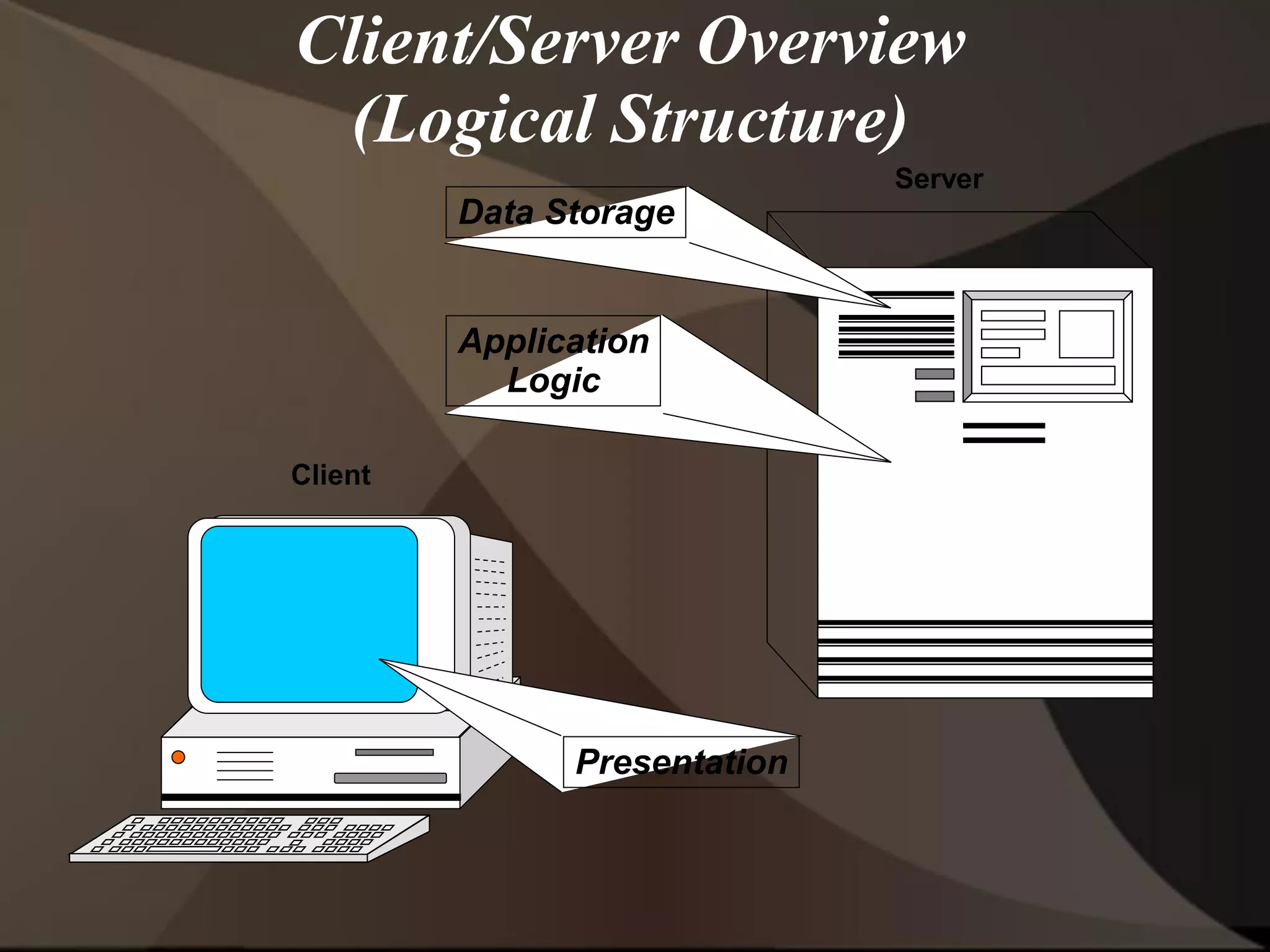
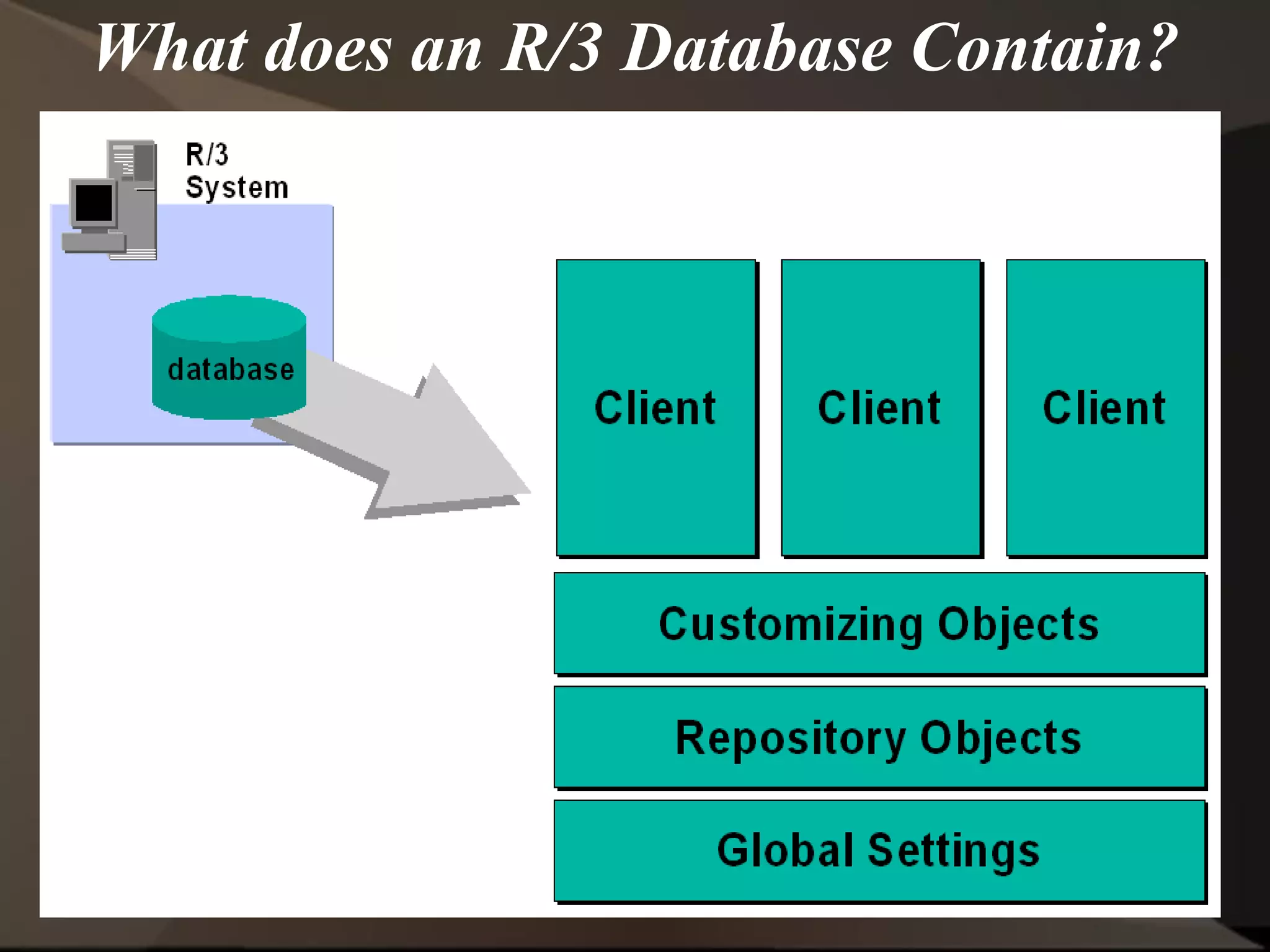
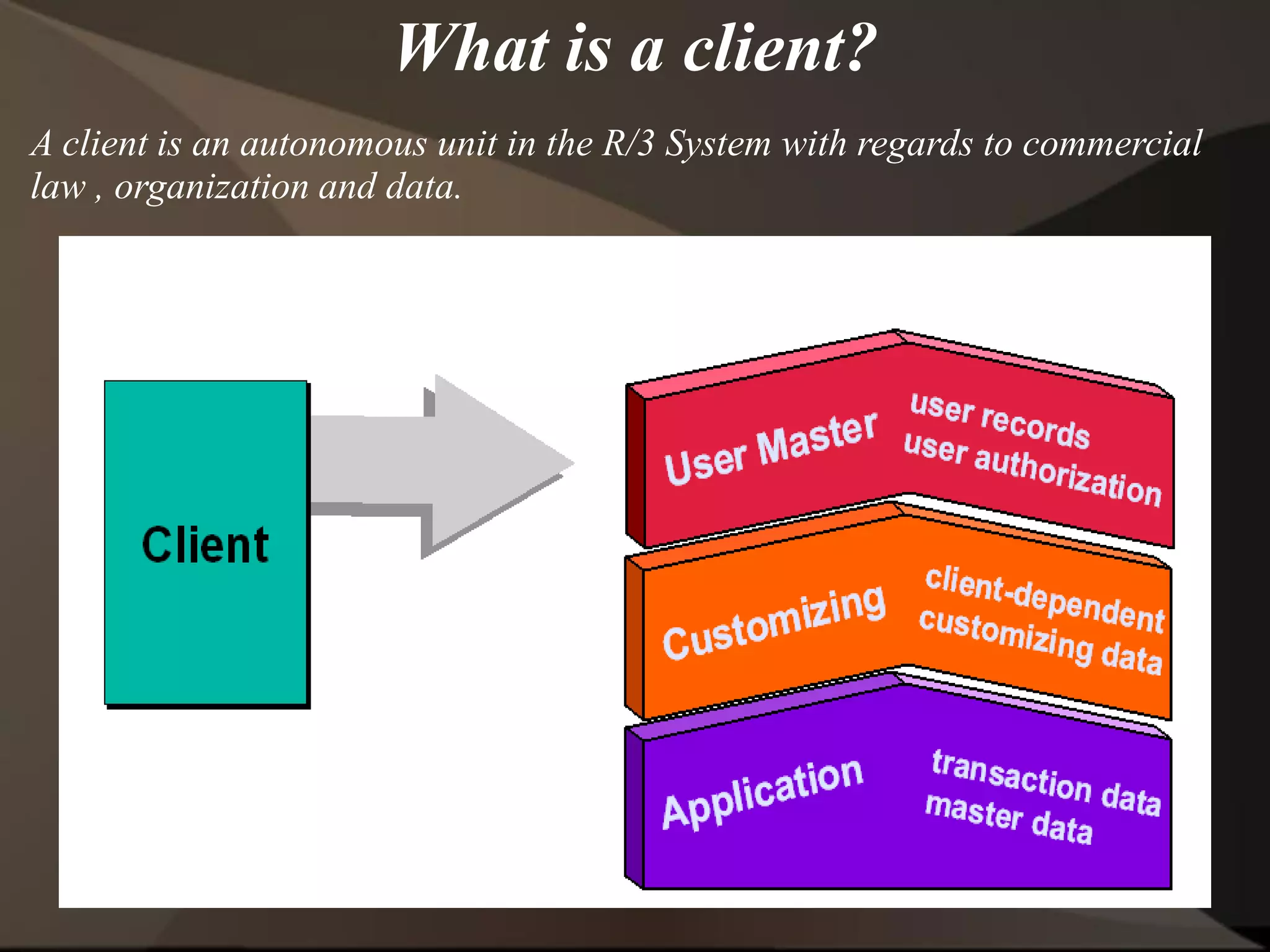
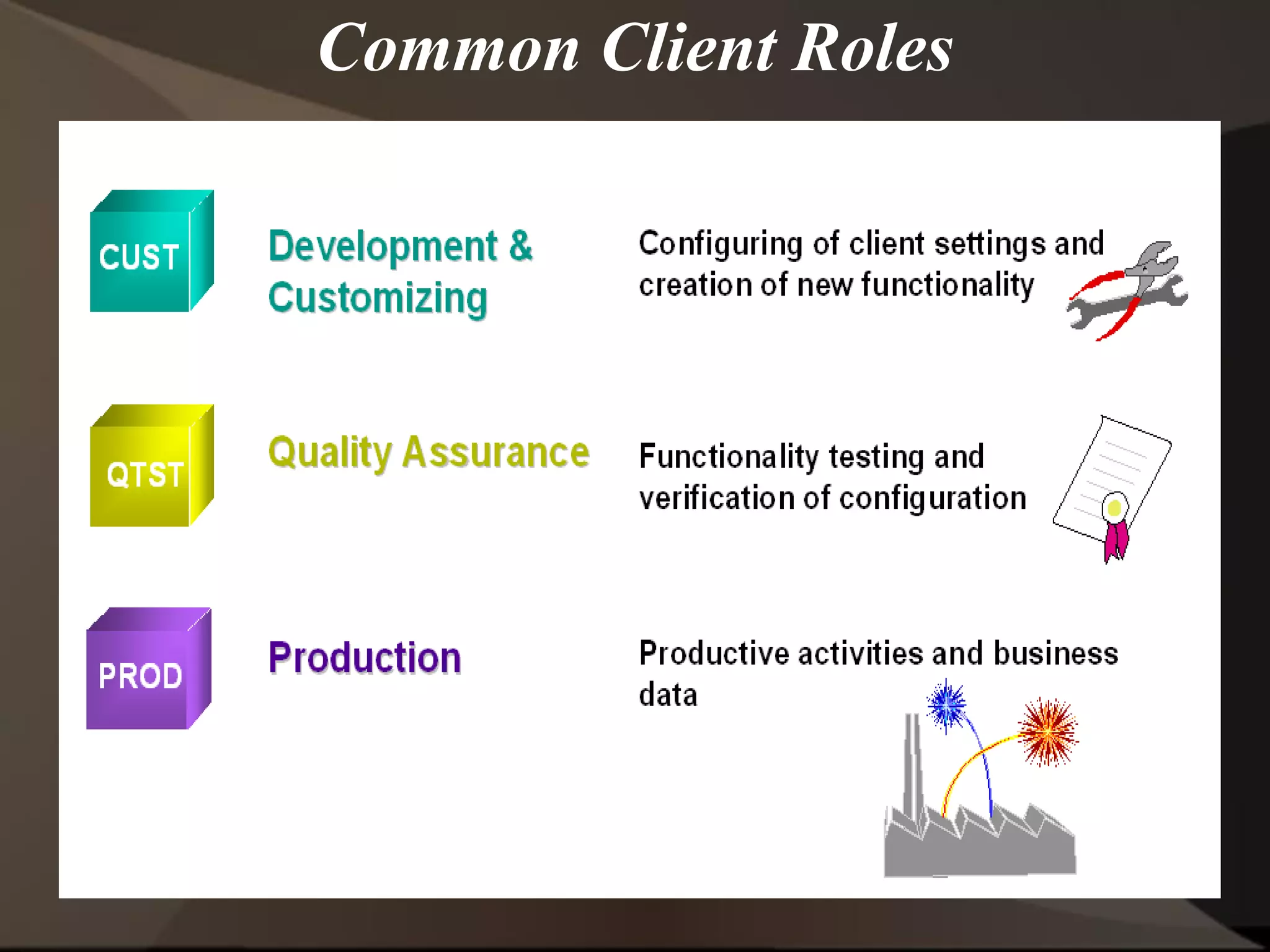
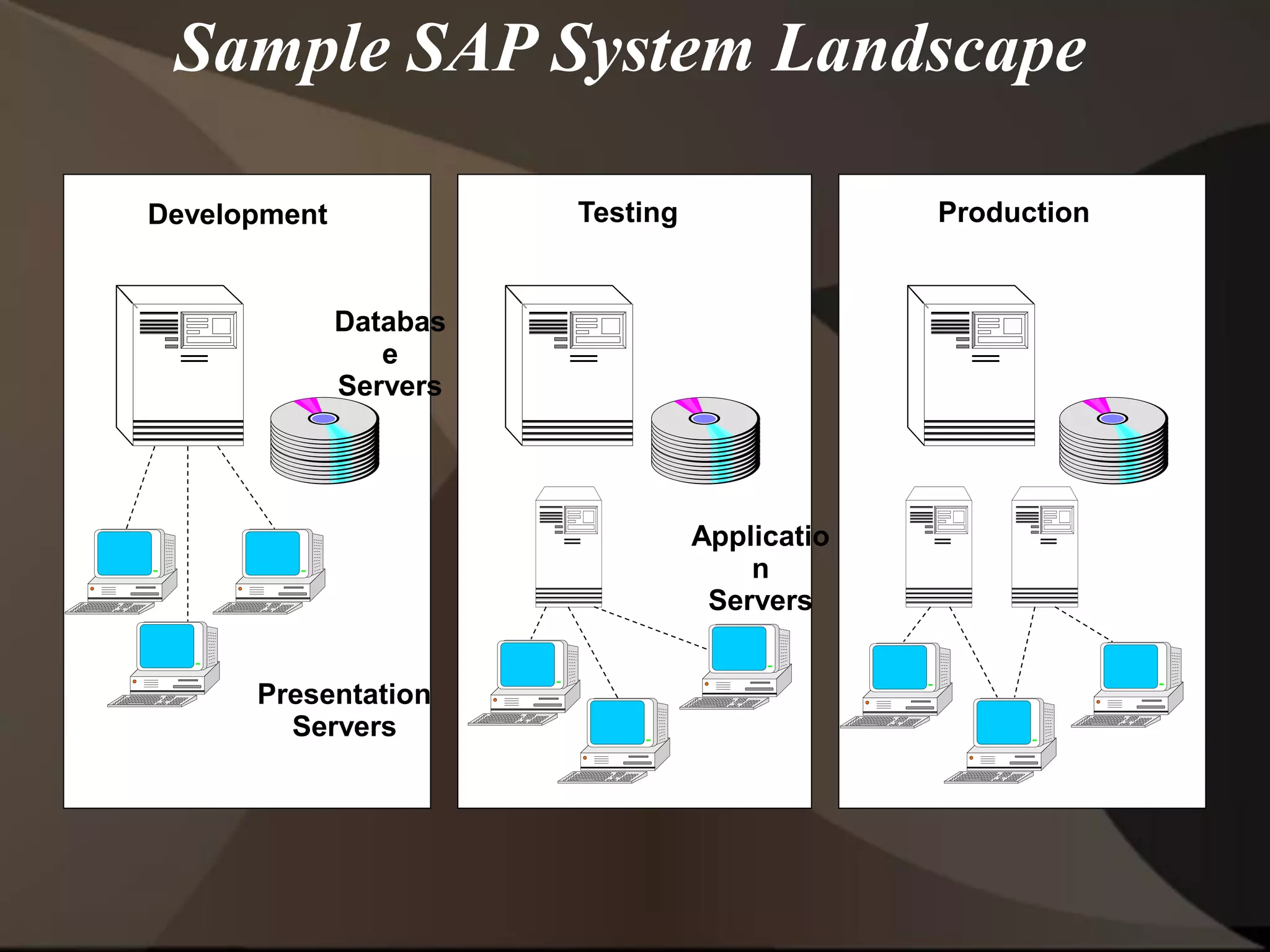
