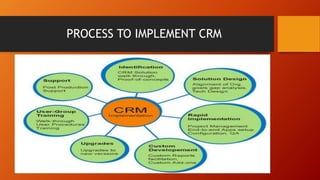
CRM involves understanding customer needs and developing strong relationships to retain customers and gain a competitive advantage. It includes collecting customer data, analyzing that data to understand customer behaviors, and using those insights to improve customer service and target marketing efforts. There are different types of CRM approaches like analytical, collaborative, operational, geographic, and sales intelligence CRM. Implementing a successful CRM strategy requires assessing current business practices, choosing an appropriate CRM model, ensuring proper IT infrastructure, and selecting partners and vendors. The goal of CRM is reduced costs, increased customer satisfaction and retention, and long-term profitability.