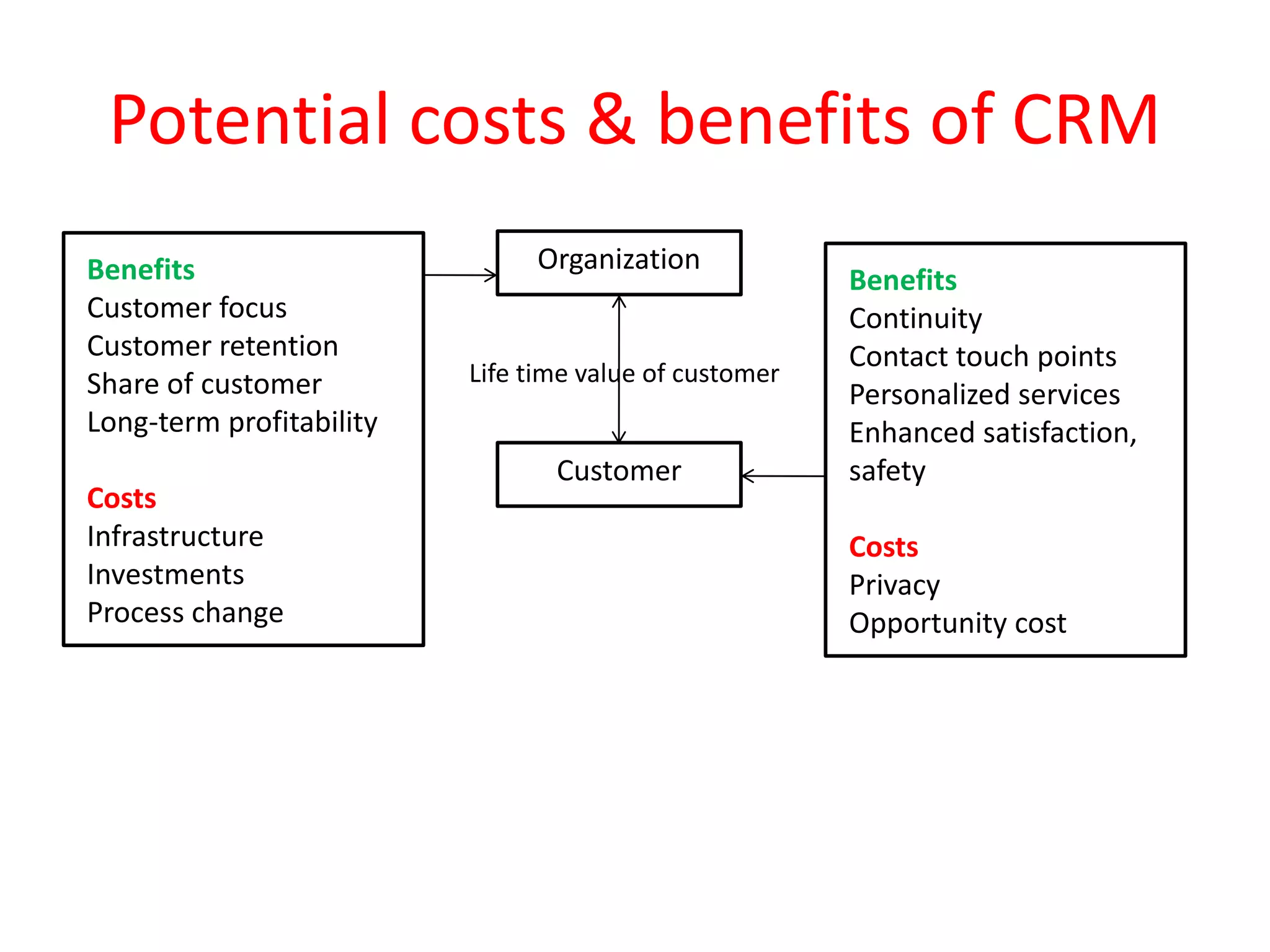
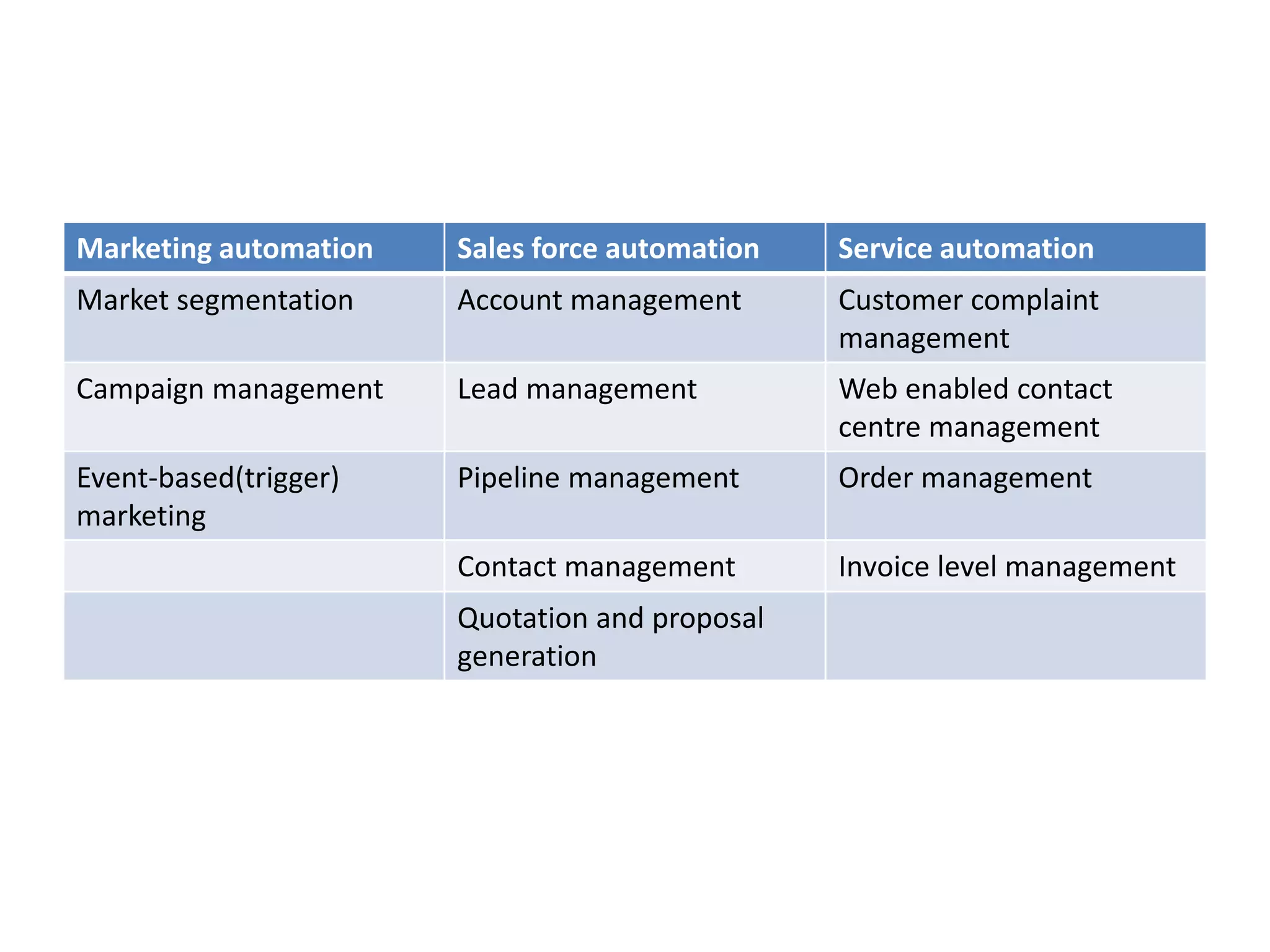
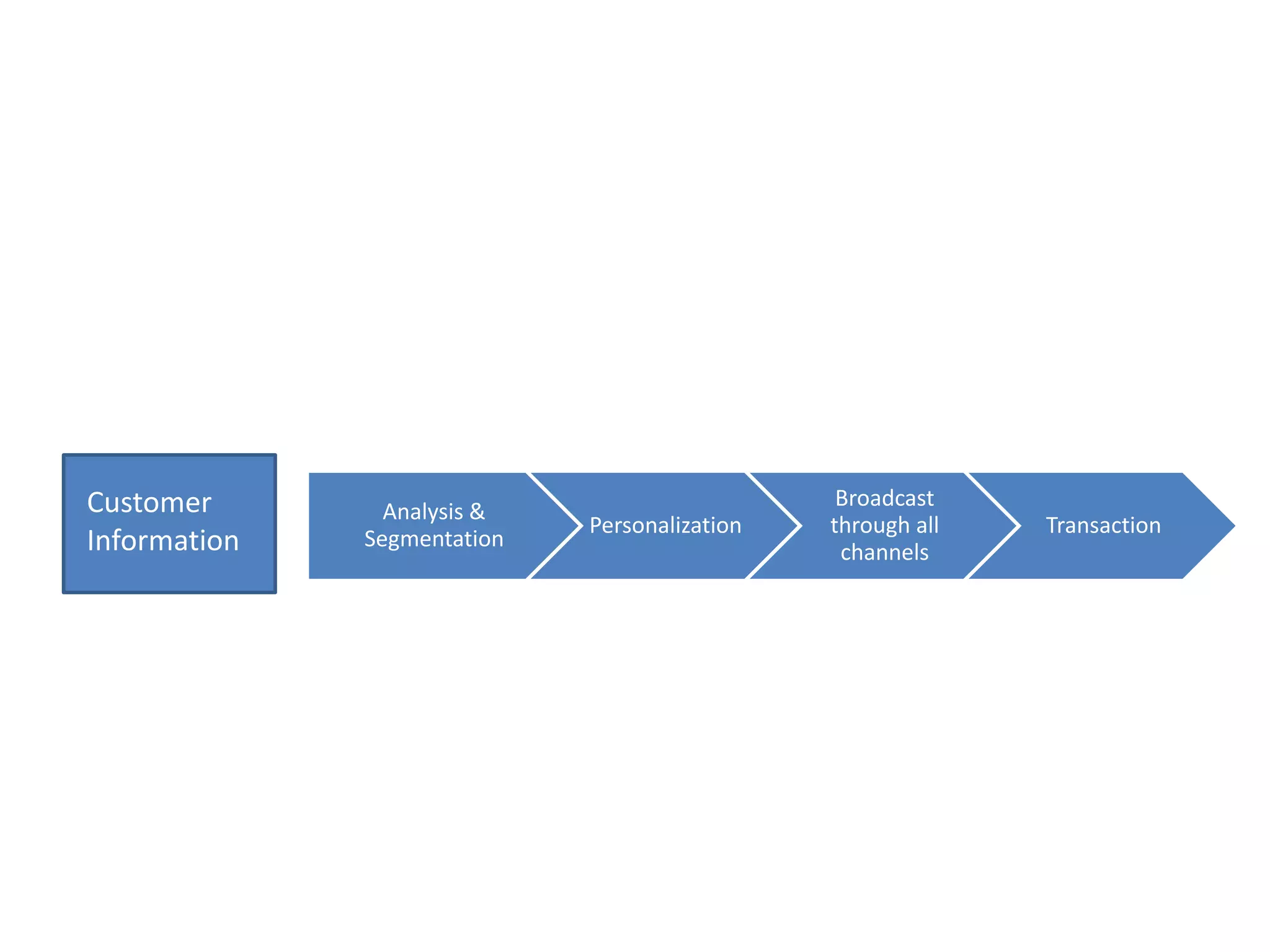