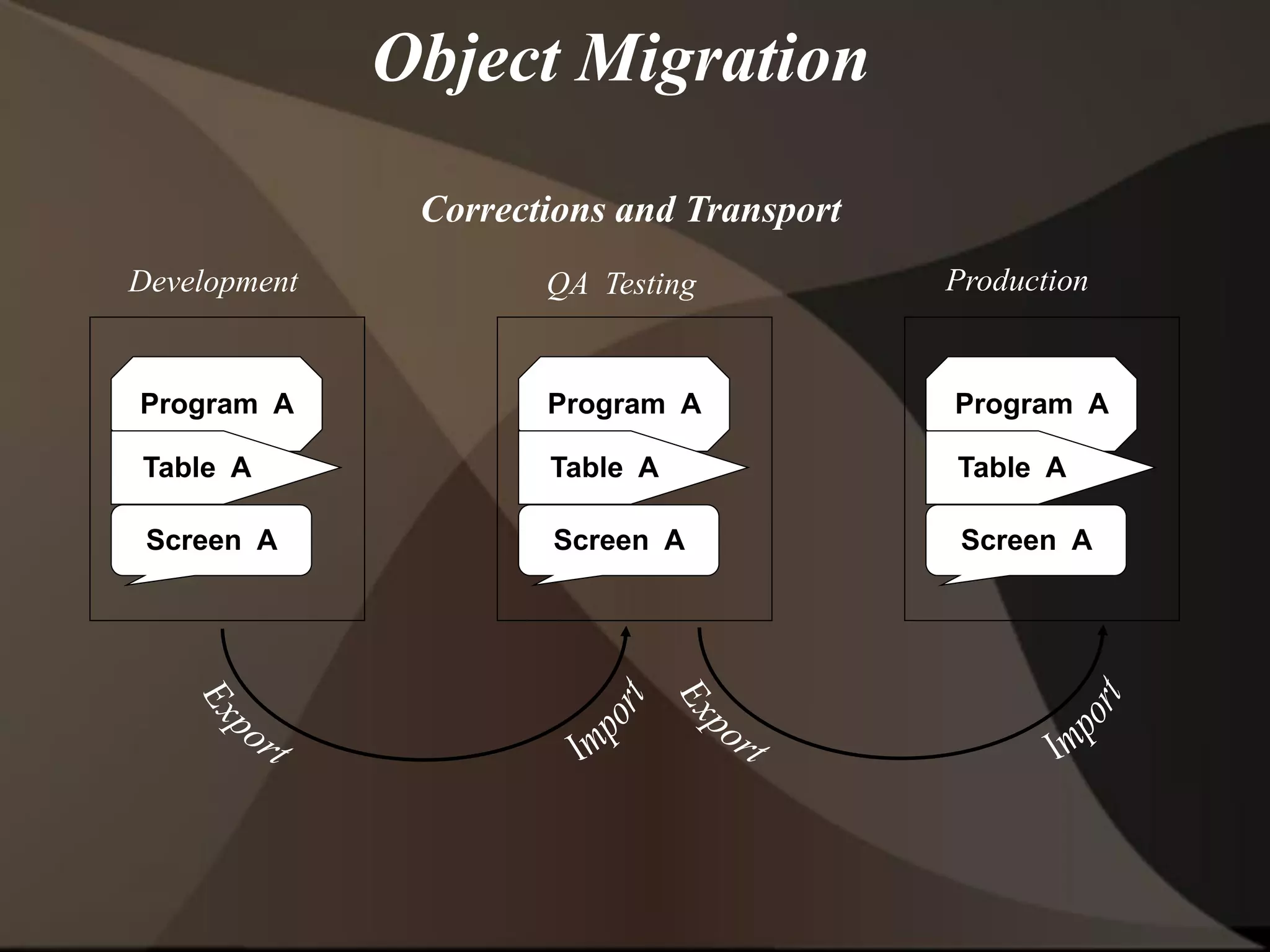
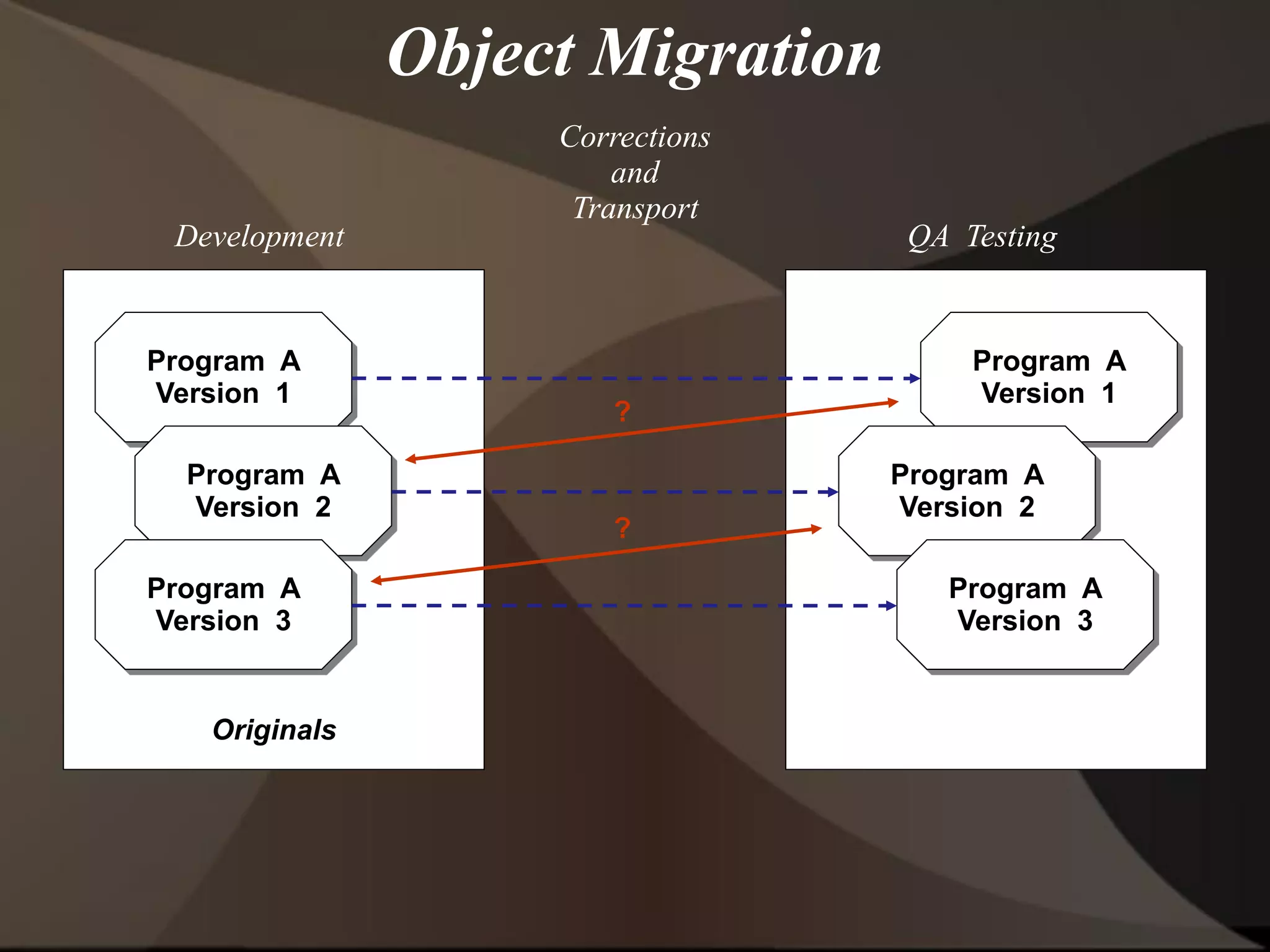
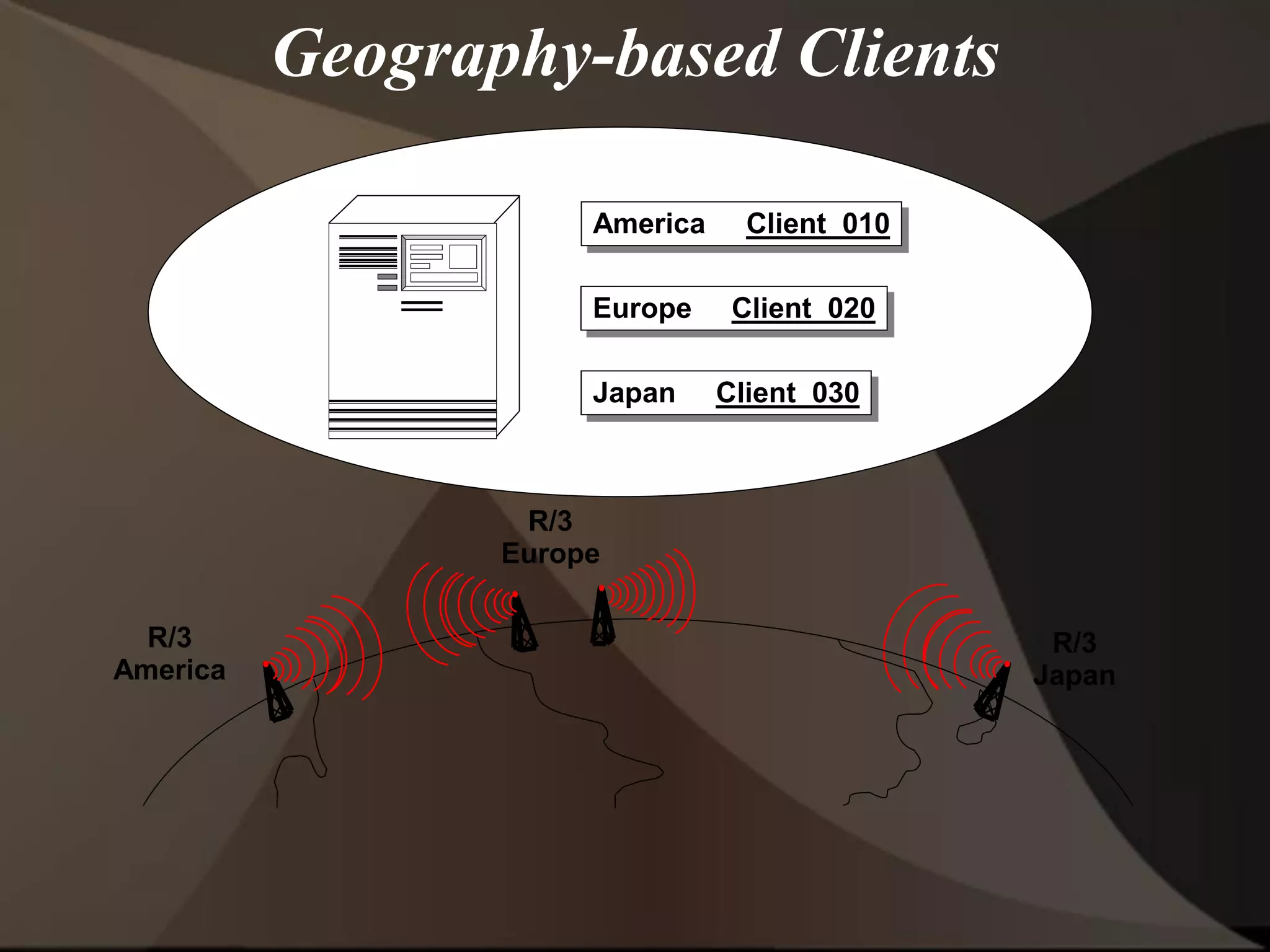
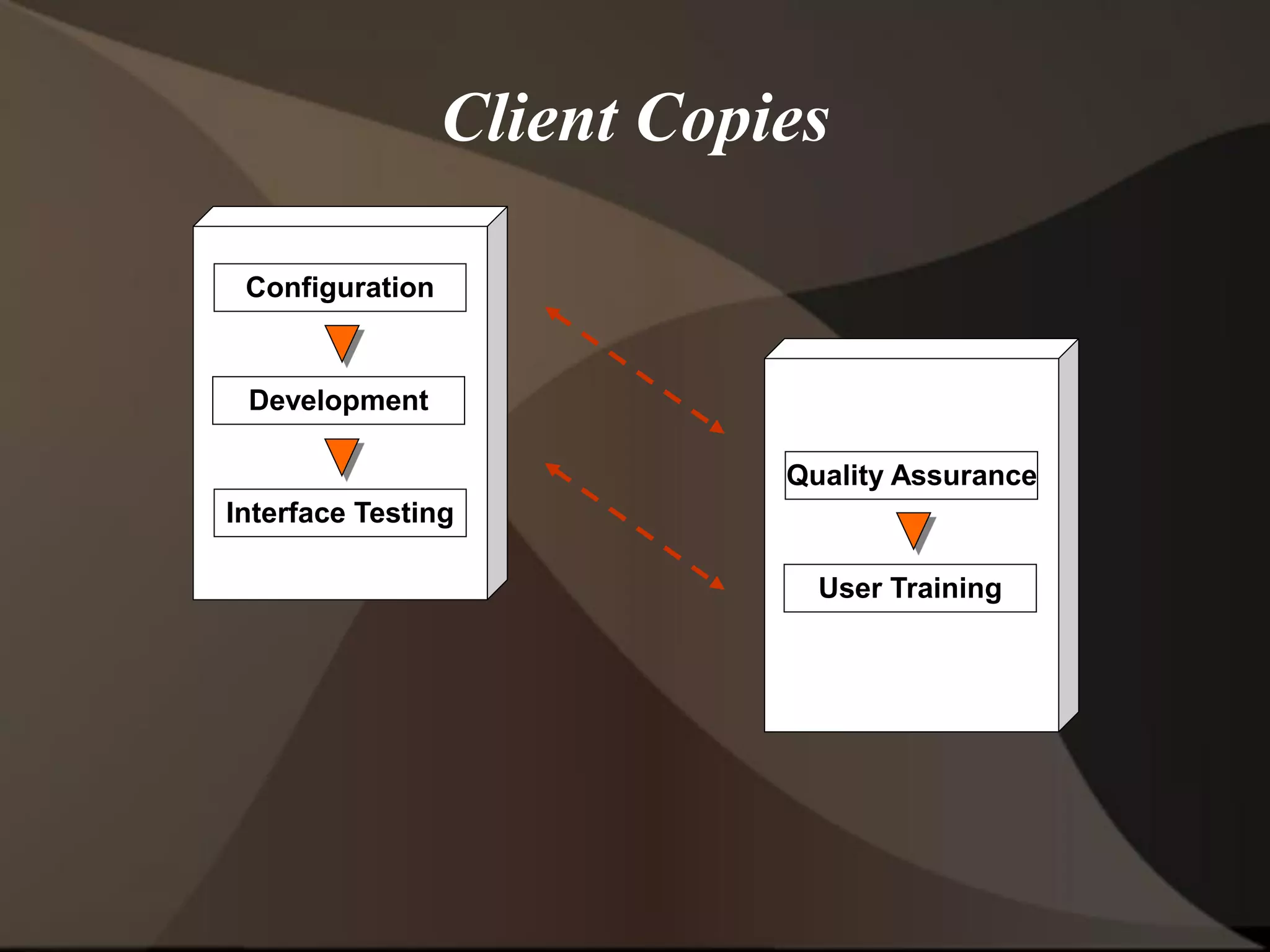
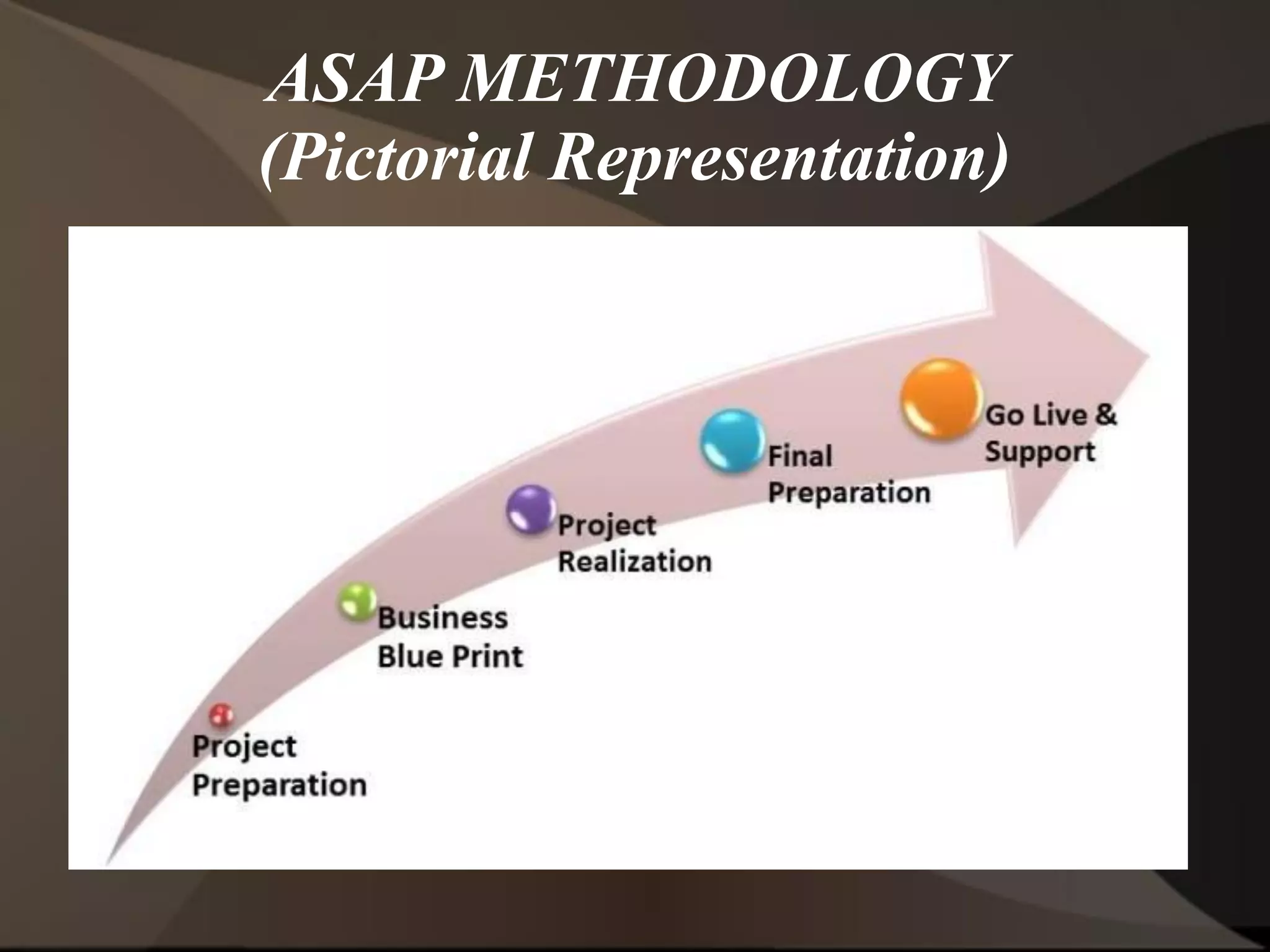
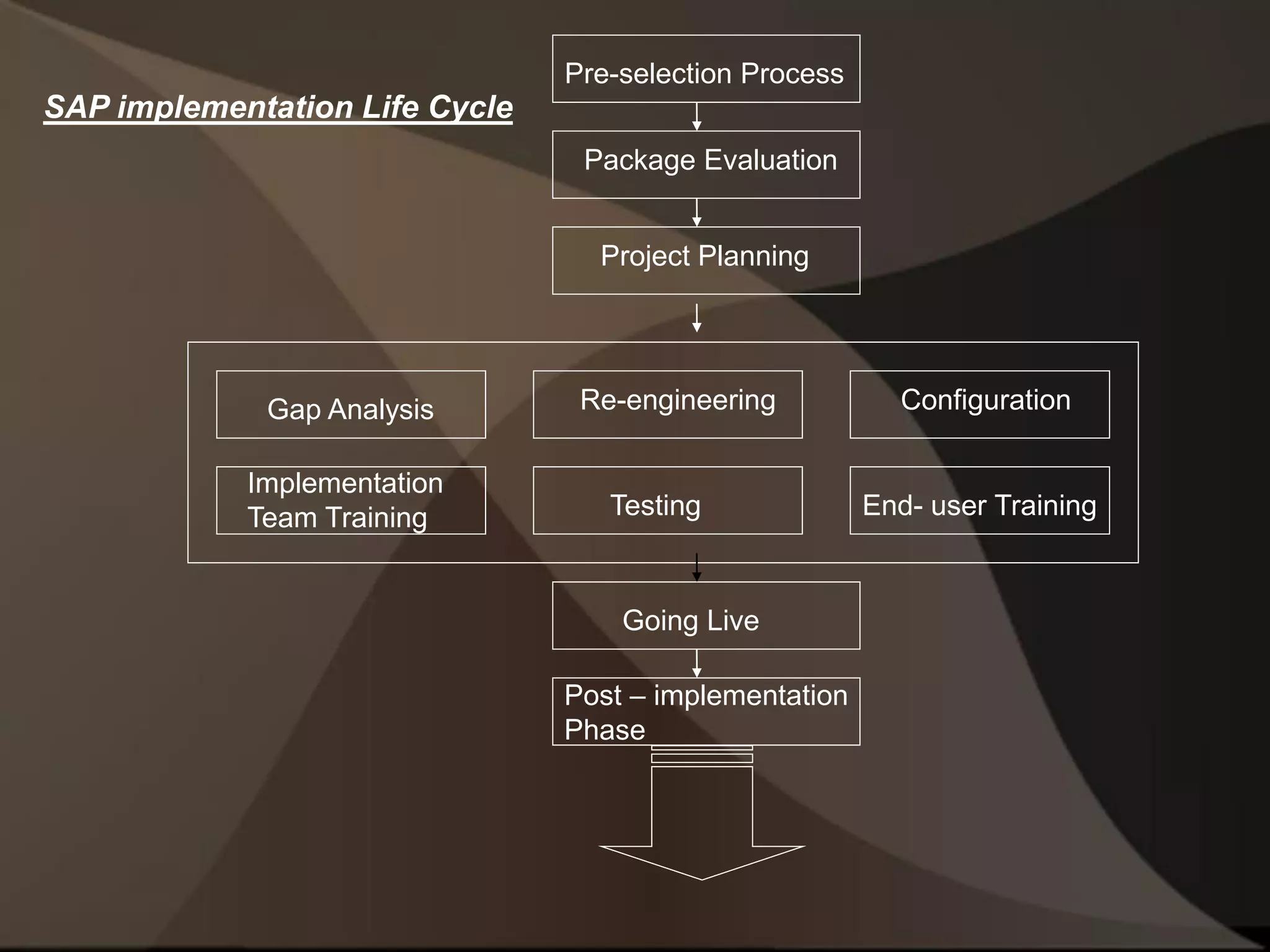
