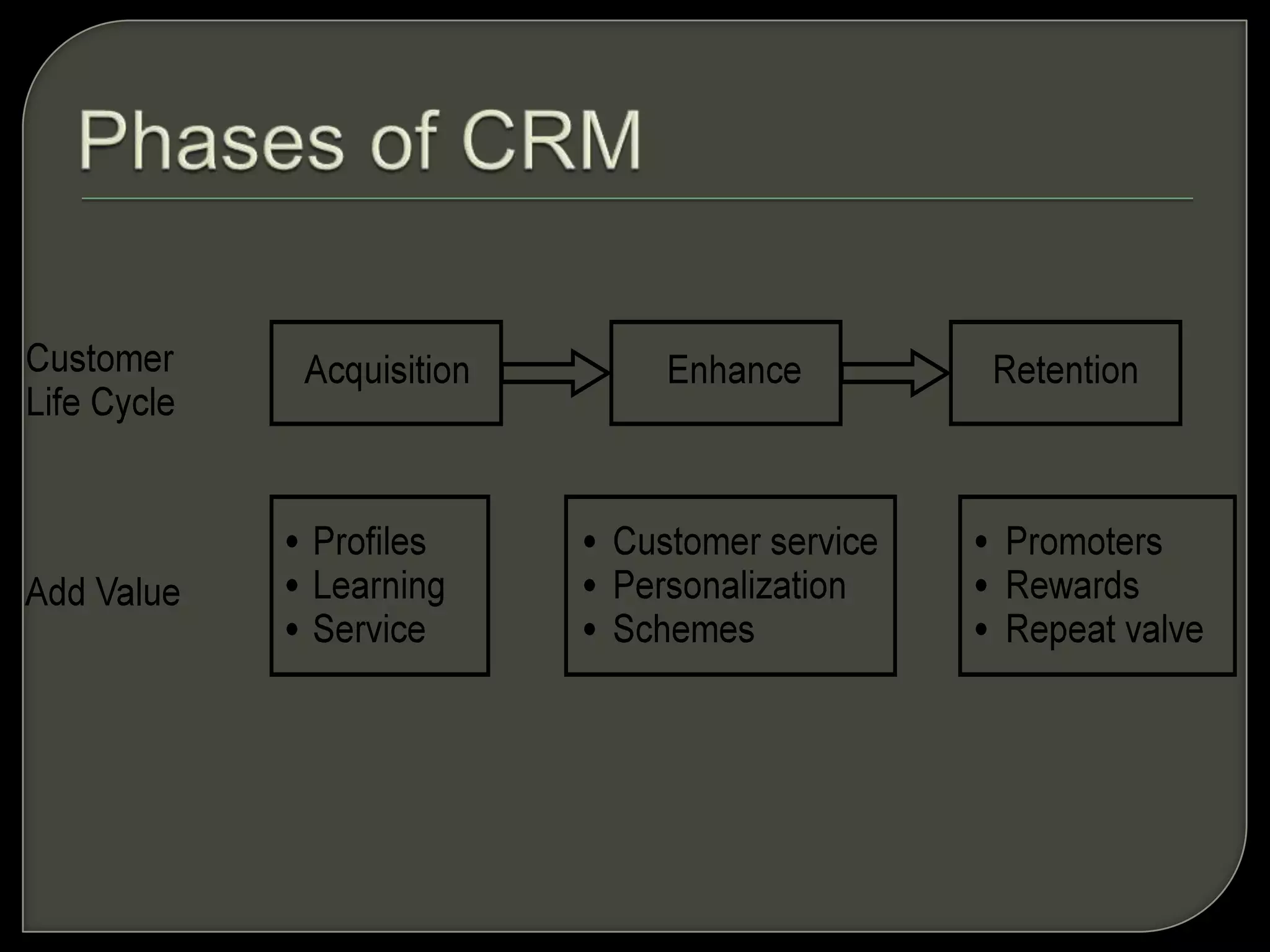
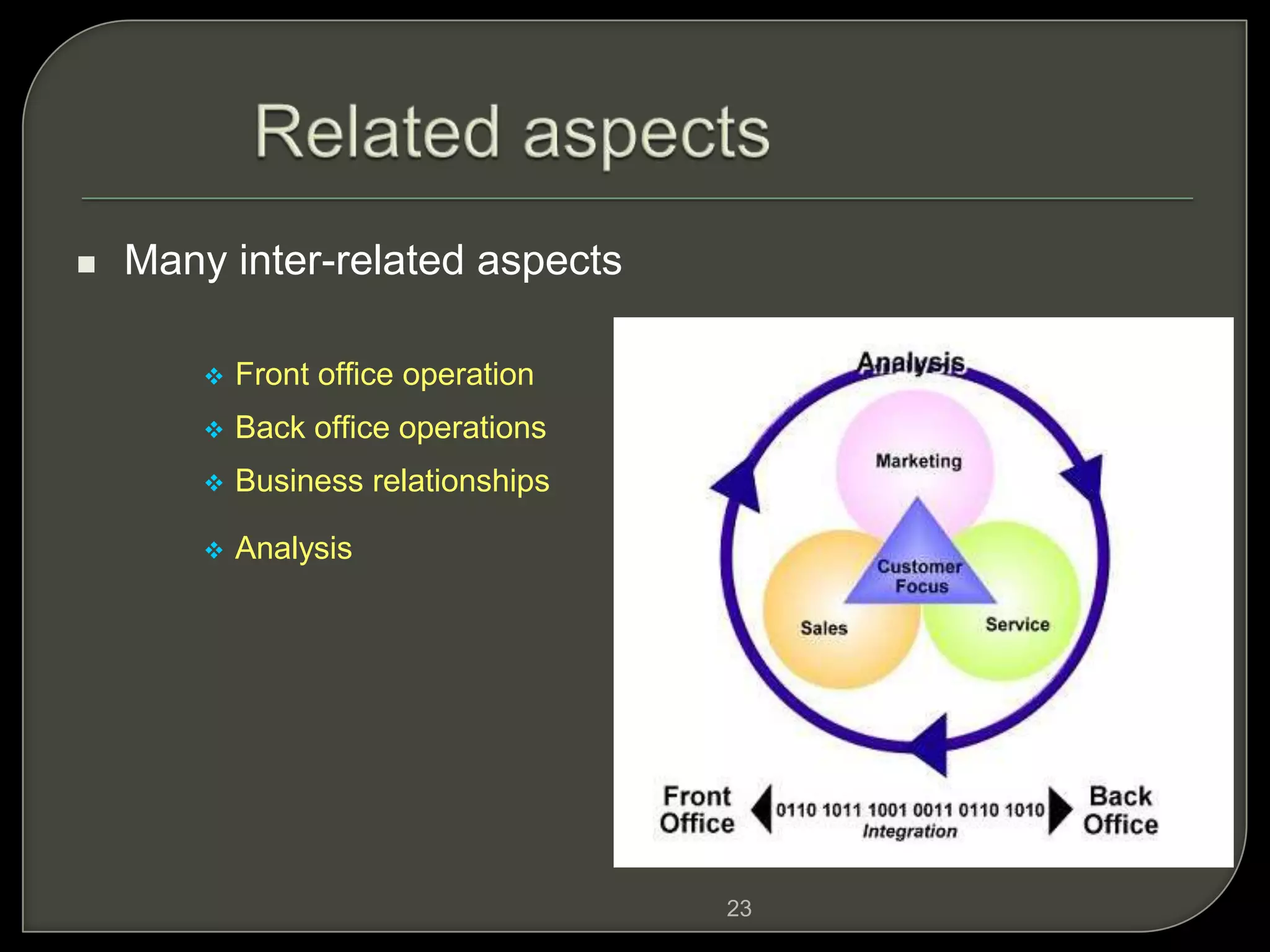
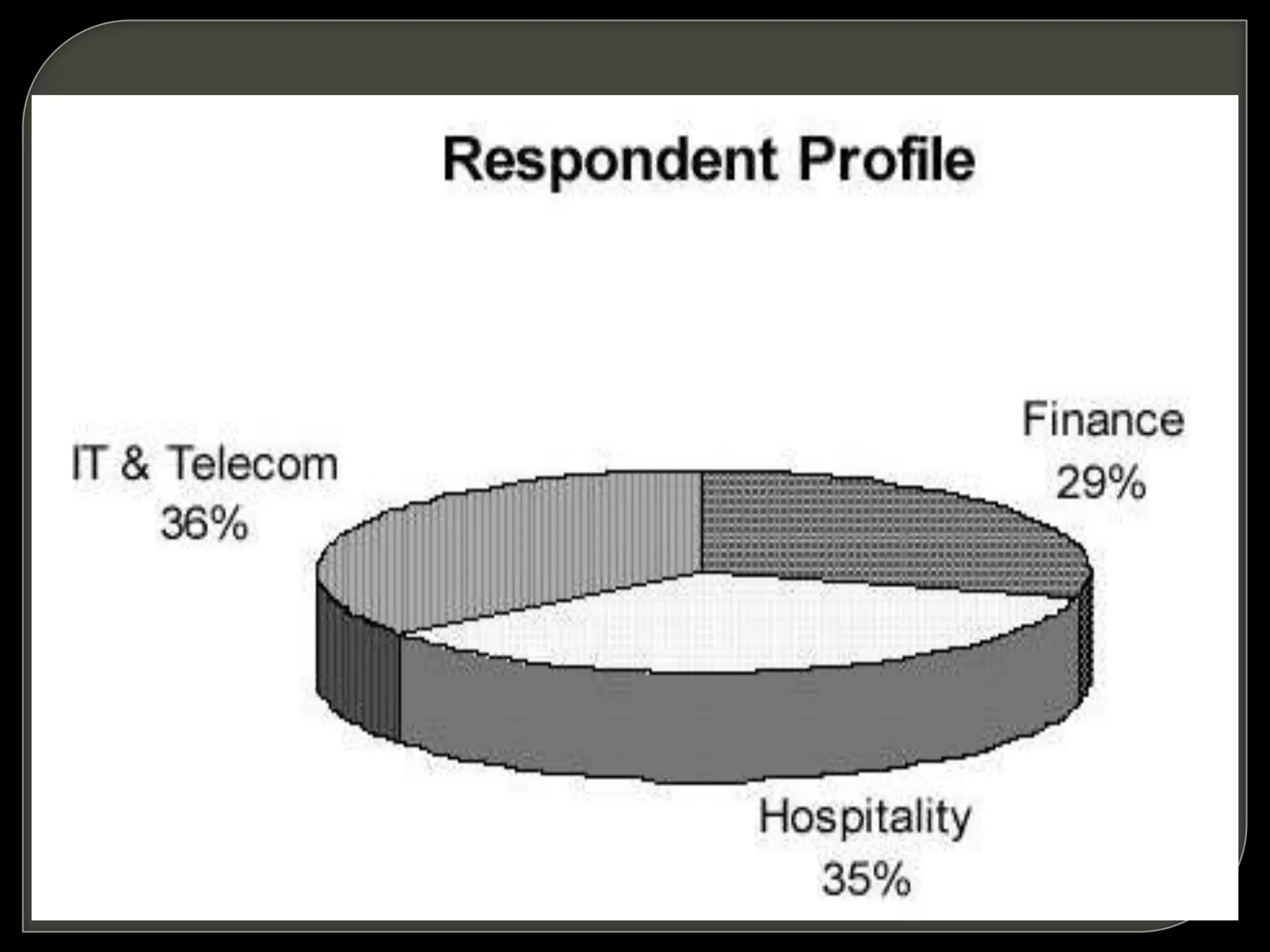
