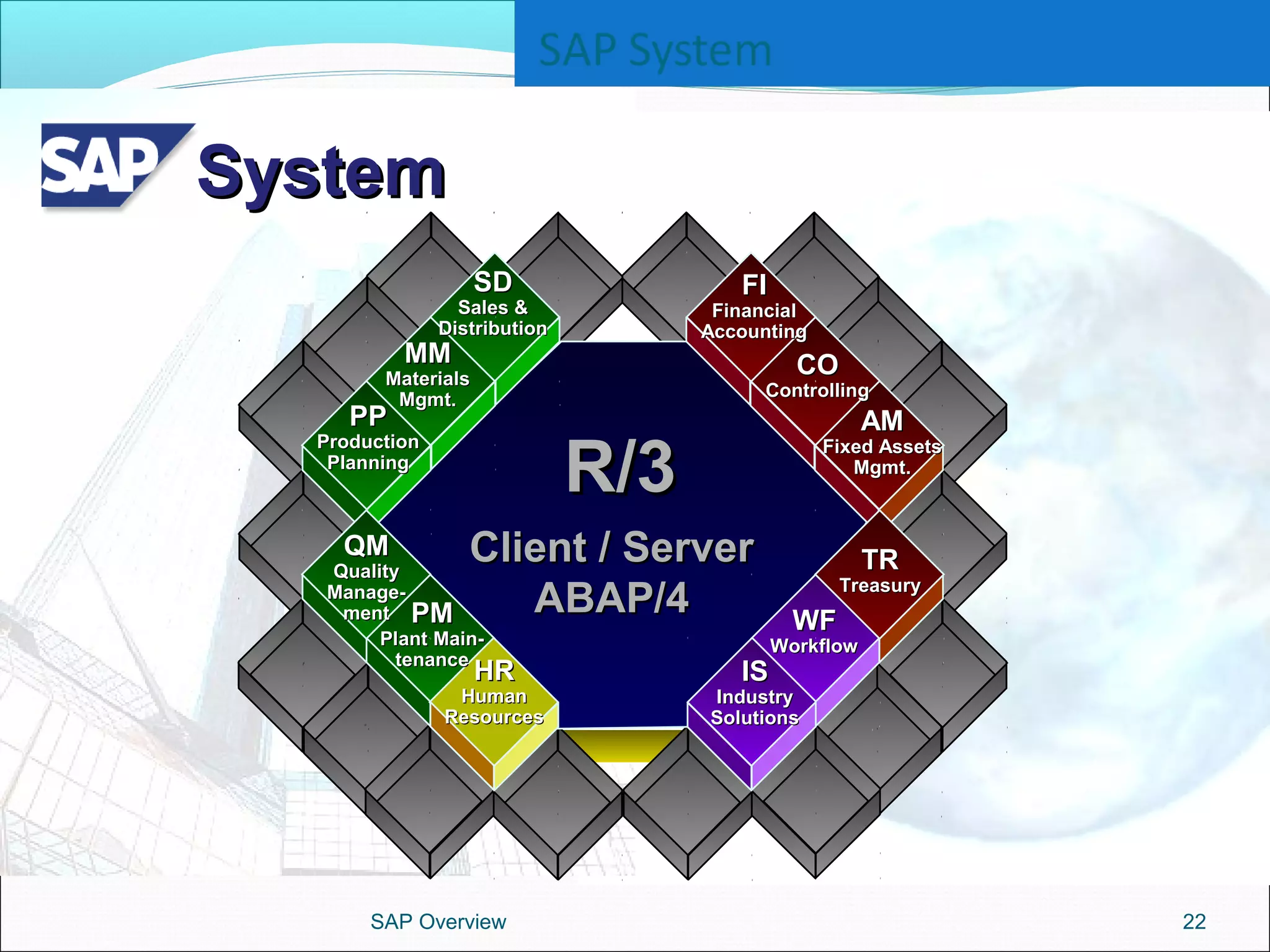
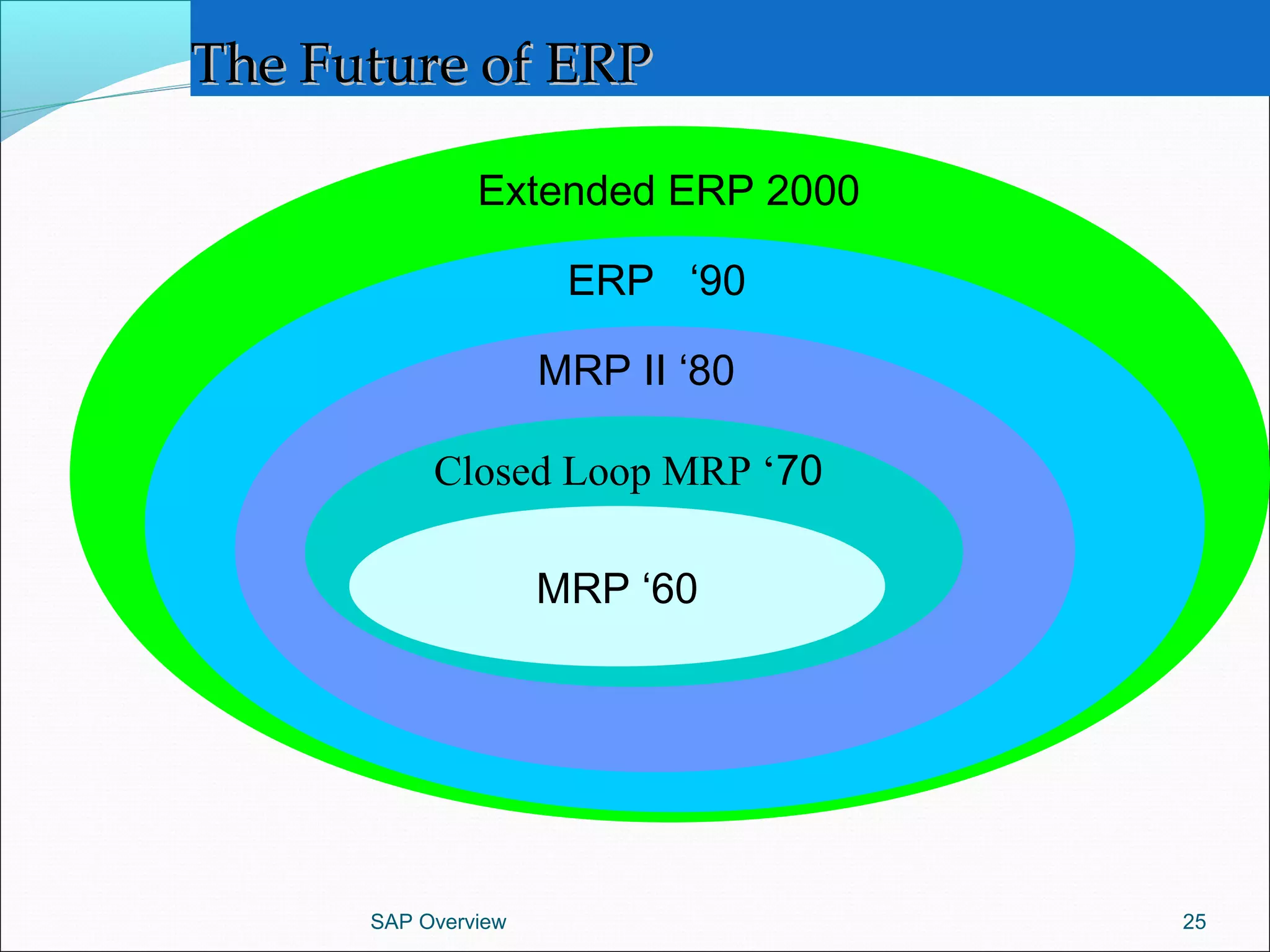
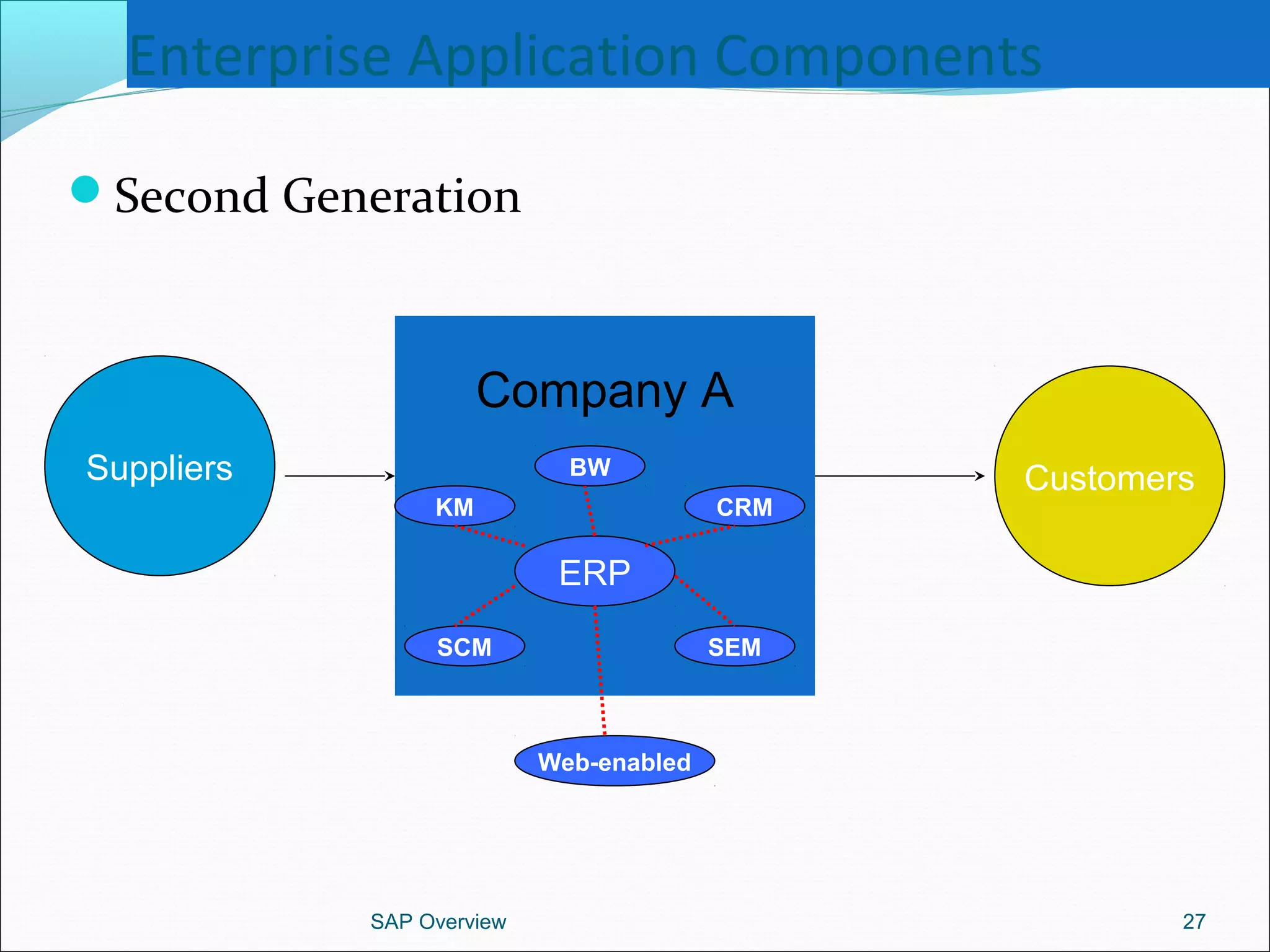