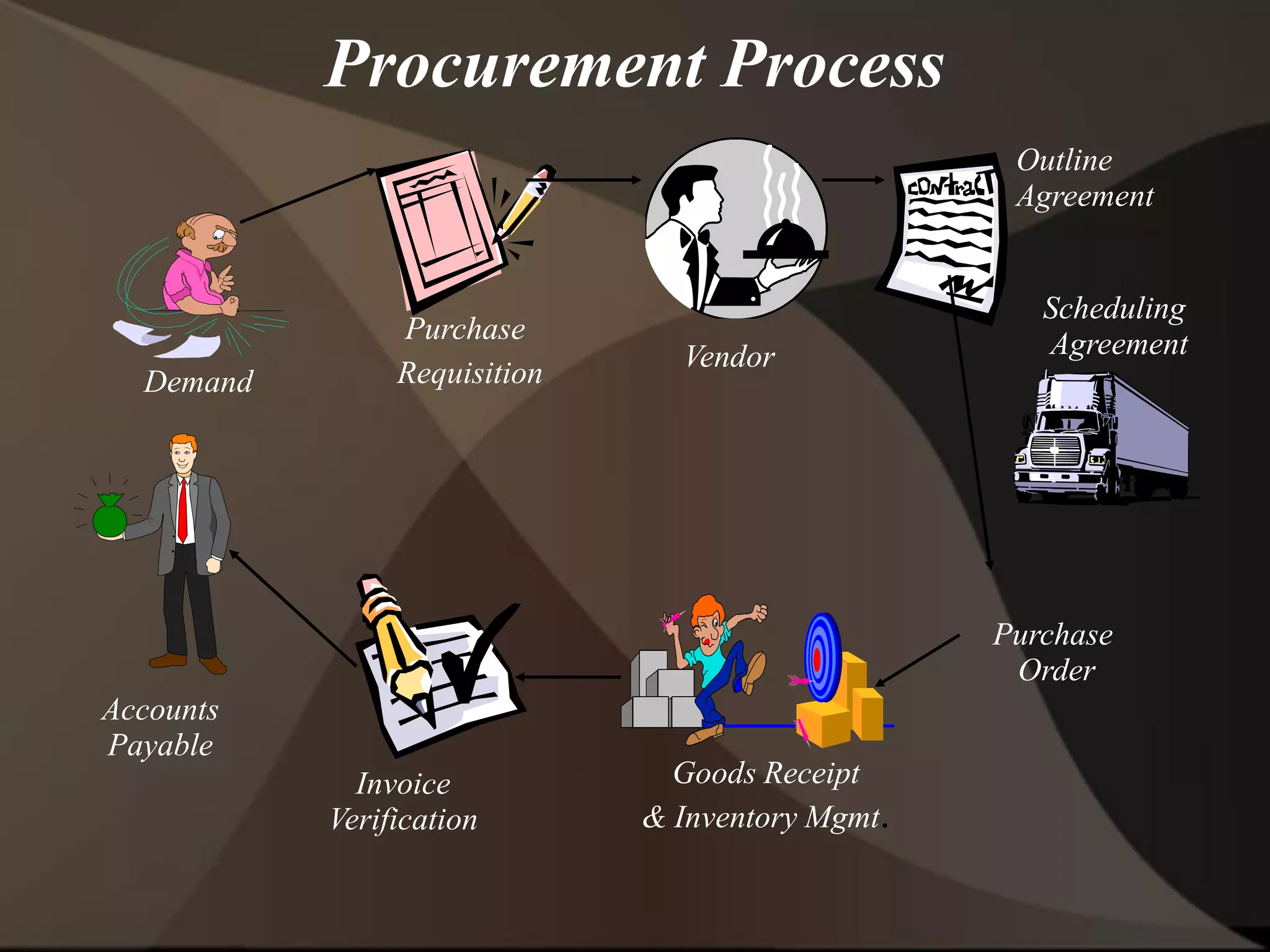
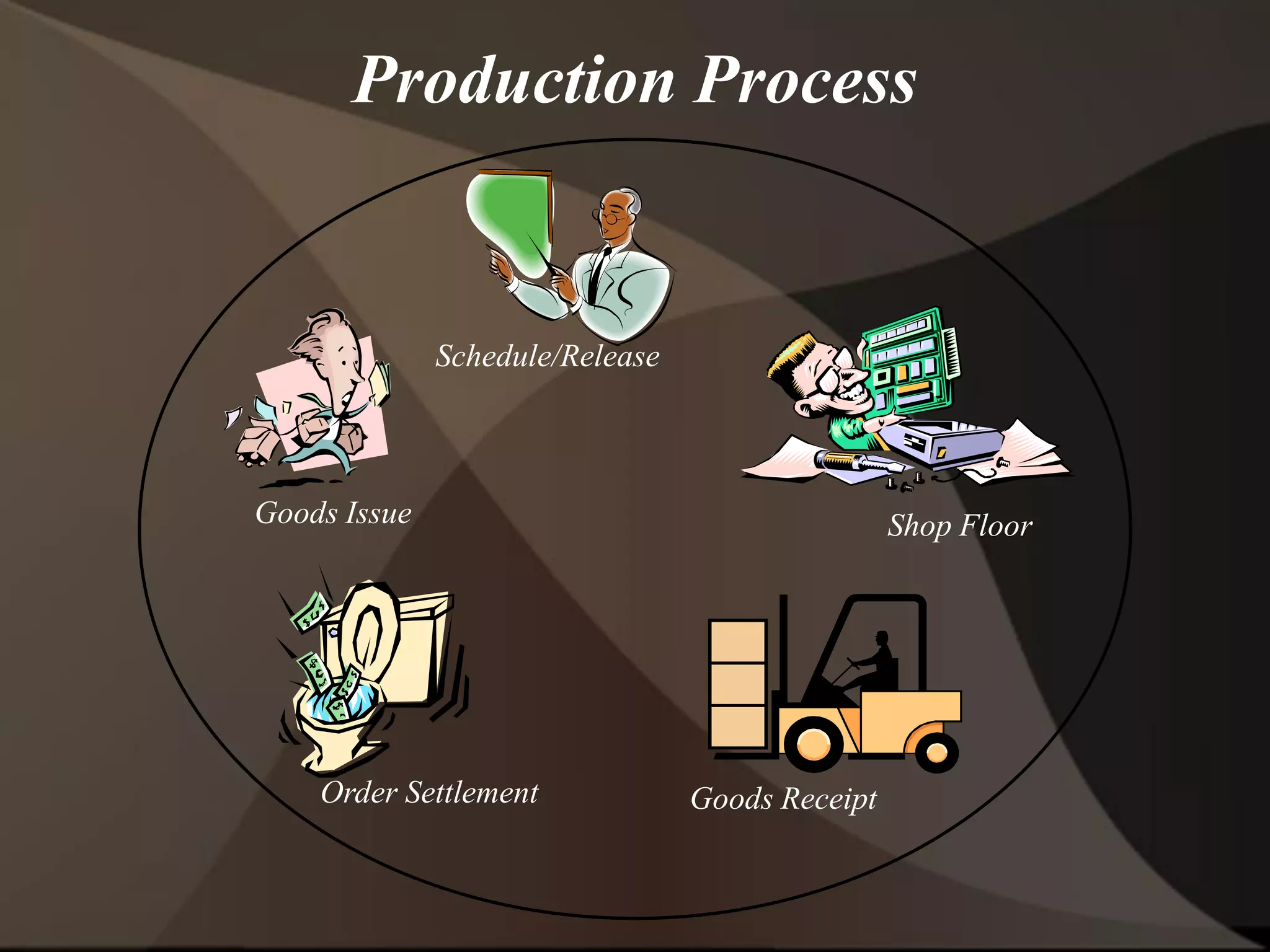
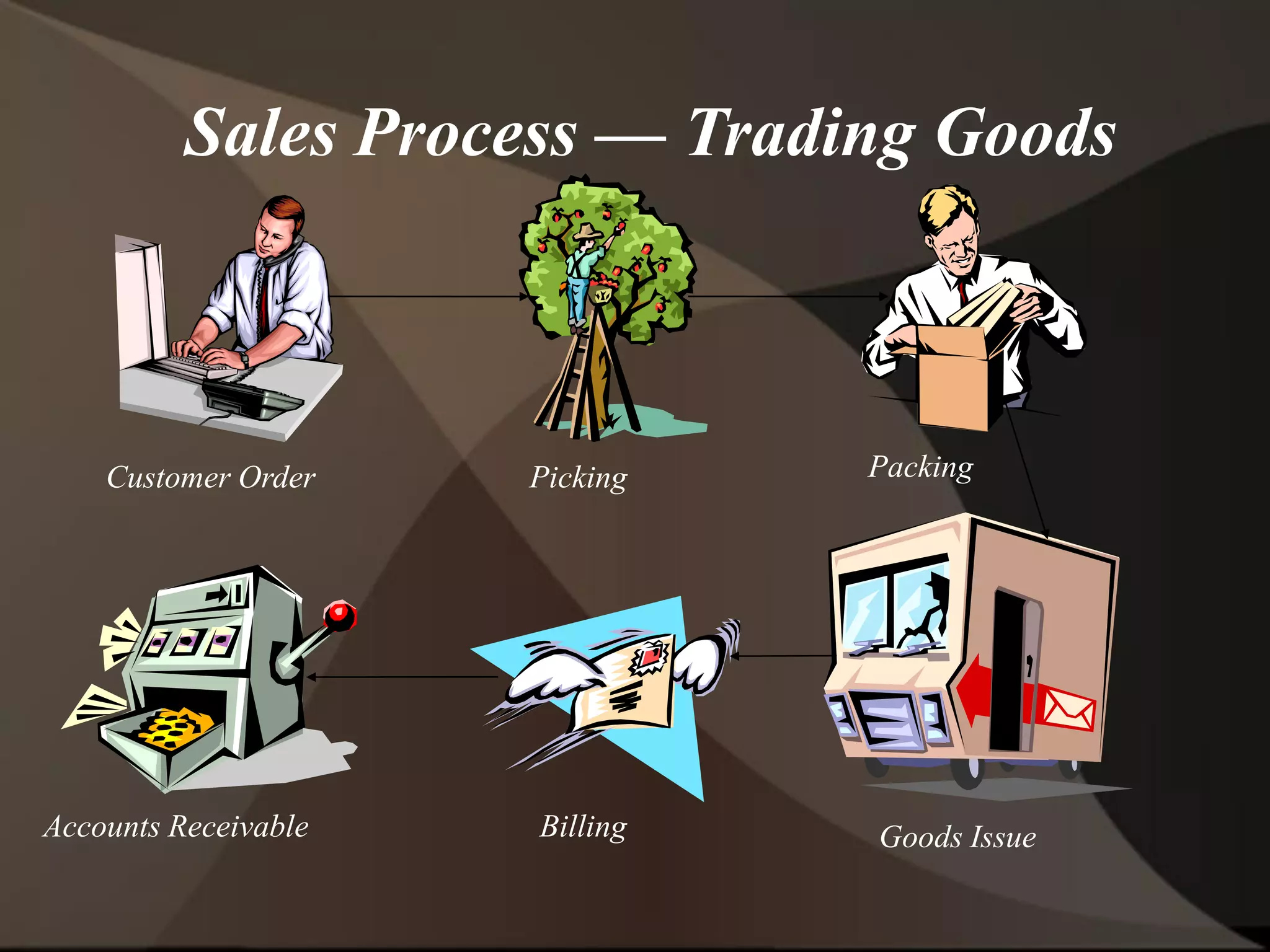
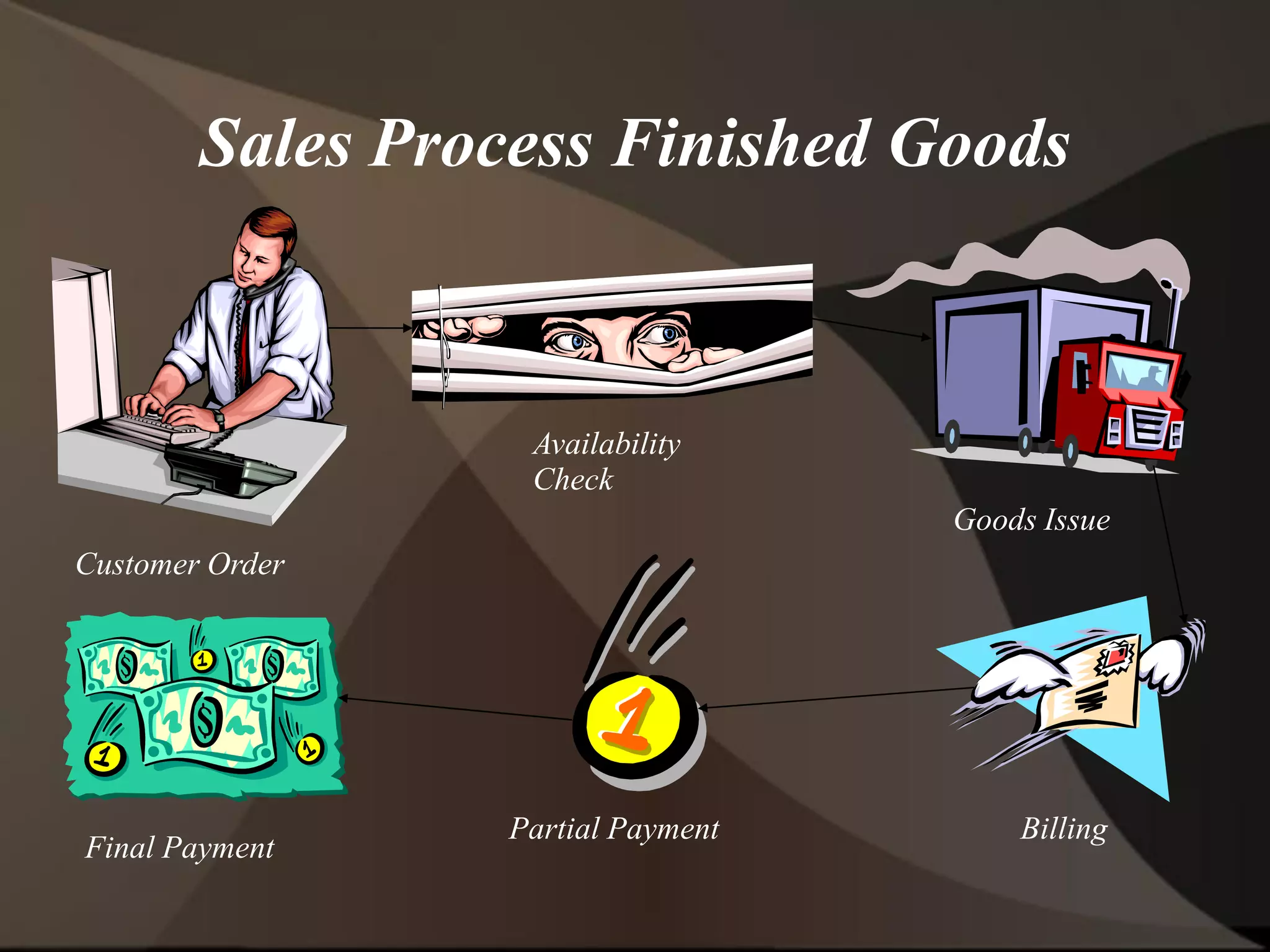
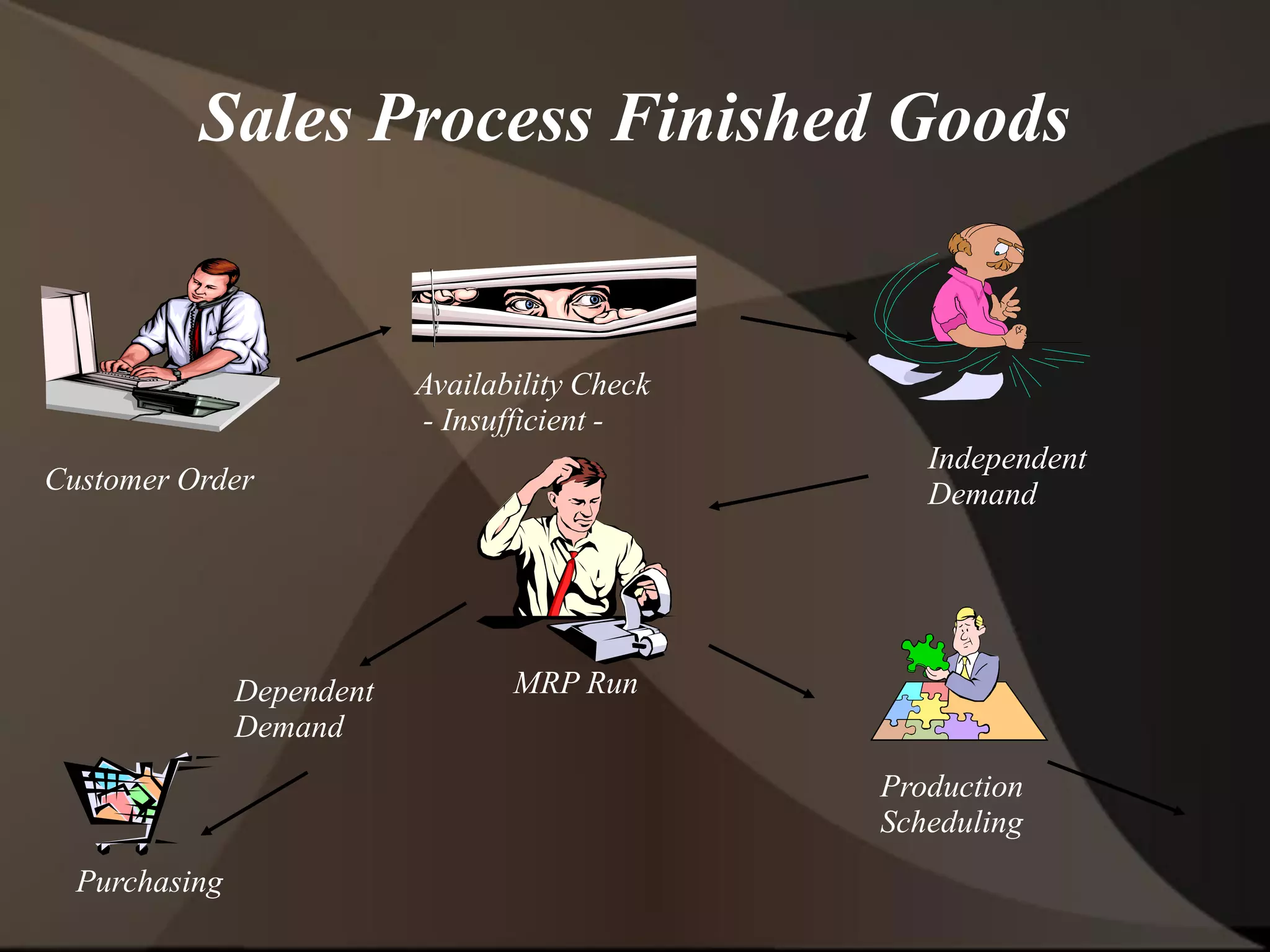