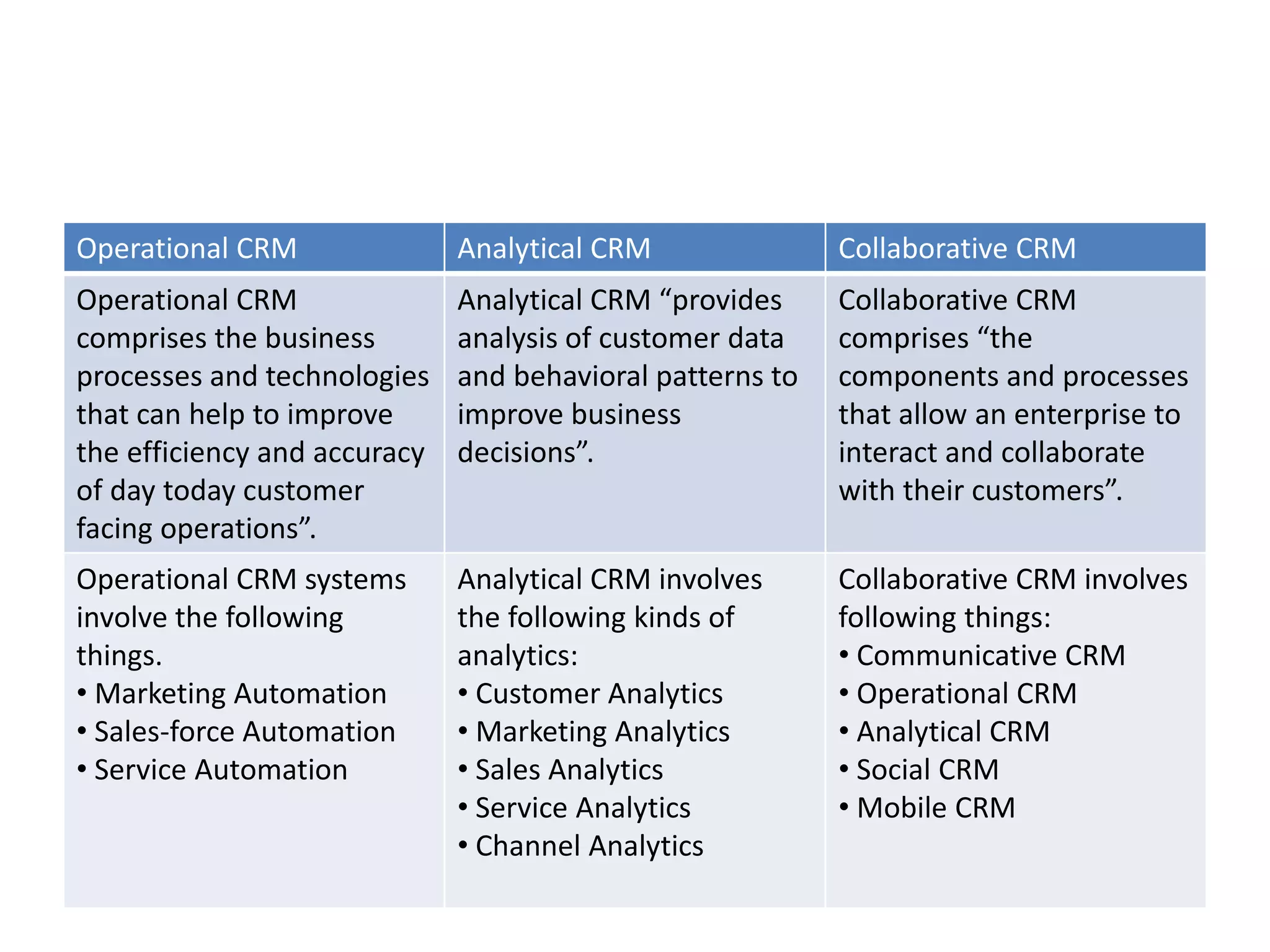
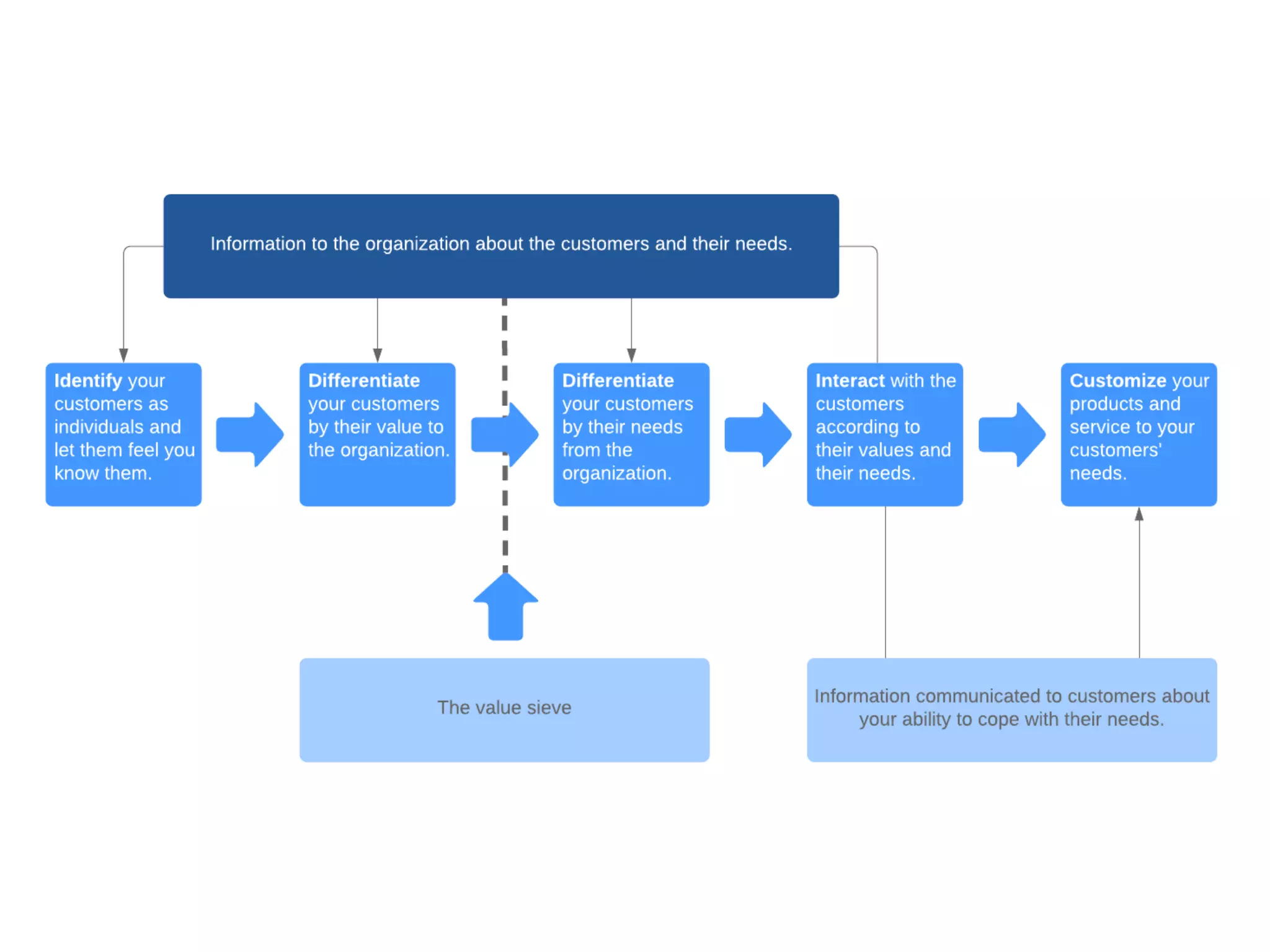
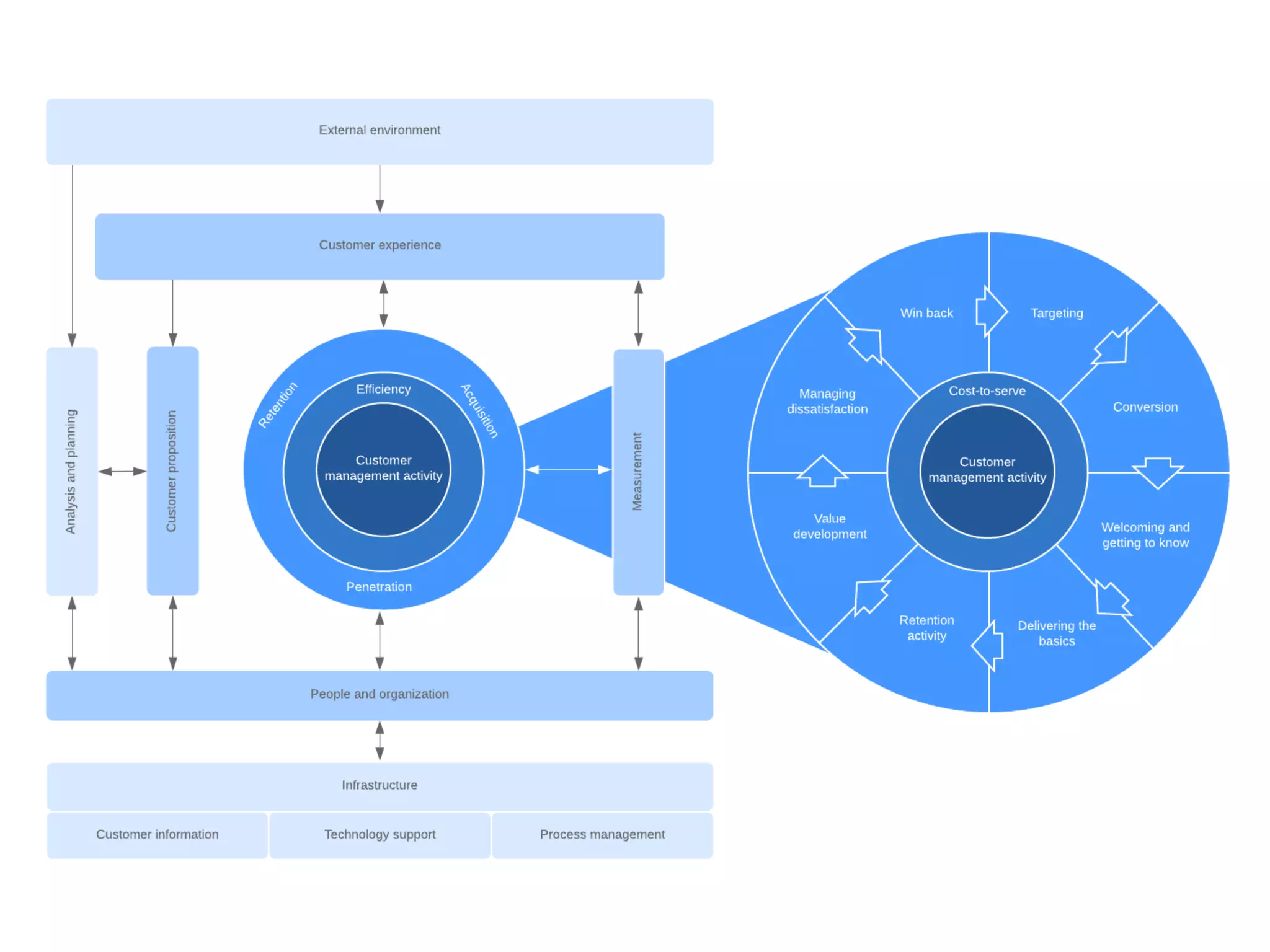