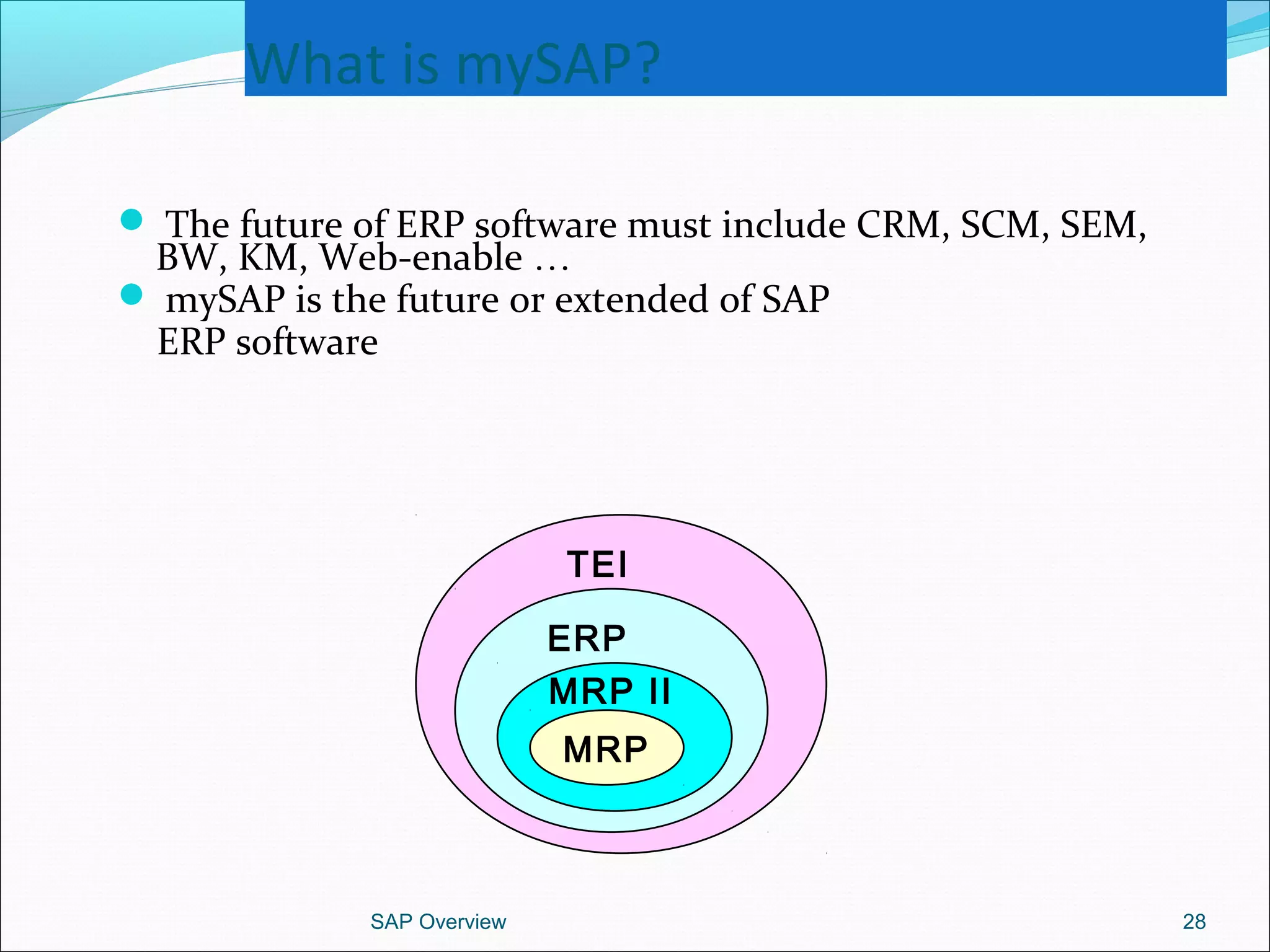
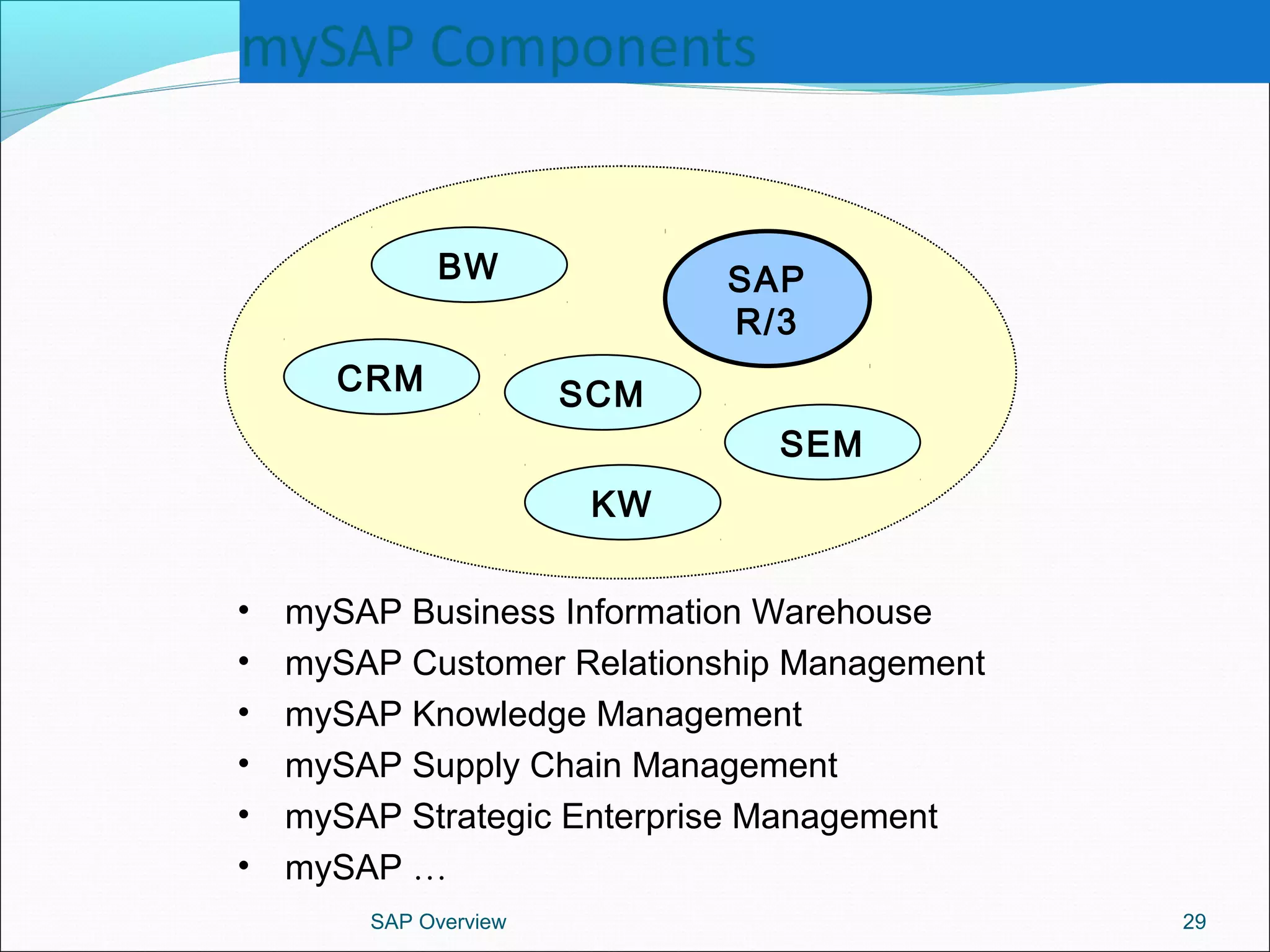