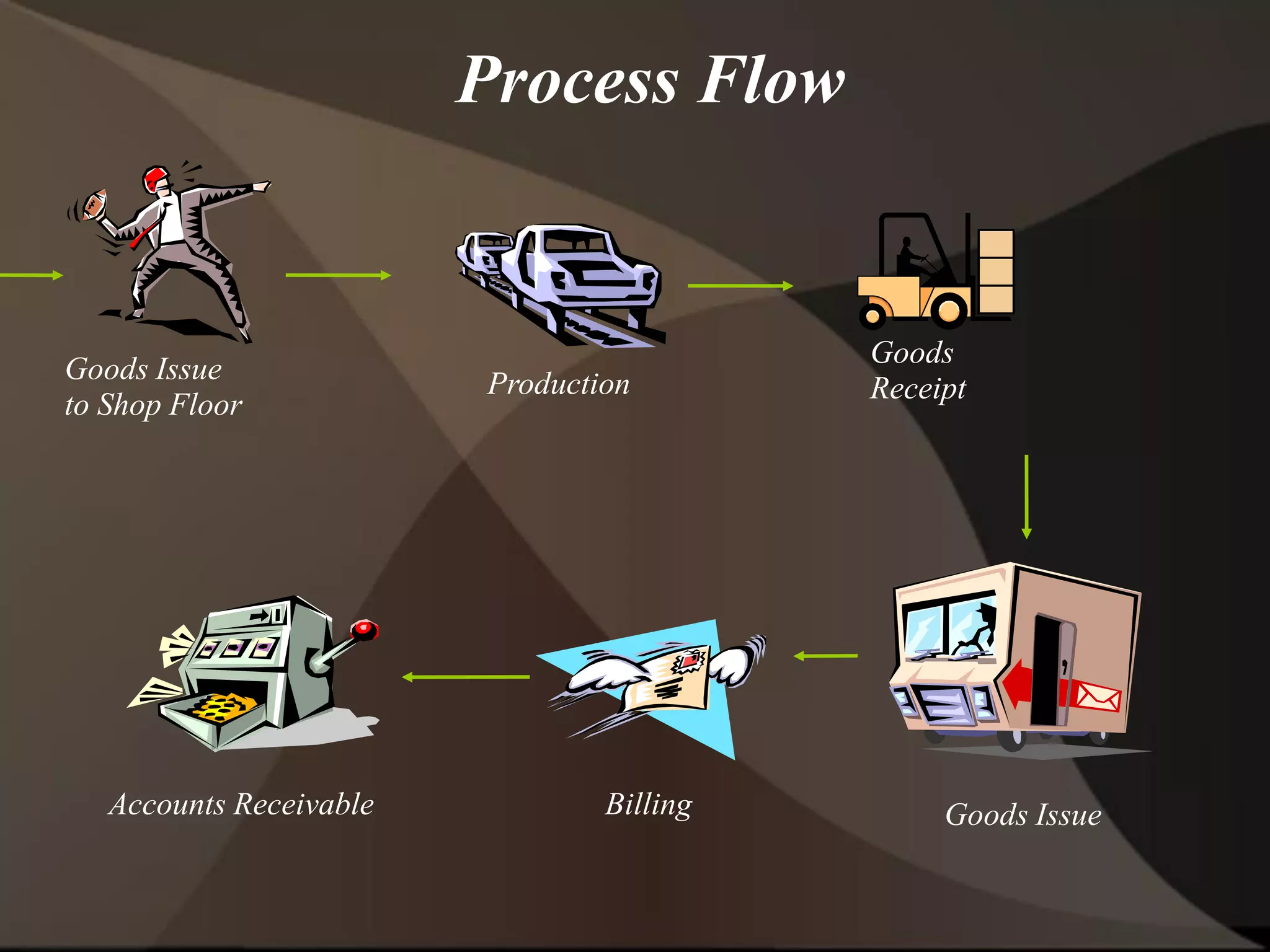
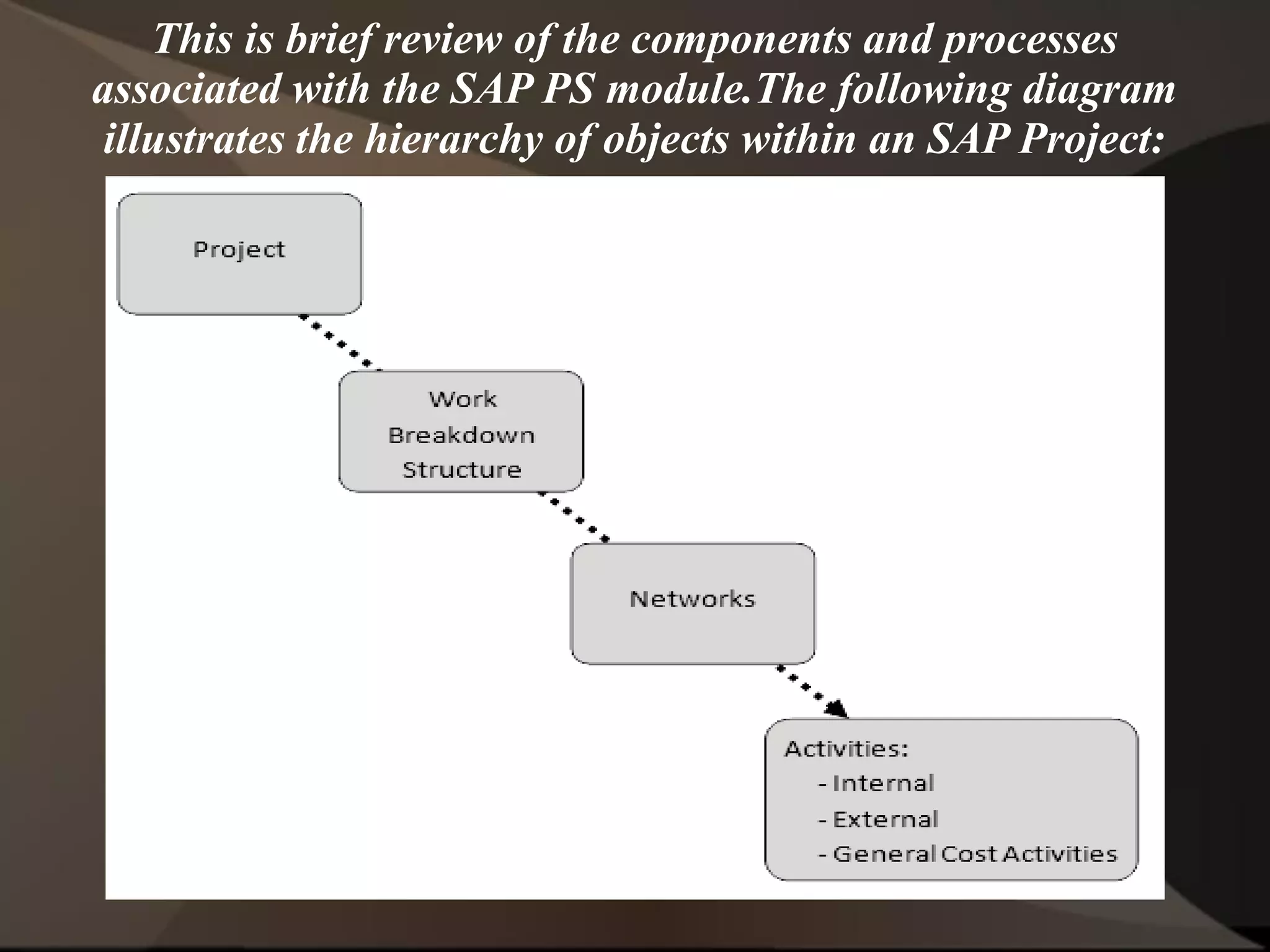
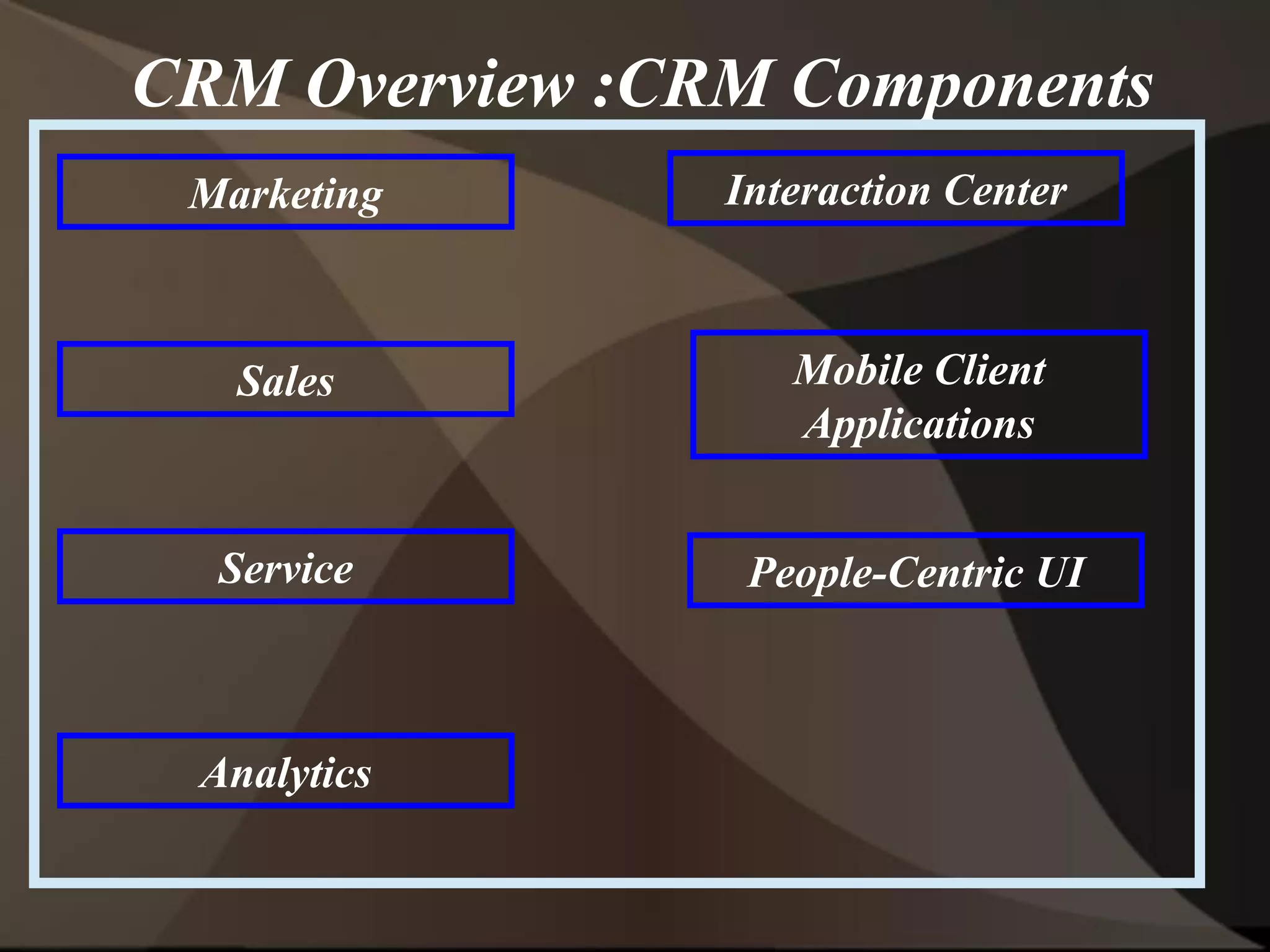
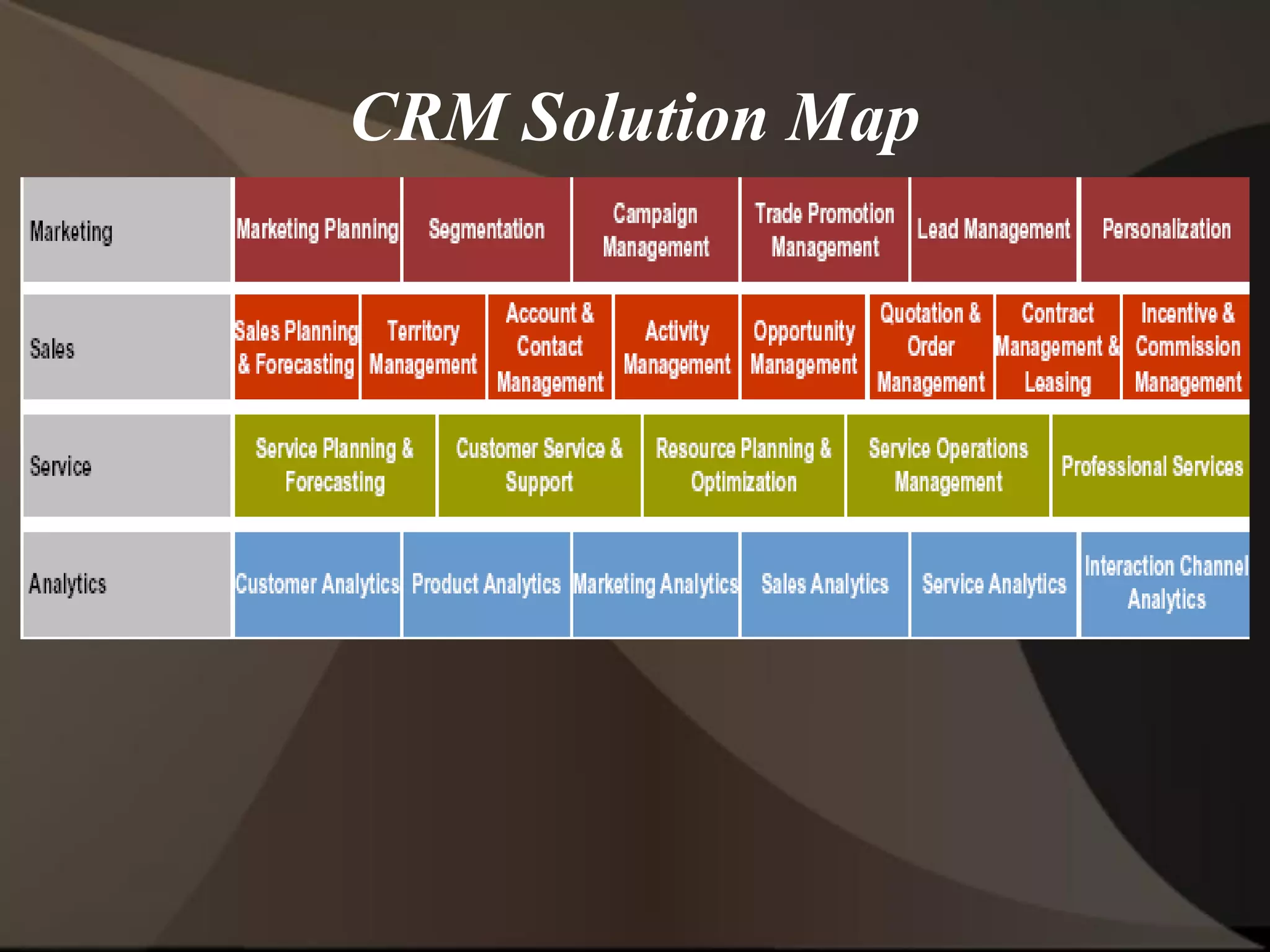
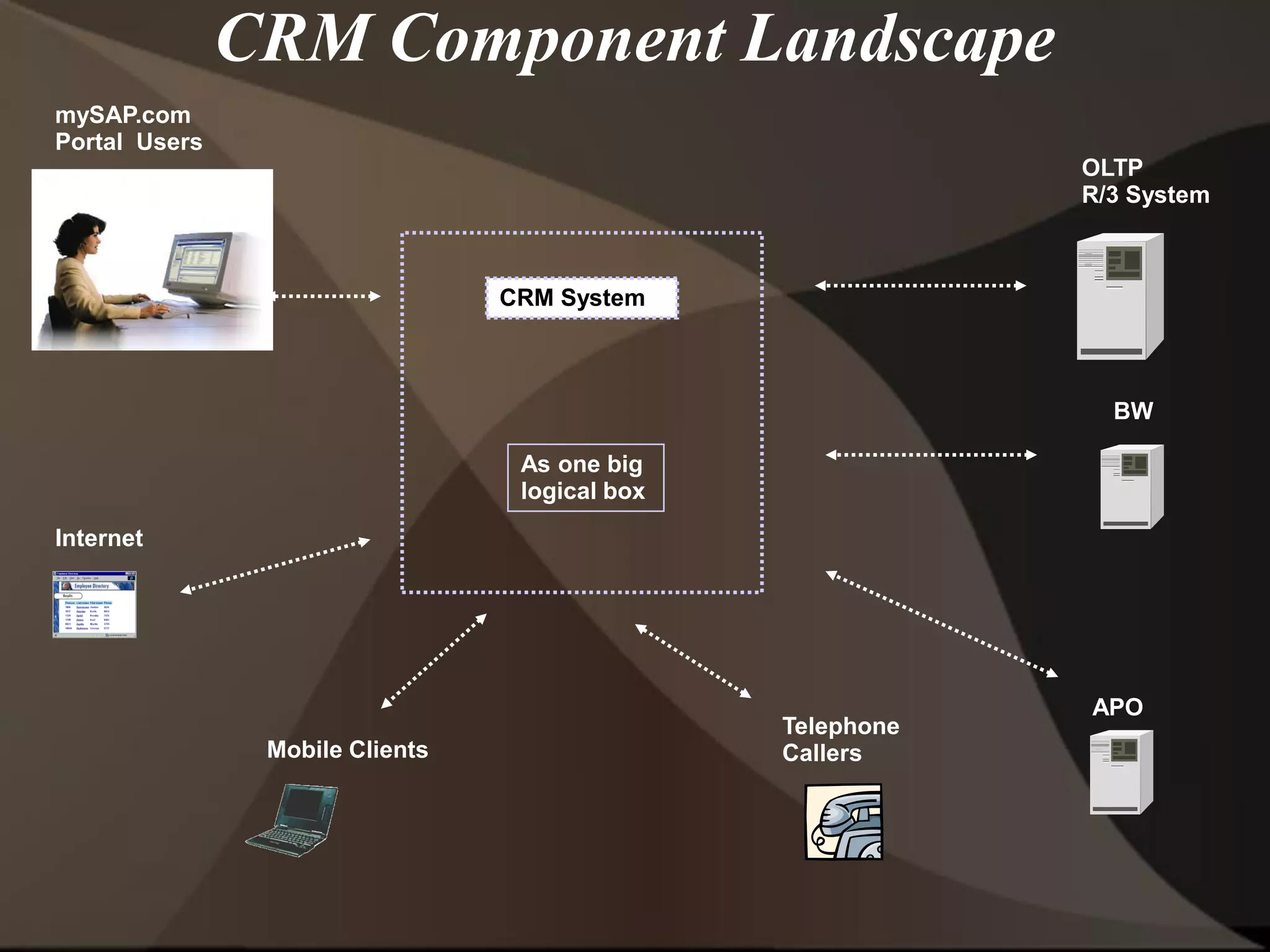
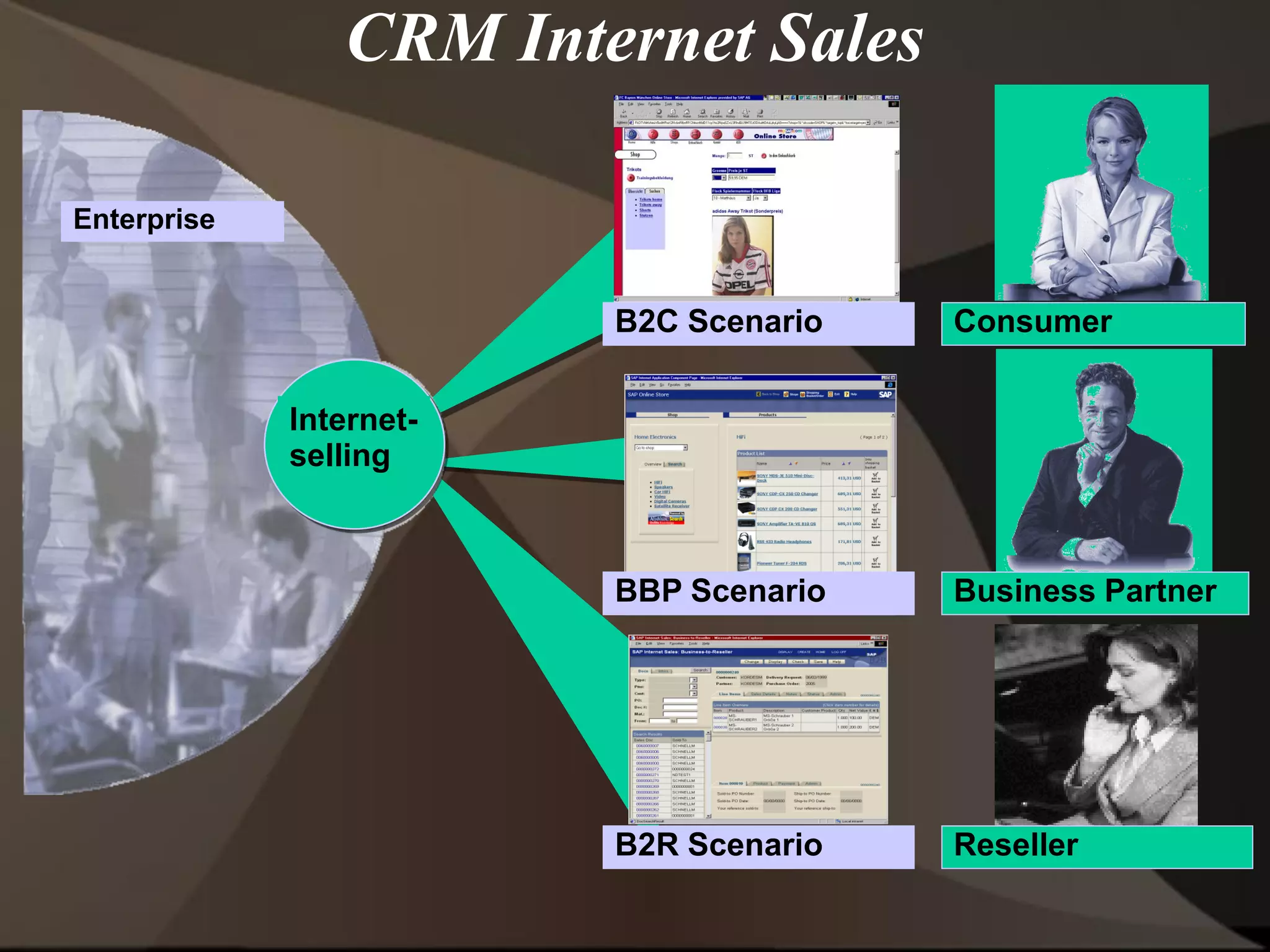