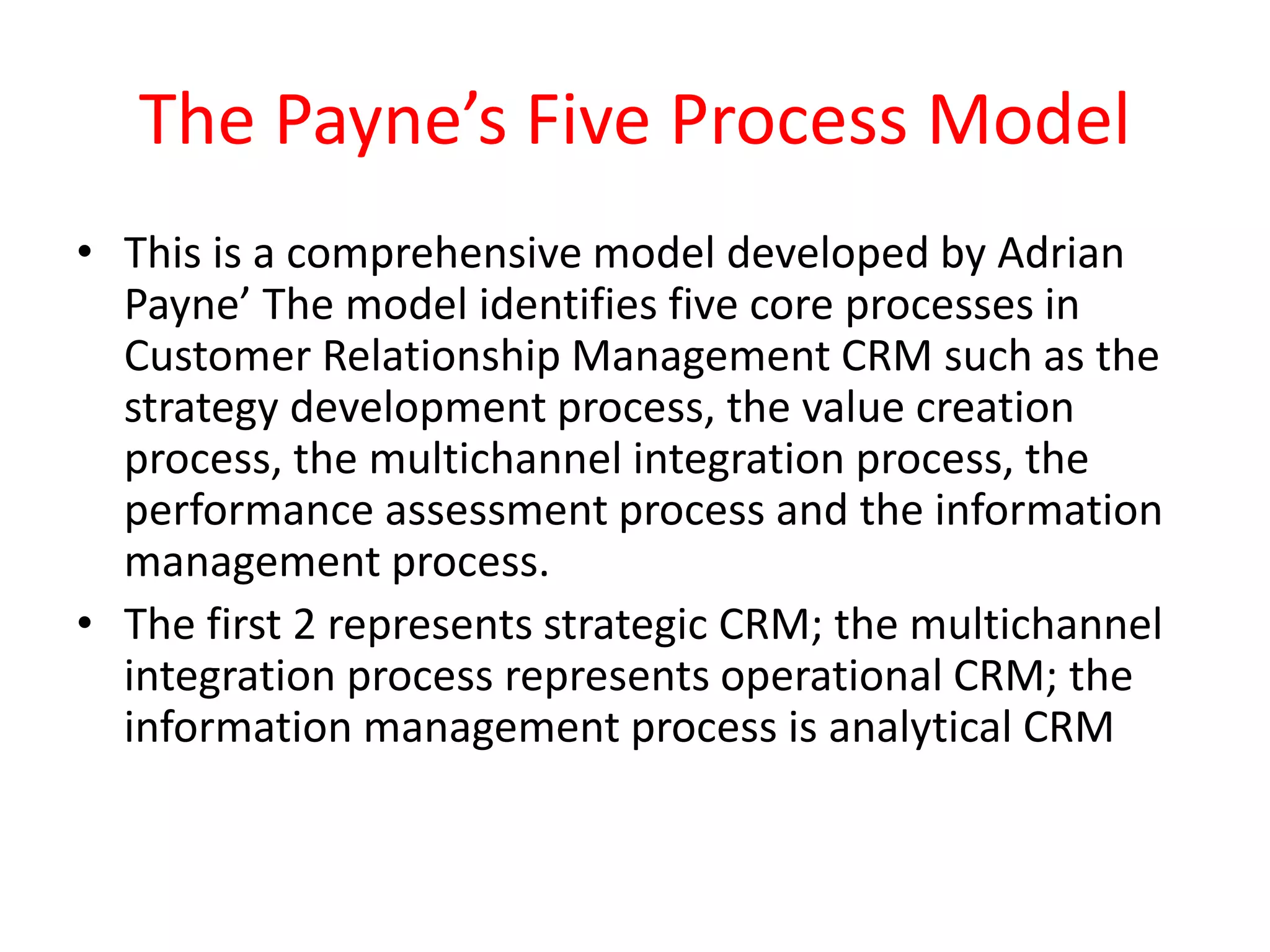
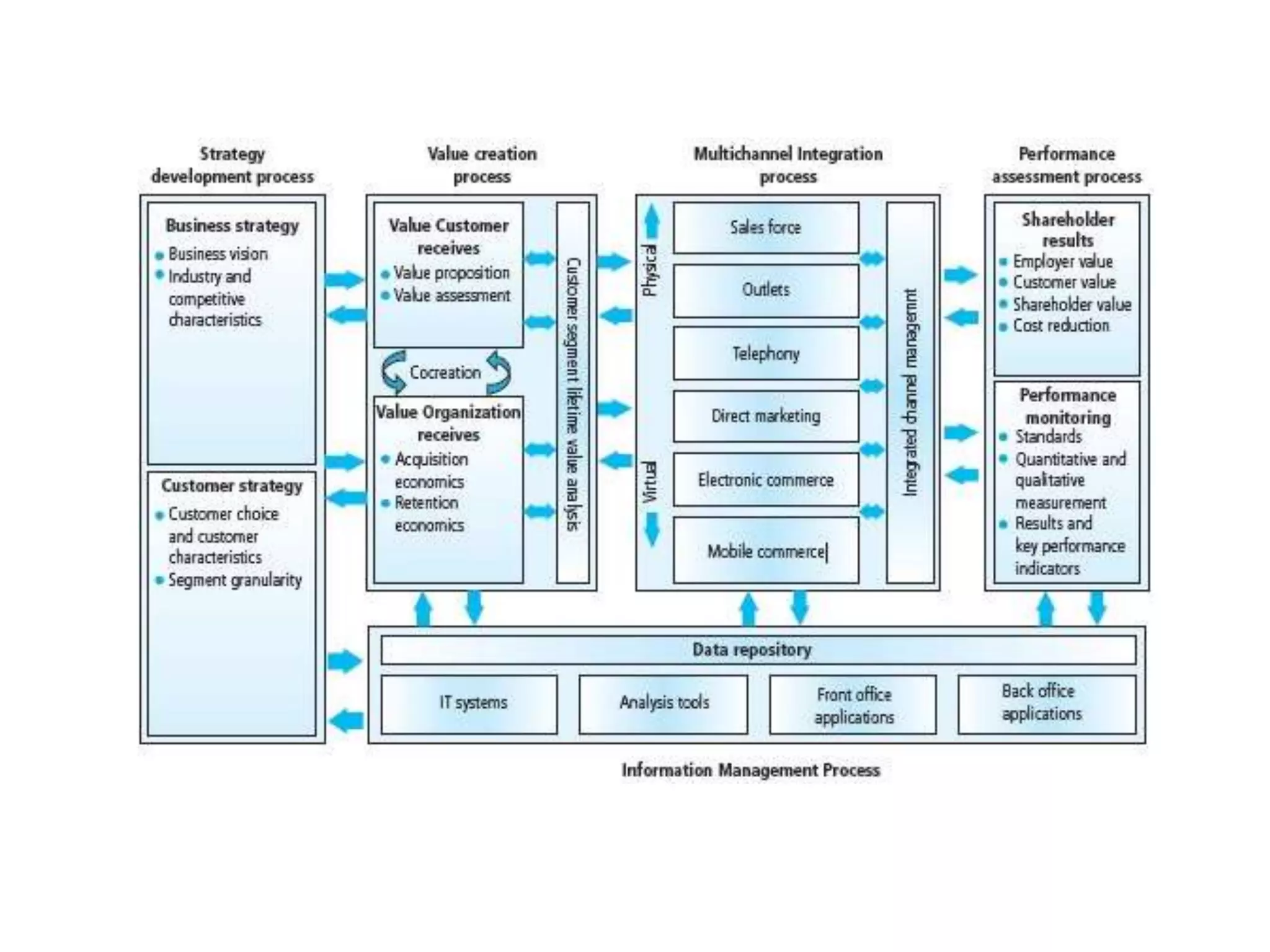
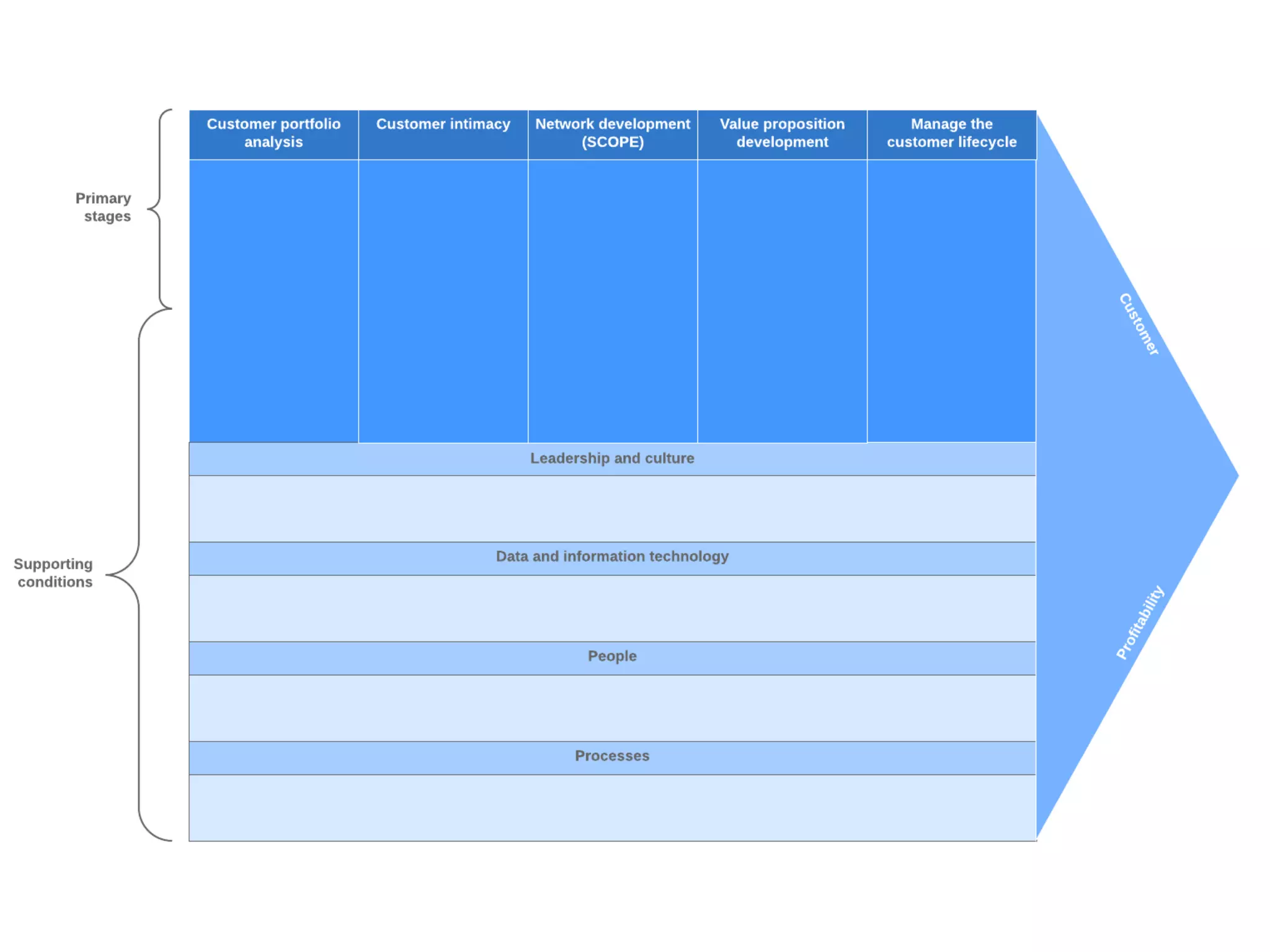
This document provides an overview of customer relationship management (CRM) concepts through 5 modules. Module 1 introduces key CRM concepts like strategic, operational, analytical and collaborative CRM. Module 3 discusses developing and managing customer databases. Module 4 covers how CRM relates to customer expenses. Module 5 focuses on managing networks to improve CRM performance, including relationships with investors, employees, and use of technologies like sales force automation. The document also discusses benefits and costs of CRM for organizations and customers, as well as common misunderstandings about CRM.