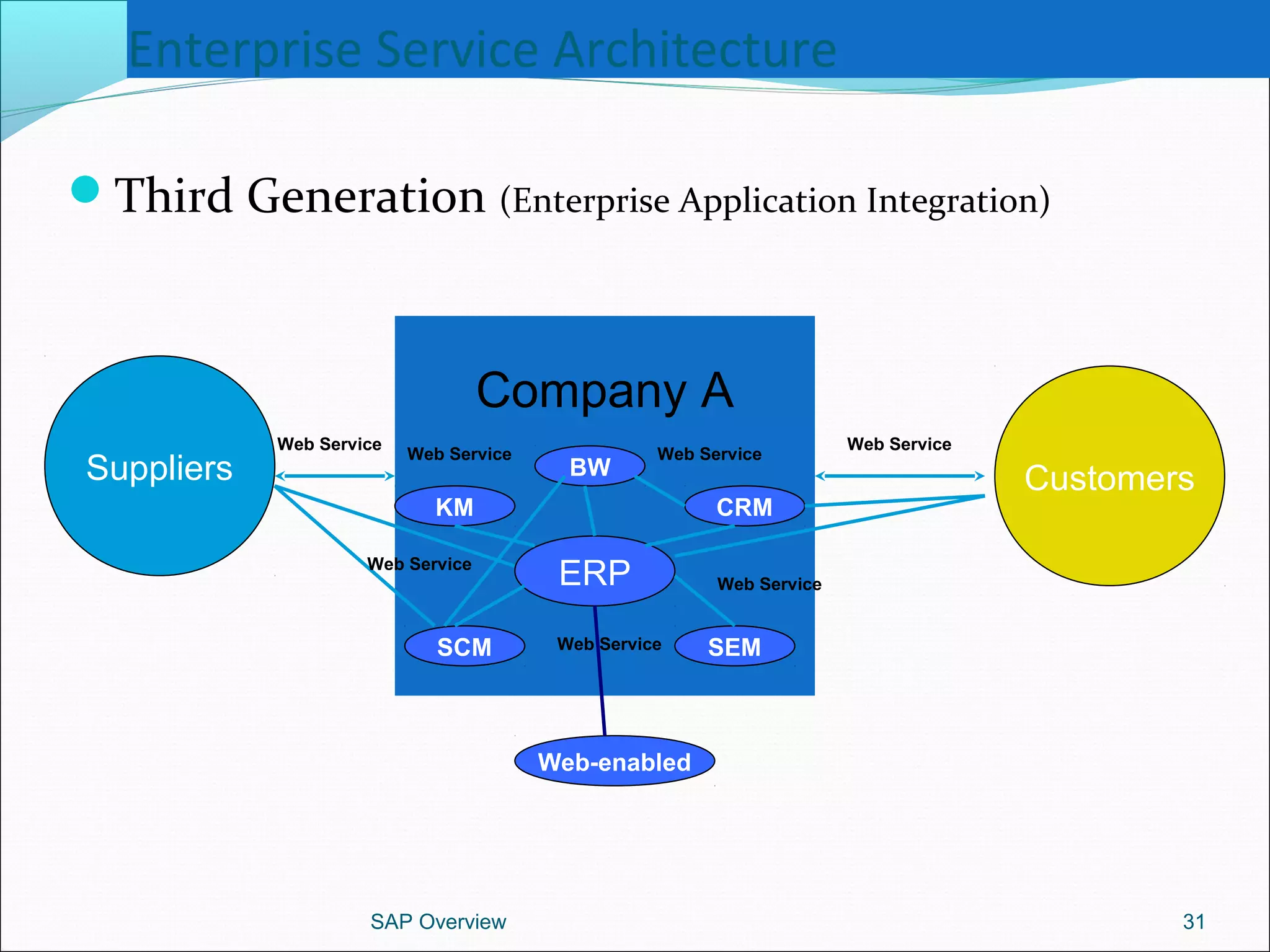
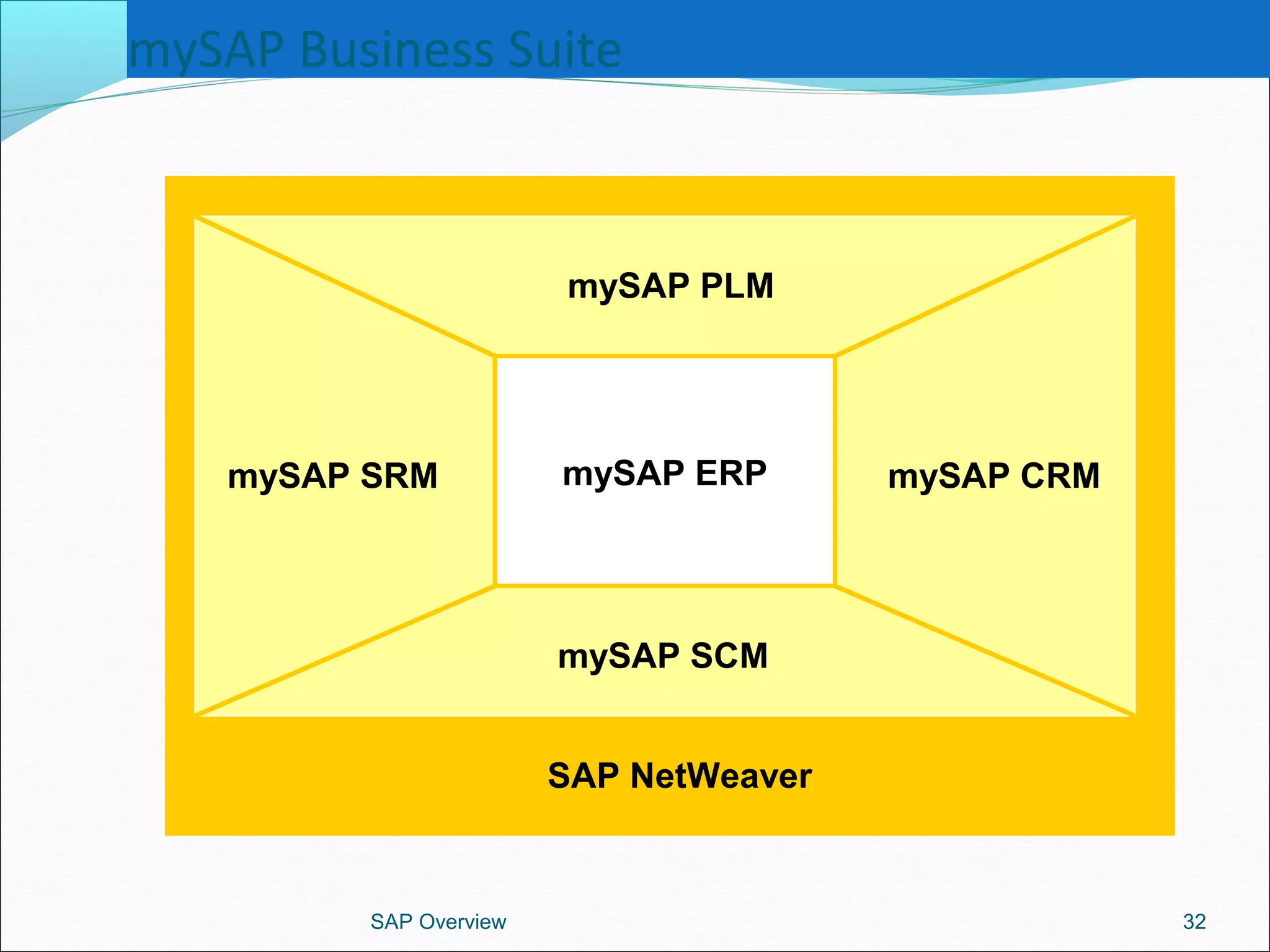
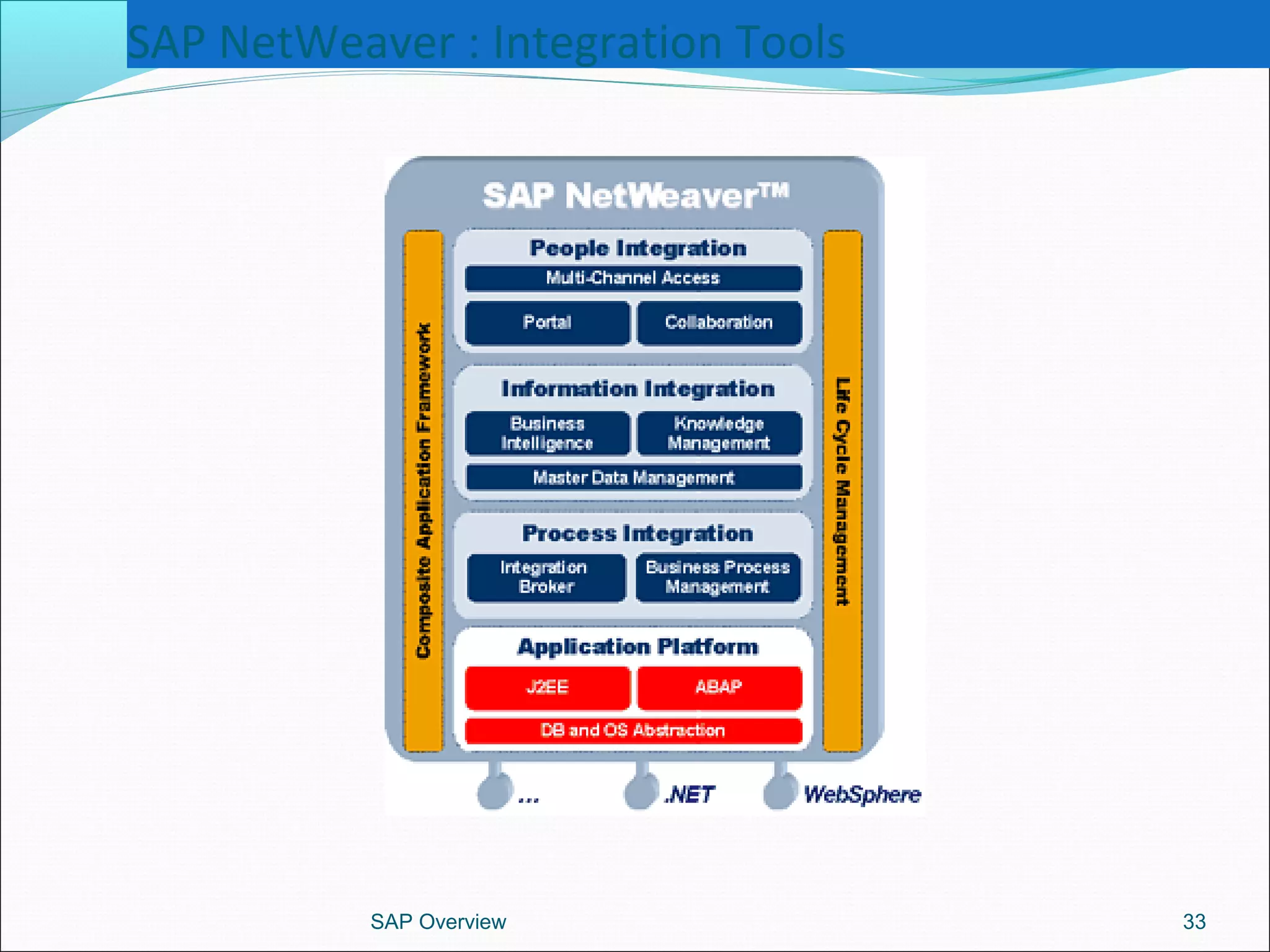