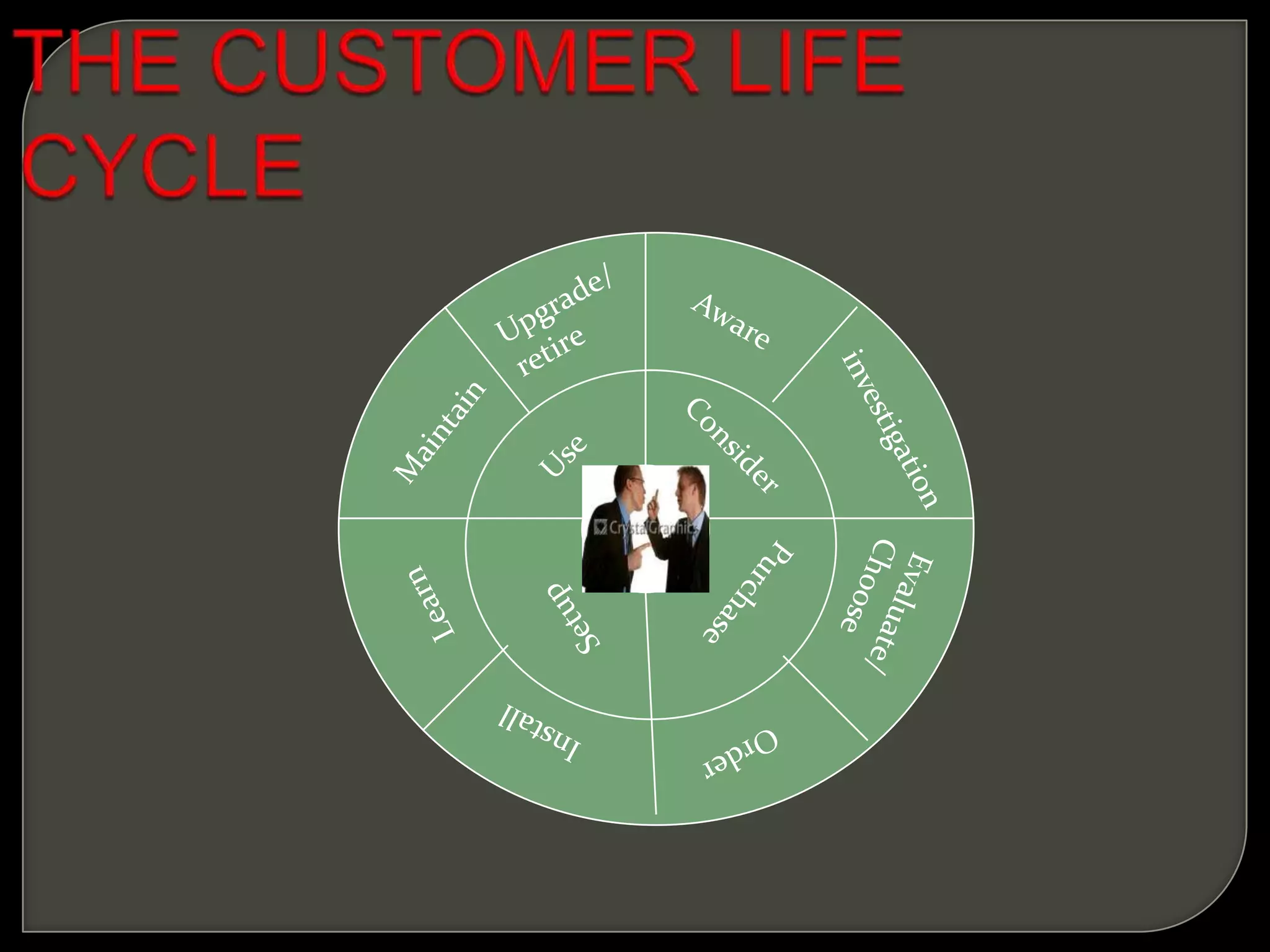
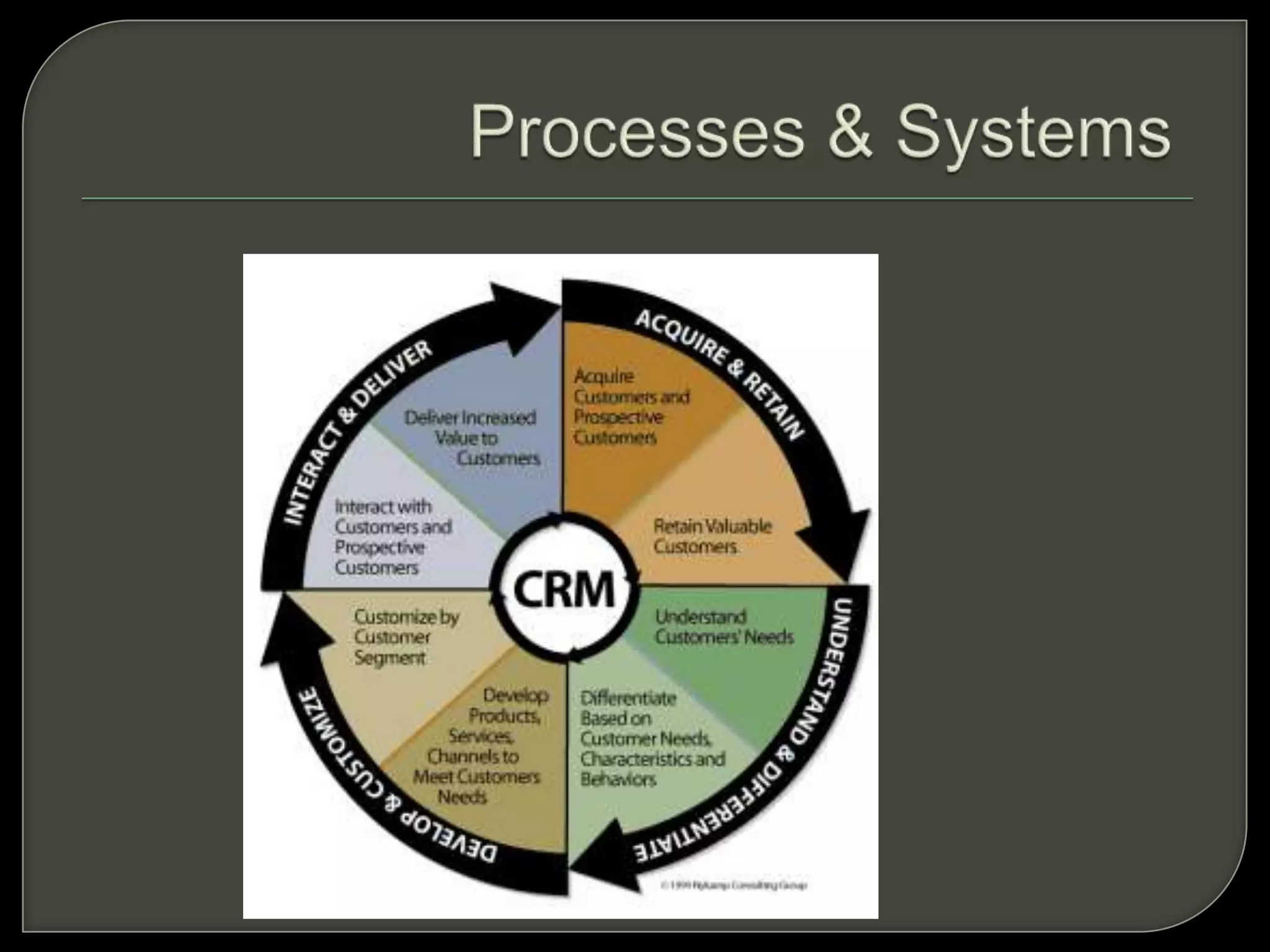
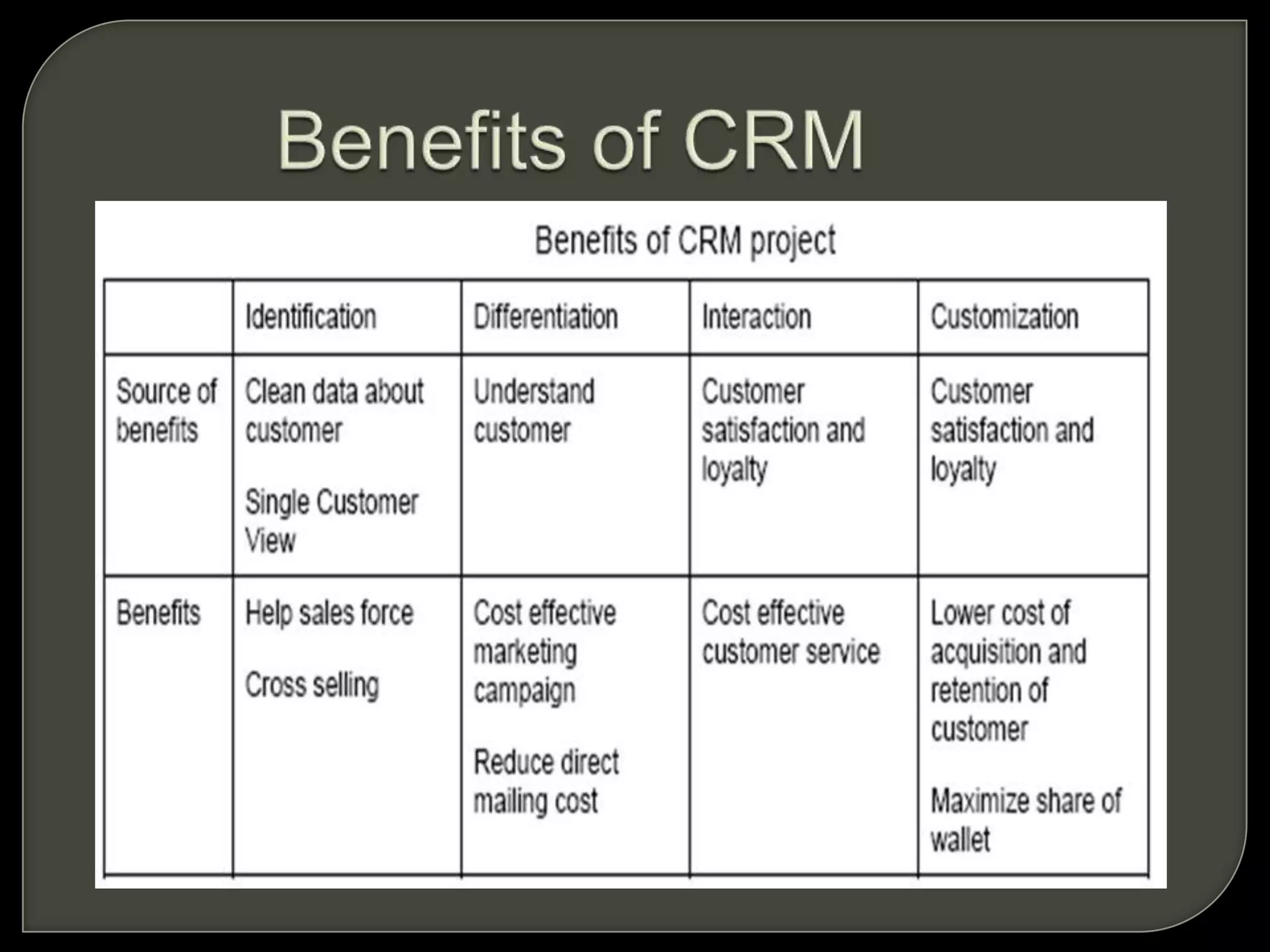
Customer relationship management (CRM) refers to the processes and technologies used to manage relationships with customers. It involves tracking customer interactions across sales, marketing, customer service, and other functions. The key components of CRM include contact and account management, sales, marketing and fulfillment, customer service and support, and retention and loyalty programs. CRM systems allow companies to better understand customer needs and provide personalized customer experiences.