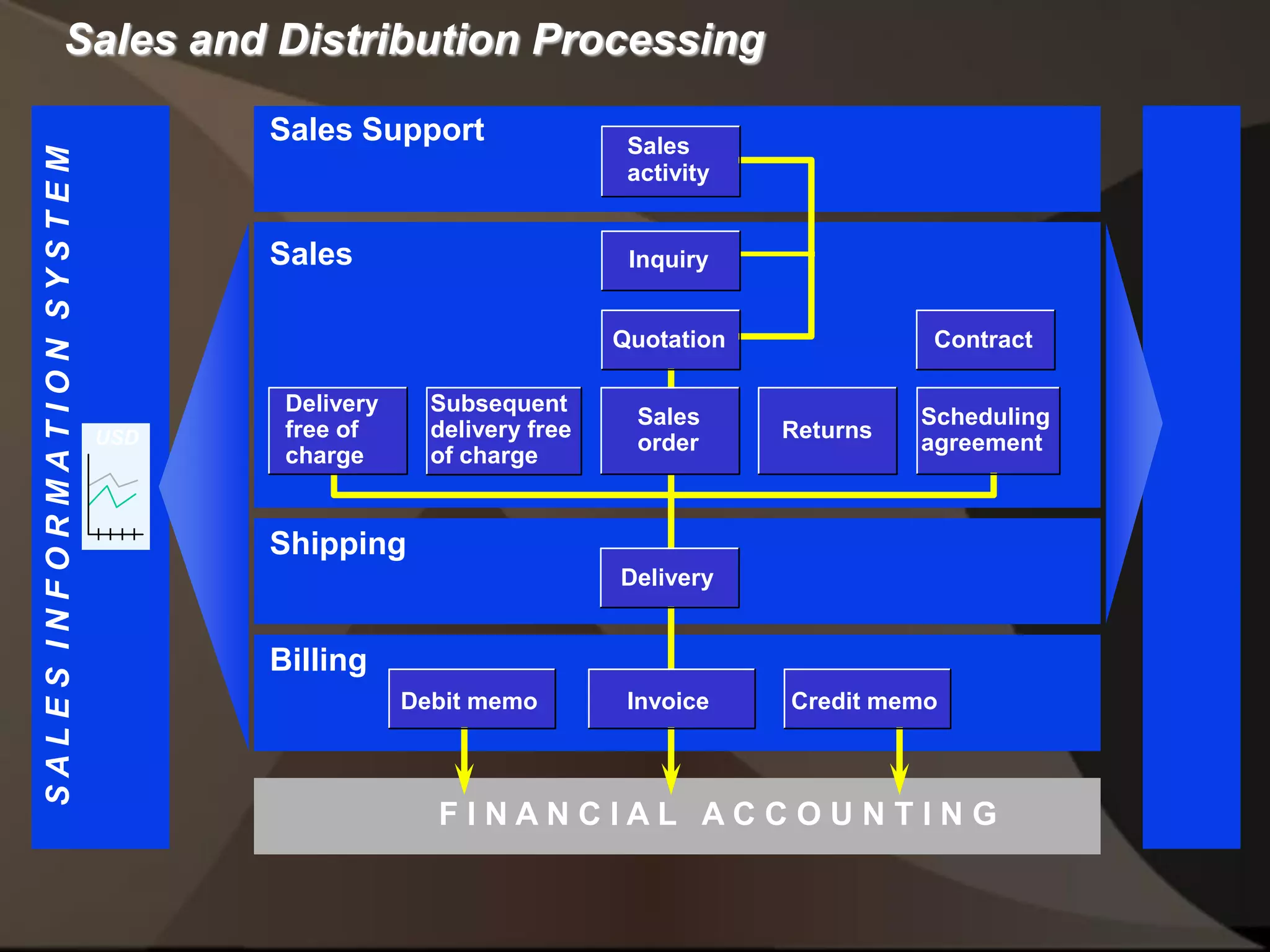
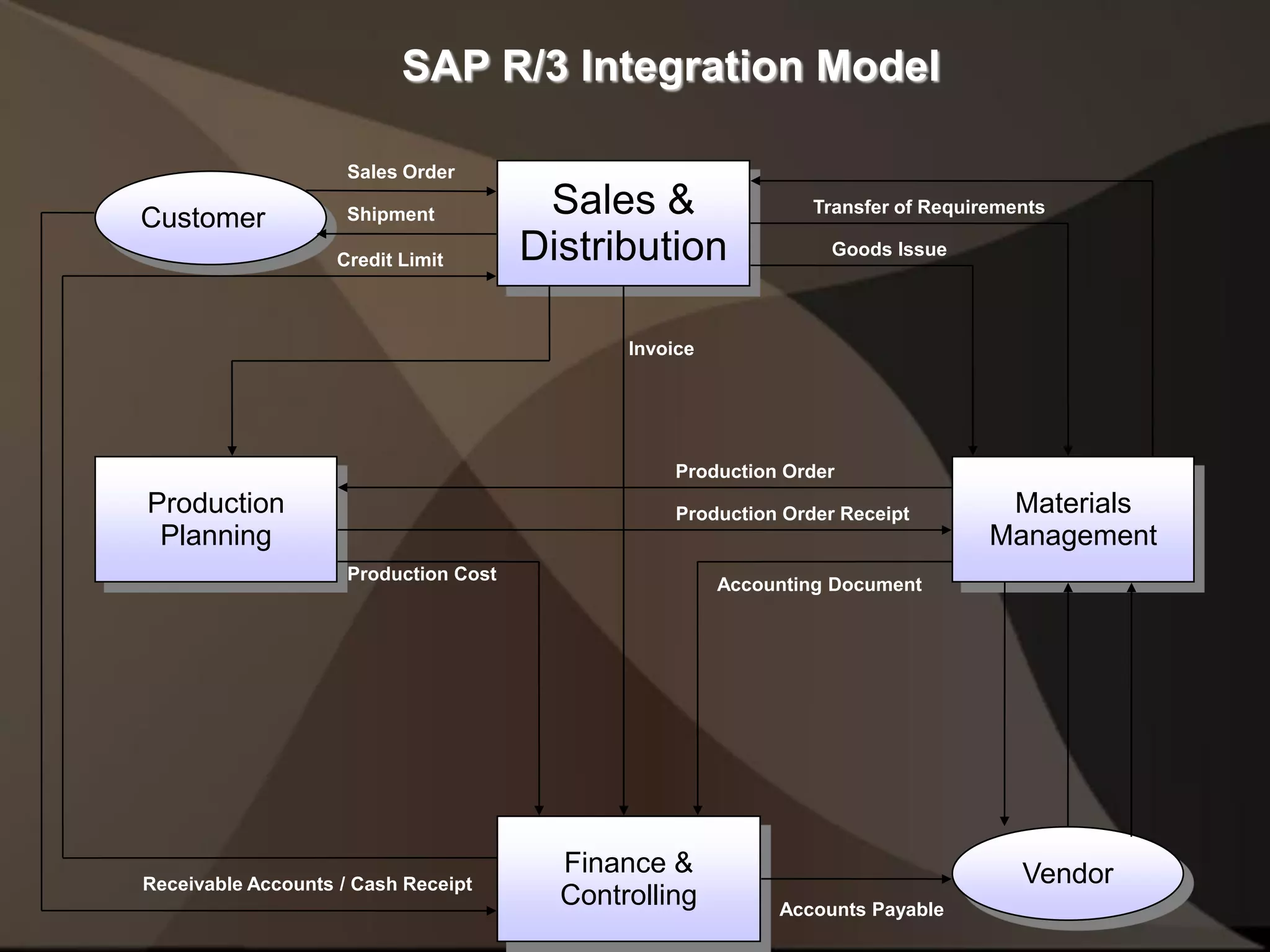
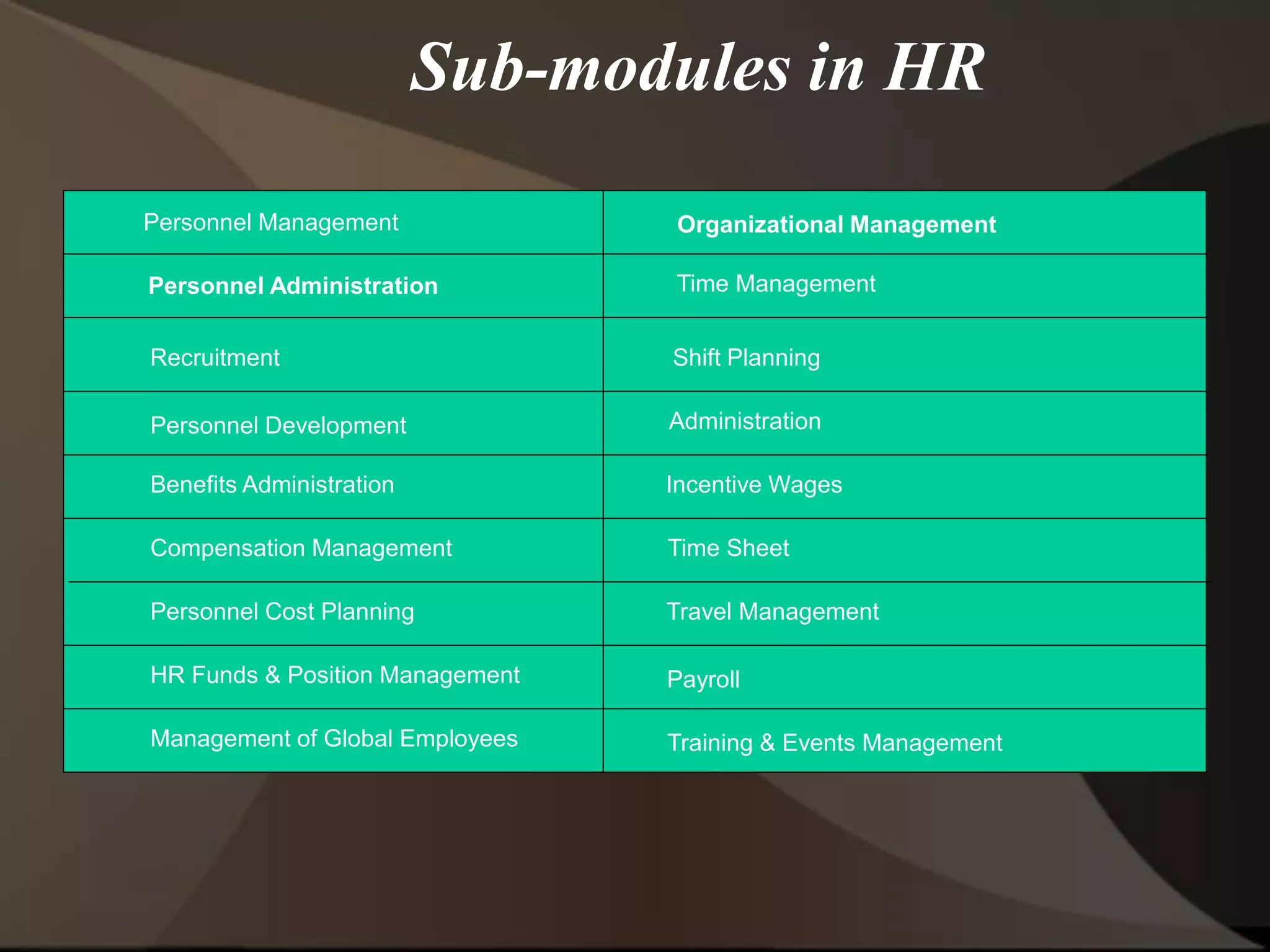
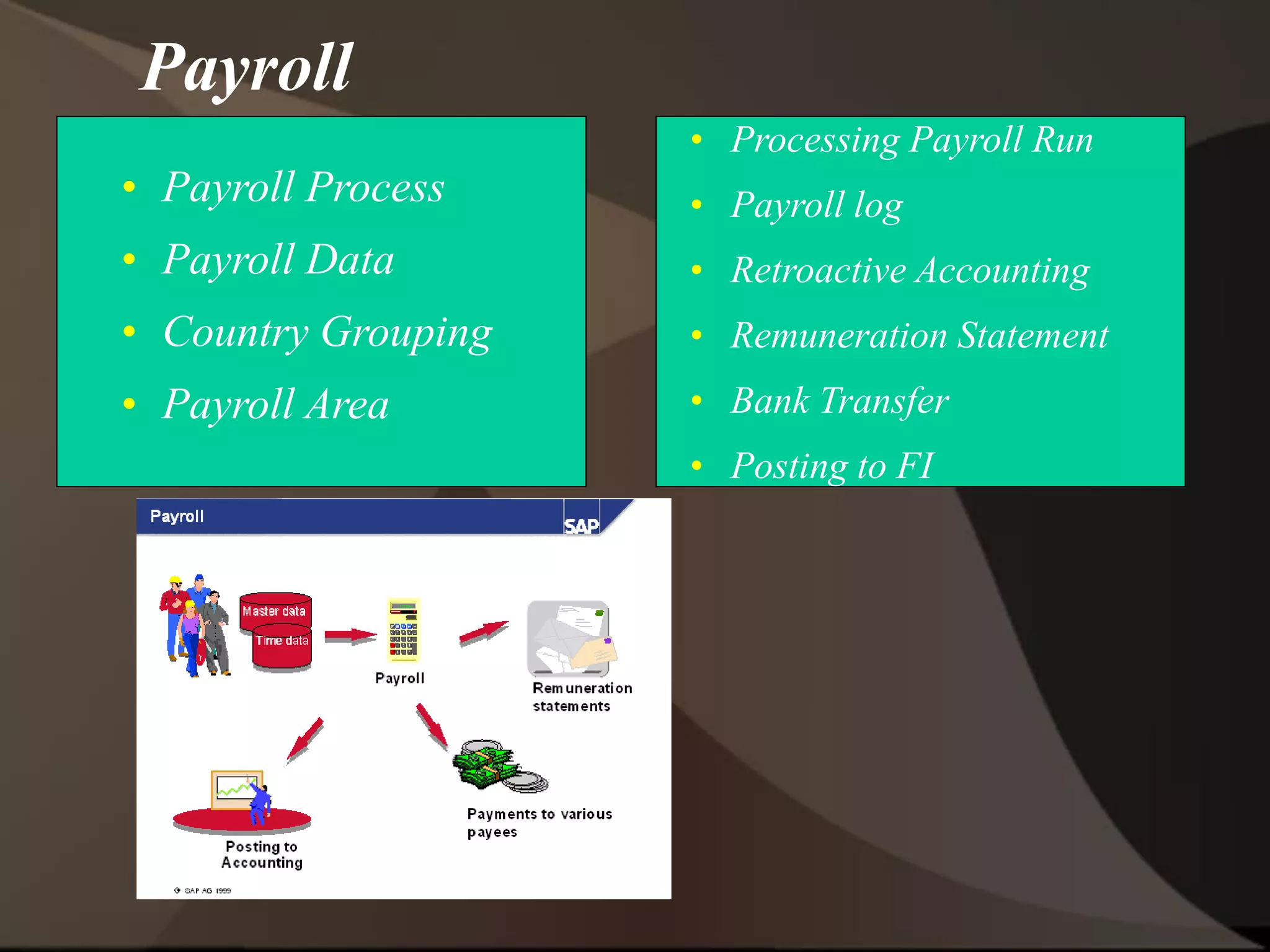
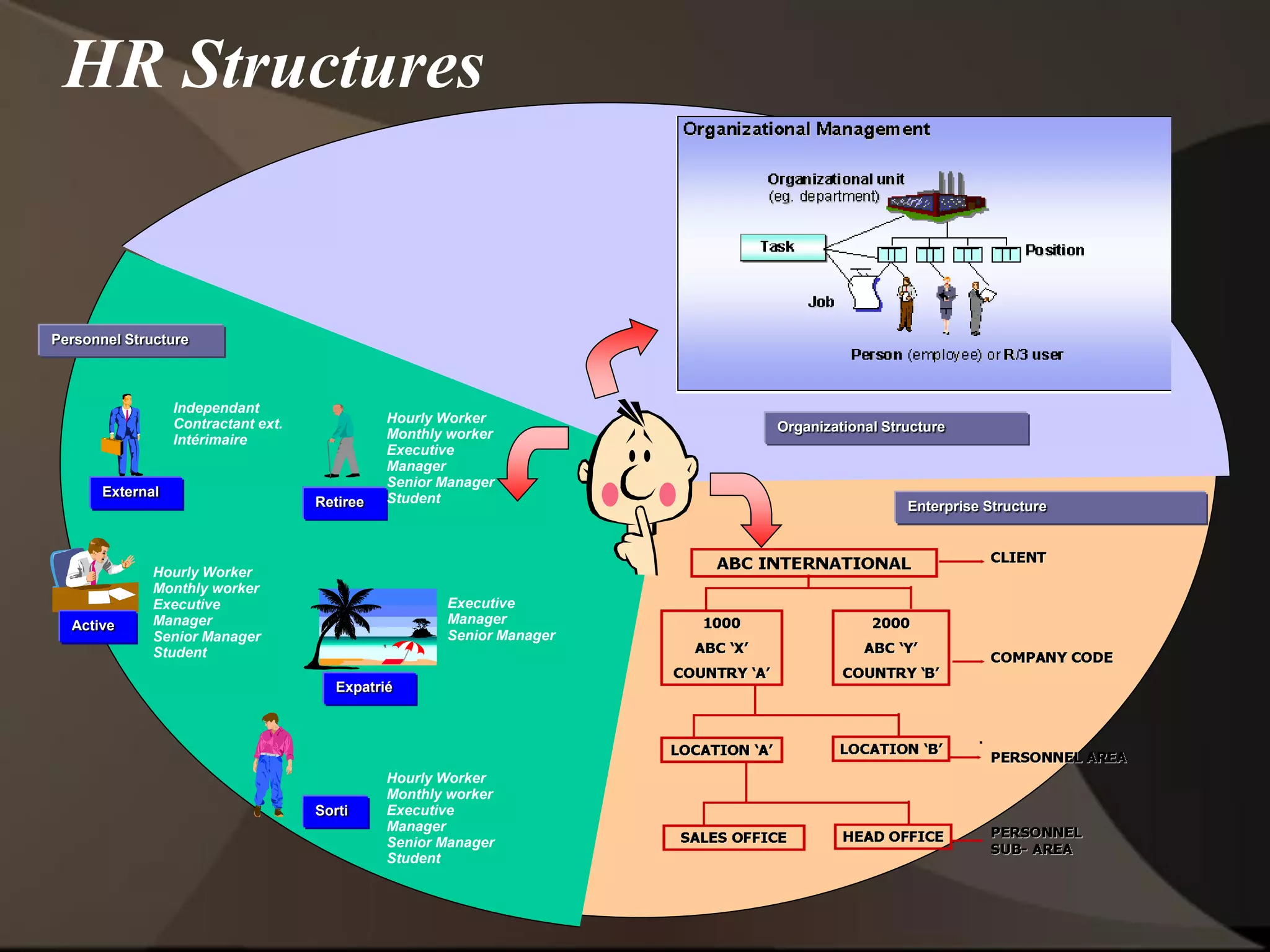