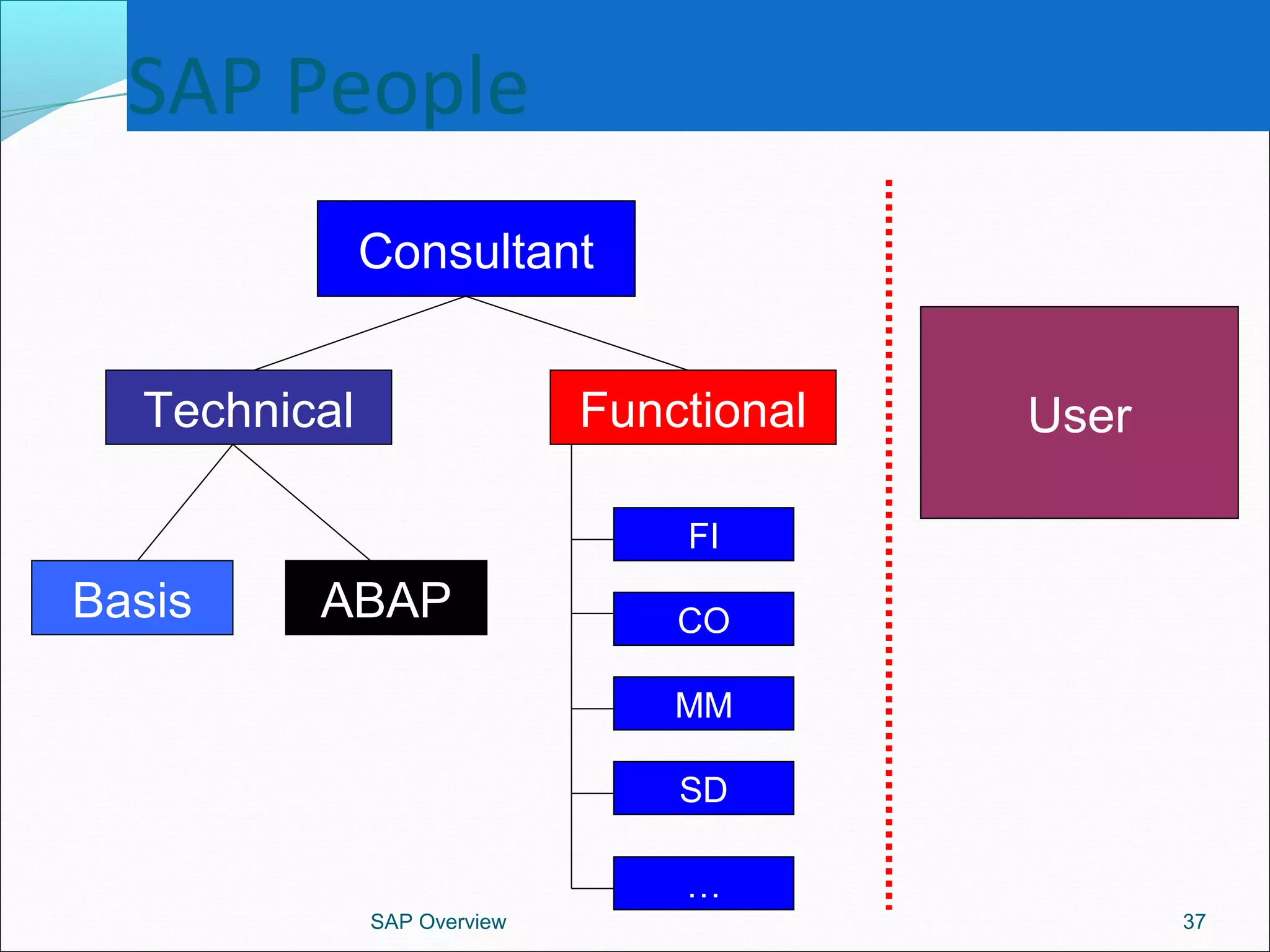
The document provides an overview of ERP systems, particularly focusing on SAP as a leading ERP software vendor. It discusses the evolution of ERP from MRP to advanced systems and highlights the features and components of SAP solutions, including integration, real-time data processing, and industry-specific applications. Additionally, it outlines the future direction of ERP with the inclusion of web-enabled services and enterprise integration capabilities.