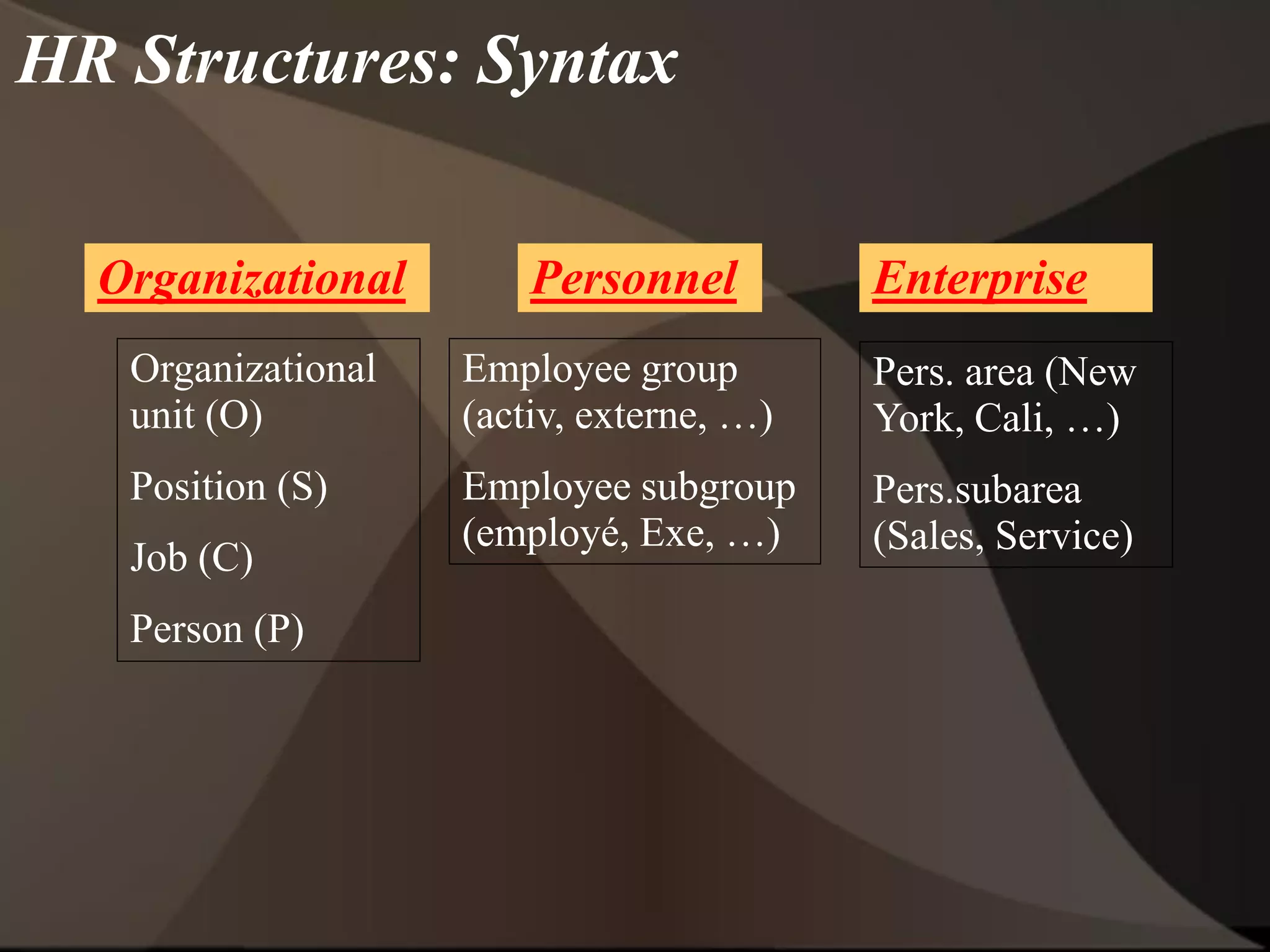
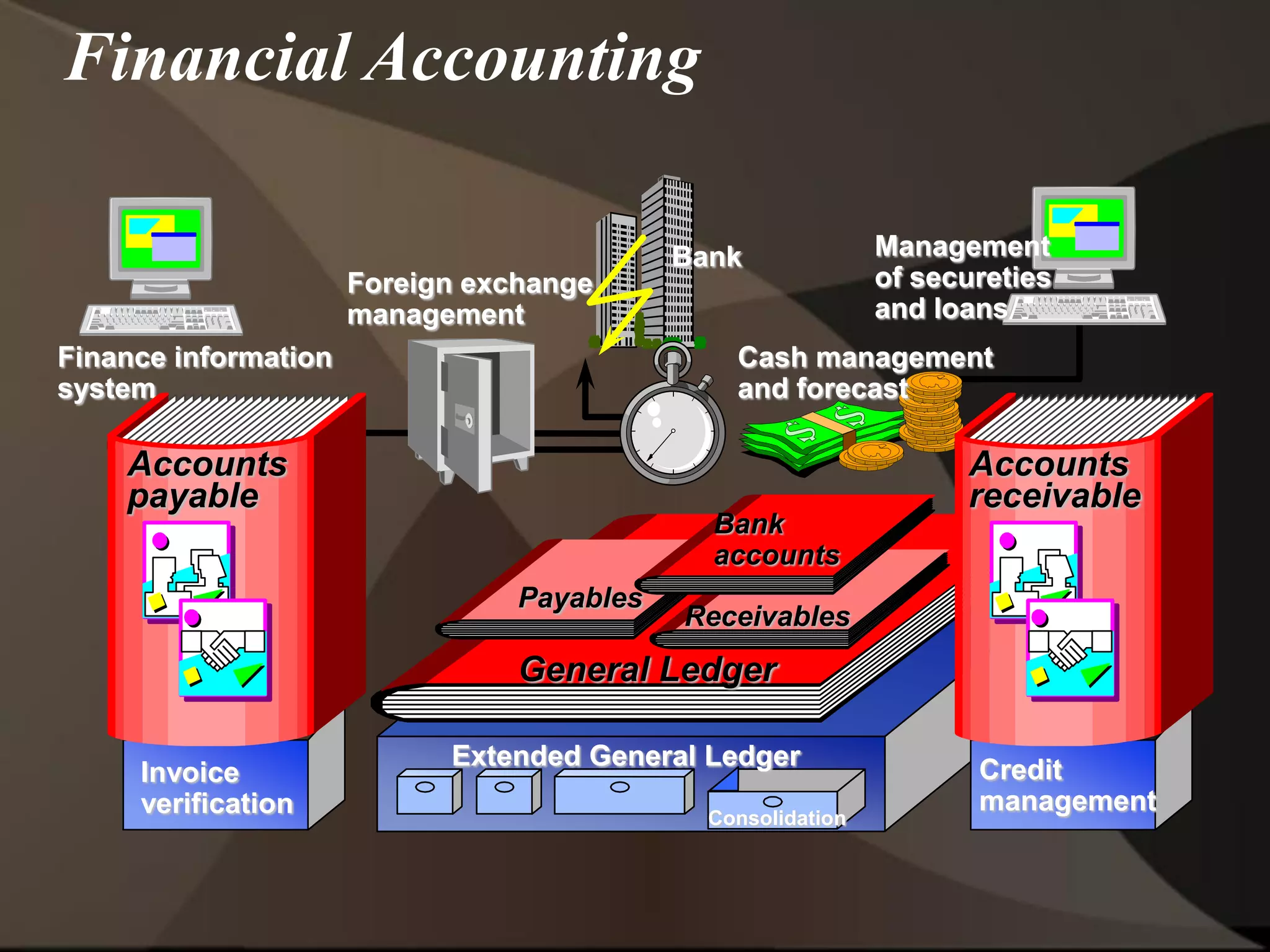
The document provides an overview of ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and SAP. It defines ERP as a system that integrates business functions like finance, manufacturing, supply chain, and human resources. SAP is an ERP software package that covers all enterprise business functions in an integrated manner. The document also discusses some key SAP modules like Sales and Distribution, Materials Management, Production Planning, Project Systems, CRM and SAP HR. It provides a brief introduction to various SAP concepts like client, three-tier architecture and ASAP methodology.